5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Mini Circuit Breaker Based on Industry Data
In the ever-evolving landscape of electrical installations, selecting the right Mini Circuit Breaker (MCB) is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the global MCB market is projected to reach USD 14.5 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 4.3%. This growth is driven by increasing safety regulations and the rising demand for sustainable energy solutions. MCBs are essential components in electrical systems, protecting circuits from overload and short circuits while enhancing overall system reliability.
Understanding the types, specifications, and applications of MCBs is essential for industry professionals aiming to optimize their electrical frameworks. With various options available, selecting the right MCB requires careful consideration of various factors to meet both operational needs and regulatory standards. This blog will outline five essential tips to guide you in making the best decision for your specific requirements.
Understanding the Importance of Mini Circuit Breakers in Electrical Systems
Mini circuit breakers (MCBs) play a critical role in modern electrical systems, designed to protect circuits from overloads and short circuits. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), electrical failures are a leading cause of property damage, with MCBs being essential in preventing such incidents. With the global energy market projected to grow, demand for advanced protective devices like MCBs is expected to rise, emphasizing their importance in safeguarding both residential and commercial installations.
Data from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) indicates that the use of MCBs has increased significantly within the past decade, with an estimated 15% annual growth rate in their adoption across various industries. This shift underscores the necessity for reliably engineered MCBs to ensure system integrity and safety. When selecting an MCB, understanding its specifications, load capacity, and tripping characteristics is crucial. Industry standards recommend assessing the application context and potential fault scenarios to select the most suitable breaker, further enhancing operational security and efficiency.
Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Mini Circuit Breaker
When selecting a mini circuit breaker (MCB), it’s essential to consider several key features that align with your specific electrical needs. Firstly, the current rating is crucial. Ensure that the MCB can handle the maximum load without tripping frequently. For example, if your appliances require a total of 20A, selecting an MCB rated for 25A provides a buffer while ensuring protection against overloads.
Another important factor is the tripping characteristics. Mini circuit breakers come in different types such as B, C, and D, suited for varying applications. For residential use, Type B breakers are typically adequate, but for industrial applications with higher inrush currents, Type C or D may be more appropriate. This selection guarantees that the breaker will trip under fault conditions while allowing safe operation under normal load.
Lastly, consider the breaking capacity of the MCB, which indicates its ability to handle fault currents. Choose a breaker with a breaking capacity that exceeds the prospective short-circuit current at your installation site to ensure optimal safety. Each of these features plays a vital role in ensuring that your electrical distribution system is safe and reliable.
5 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Mini Circuit Breaker Based on Industry Data
| Feature |
Description |
Industry Data |
| Rated Current (A) |
The maximum current that the breaker can handle |
Most common ratings: 6, 10, 16, 20, 25 A |
| Tripping Curve Type |
Characterizes the breaker's response to overloads |
Types: B, C, D (B for residential, C for commercial) |
| Voltage Rating (V) |
The maximum voltage that the breaker can operate at |
Typical voltages: 120, 240, 400 V |
| Mounting Type |
How the breaker will be installed |
Common types: DIN rail, panel mount |
| Short Circuit Rating (kA) |
The maximum short circuit current the breaker can safely interrupt |
Common ratings: 6, 10, 15 kA |
Analyzing Industry Standards for Mini Circuit Breaker Selection
When selecting the right mini circuit breaker (MCB), understanding industry standards is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical systems. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60947-2, MCBs are designed to provide overload and short-circuit protection, which underlines the importance of adhering to recognized benchmarks during the selection process. Data from recent market reports indicate that the global MCB market was valued at approximately USD 3.2 billion in 2021, with projections estimating an annual growth rate of 6.5% through 2028. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on these devices in residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Moreover, the choice of an MCB should also reflect compliance with local codes and regulations. For example, the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the U.S. mandates specific ratings and amperages for various applications, which can significantly influence selection criteria. Research shows that over 70% of electrical professionals emphasize the importance of selecting MCBs that meet or exceed these regulatory standards to mitigate risks. By analyzing such data, manufacturers can align their products with the latest compliance requirements, thus enhancing safety and reliability in power distribution systems.
Power Capacity Ratings of Mini Circuit Breakers
This chart represents the common usage percentages for different power capacity ratings of mini circuit breakers. The data highlights the most frequently chosen ratings in a typical installation scenario.
Evaluating Manufacturer Reputation and Product Reliability
When selecting the right mini circuit breaker (MCB), evaluating the manufacturer's reputation and product reliability is paramount. According to a 2022 report by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), 45% of electrical failures in residential and commercial buildings can be attributed to substandard circuit breakers. Consequently, choosing a reputable manufacturer can significantly reduce the risk of electrical incidents.
Tip 1: Research the brand history. Manufacturers with over 20 years of experience in the industry, such as Siemens and Schneider Electric, often produce MCBs that meet rigorous safety and performance standards. Their long-standing presence typically reflects a commitment to quality and reliability.
Tip 2: Review product certifications. An MCB that meets international standards, such as those established by UL and IEC, not only vouches for its quality but also ensures compliance with safety regulations. In a recent market analysis, products with proper certifications saw a 30% higher customer satisfaction rating.
Tip 3: Analyze customer feedback. A manufacturing company that consistently receives high ratings from users—especially concerning reliability—should be prioritized. Reports show that MCBs with comprehensive warranties and positive reviews tend to have a lower failure rate, making them a safer investment for your electrical needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing Mini Circuit Breakers
When selecting mini circuit breakers (MCBs), professionals often overlook critical factors, leading to common mistakes that can compromise safety and efficiency. According to a recent report from the Electrical Safety Foundation International (ESFI), approximately 60% of electrical fires in commercial settings are linked to improper circuit breaker selection. This statistic underscores the need for careful consideration when choosing MCBs to avoid potential hazards.
One common mistake is underestimating the load capacity. Industry experts recommend following the National Electrical Code (NEC), which stipulates that MCBs should be rated appropriately for the load they will carry. For instance, a report by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) indicated that overloading circuit breakers is a leading cause of electrical failures, resulting in significant operational downtimes and safety risks.
Additionally, ignoring environmental factors can also lead to poor choices in breaker selection. For example, MCBs need to be rated for temperature and humidity conditions specific to their installation site. Choosing MCBs with appropriate Ingress Protection (IP) ratings can prevent malfunction in harsh environments. A 2021 industry survey noted that 40% of electrical failures were attributed to inadequate protection in hostile conditions, illustrating the importance of understanding environmental factors before making a purchase.

Home
About Us
Products
Terminal Power Distribution Electric
AC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY06H-125 MCB 10-15KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06H-125 MCB 10-15KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY06-125 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06-125 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY05H-40 MCB Single Modular 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY05H-40 MCB Single Modular 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY05-32 MCB Single Modular 3KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY05-32 MCB Single Modular 3KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY04-63 MCB 6-10KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY04-63 MCB 6-10KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY03H-63 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03H-63 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY03-63 MCB 4.5KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03-63 MCB 4.5KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY02-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY02-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY01-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY01-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
MCB Accessories
Main Switch
RCBO RCCB
 BY07L-63 RCCB 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker
BY07L-63 RCCB 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker
 BY05HL-40 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY05HL-40 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
 BY05L-32 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY05L-32 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
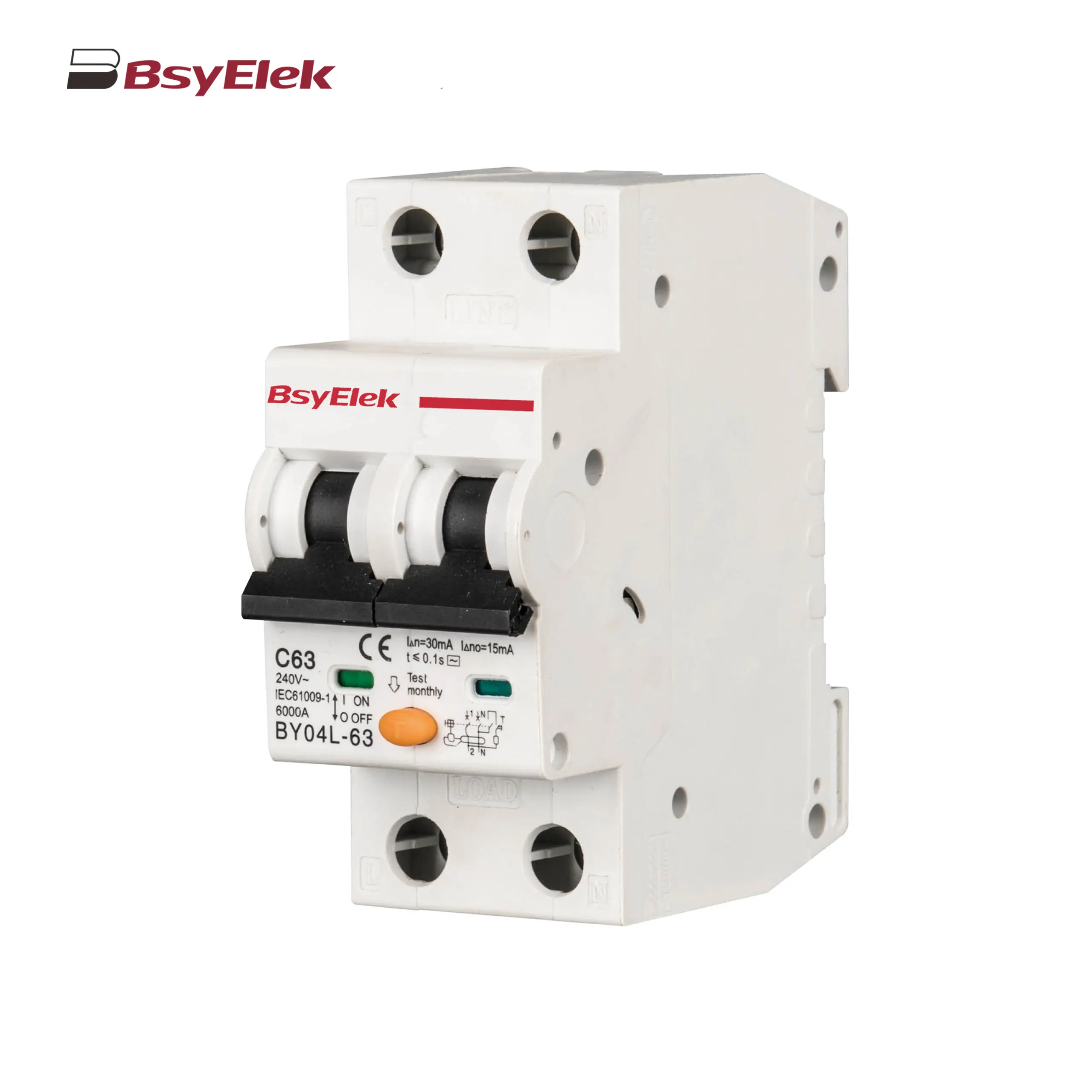 BY04L-63 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY04L-63 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
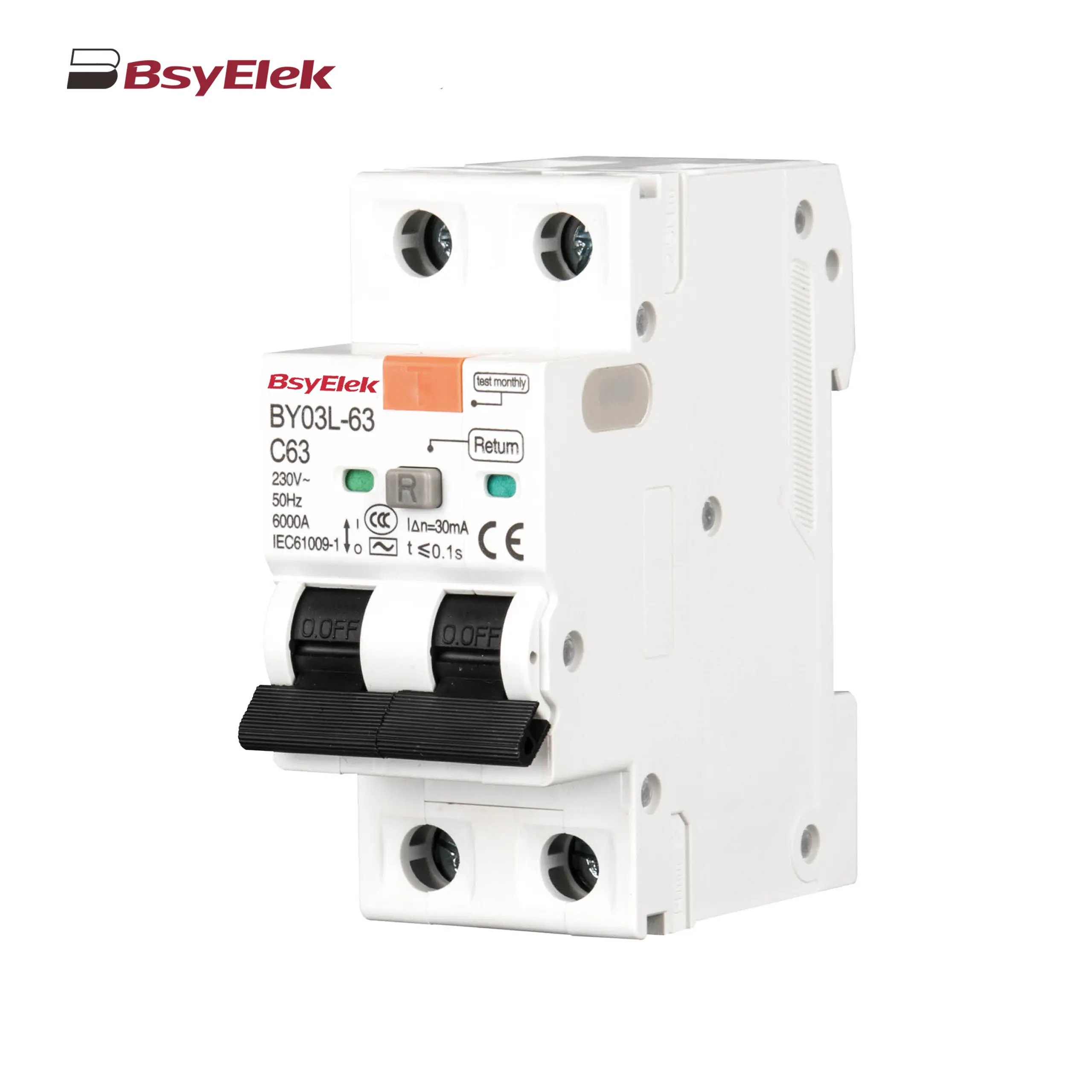 BY03L-63 RCBO 4.5KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY03L-63 RCBO 4.5KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
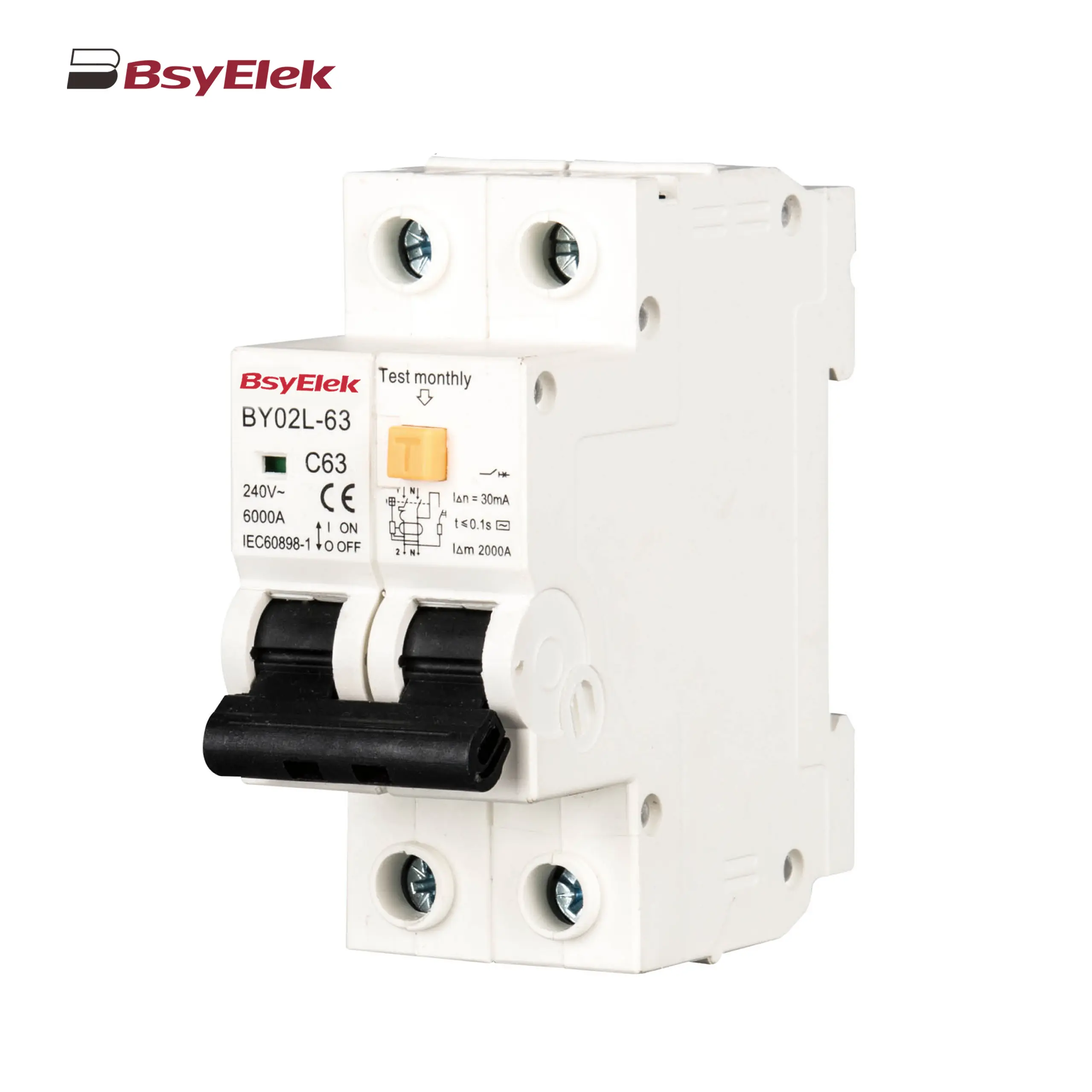 BY02L-63 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY02L-63 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
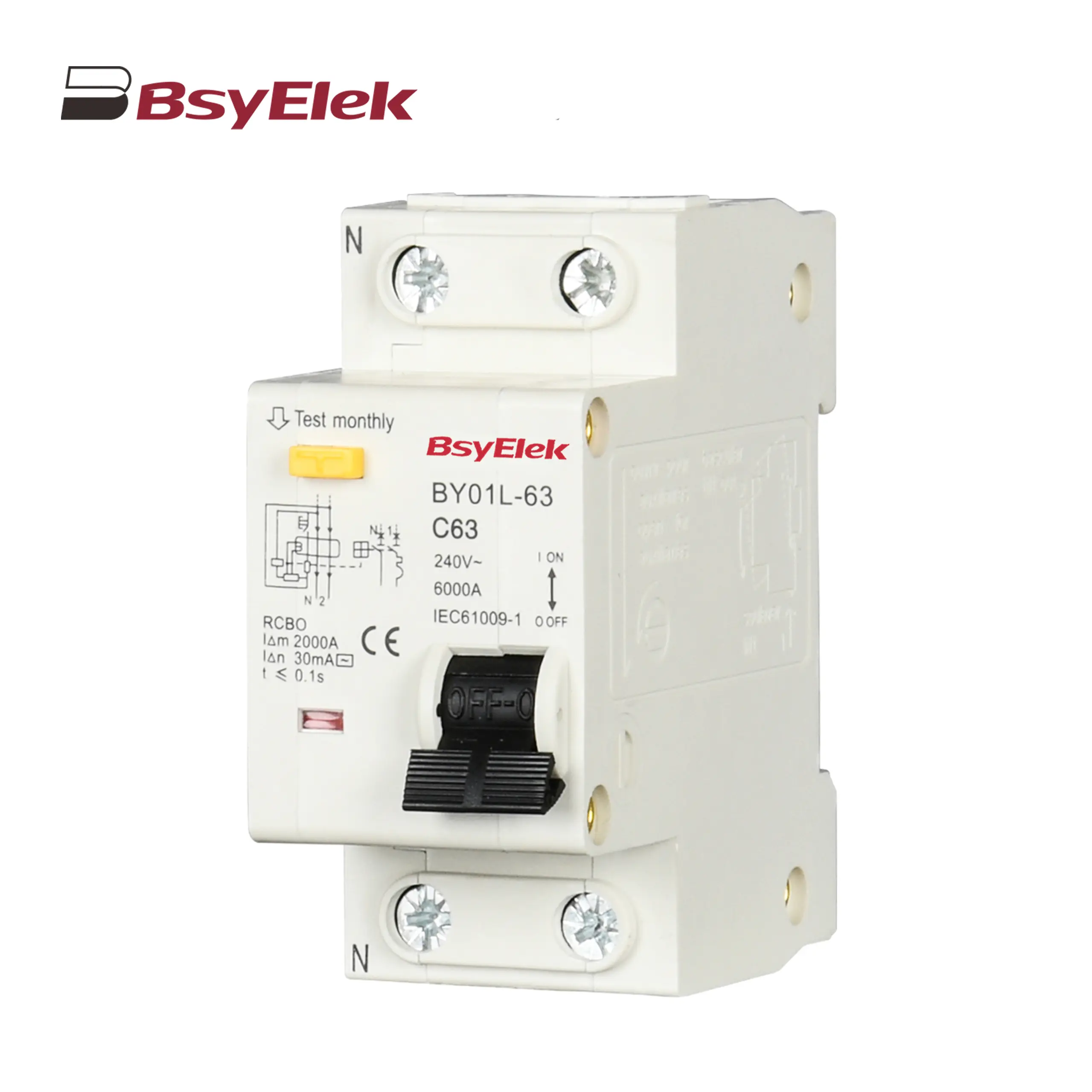 BY01L-63 RCBO 1P+N 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY01L-63 RCBO 1P+N 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
Resettable Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
AC Contactor
AC Surge Protective Device
Changeover Switch
Photovoltaic System Protection
DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY06H-125DC MCB 10-15kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06H-125DC MCB 10-15kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY06-125DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06-125DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY04-63DC MCB 6-10kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY04-63DC MCB 6-10kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY03H-63DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03H-63DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY03-63DC MCB 4.5kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03-63DC MCB 4.5kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY02-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY02-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
 BY01-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY01-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
RCD
DC Surge Protective Device
DC Fuse
PV Isolator Switch
PV Connector
Cable Gland
PV Cable
PV Knife Switch
DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
Industrial Power Distribution Electric
Distribution Box
Air Conditioning System
Definite Purpose Magnetic Contactor
Condensate Pump
 BY-5018 1.8M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-5018 1.8M Engineering Drainage Pump
 BY-5050 5M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-5050 5M Engineering Drainage Pump
 BY-11 1.2M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-11 1.2M Engineering Drainage Pump
 SBH-05 0.7M Original Drainage Pump of Duct Type Air Conditioner
SBH-05 0.7M Original Drainage Pump of Duct Type Air Conditioner
 BY-24A/40A 10M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-24A/40A 10M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
 BY-50A 12M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-50A 12M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
 BY-24B/40B 10M Split Type Drainage Pump
BY-24B/40B 10M Split Type Drainage Pump
 BY-100L 2M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-100L 2M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
 BY-360L 6M Large Displacement Drainage Pump
BY-360L 6M Large Displacement Drainage Pump
 BY-24C/40C 10M Corner Drainage Pump
BY-24C/40C 10M Corner Drainage Pump
News
Top Blog
Company News
Industry Dynamics
What is a miniature circuit breaker (MCB)?
PG Series Waterproof Cable Glands with Washer for Harsh Environments
LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch ensures reliable power transfer
BYX2 AC contactor series: reliable power control for modern electrical systems
High-performance 1000V DC fuse holder optimizes solar photovoltaic system protection
BY07L-63 Residual Current Circuit Breaker Ensures Global Electrical Safety
BYQ5 ATS Isolation Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch: Features and Benefits
Support
Blog
Contact Us




 OF SD MX OF MCB Miniature Circuit Breaker Accessories
OF SD MX OF MCB Miniature Circuit Breaker Accessories BYG1-125 Main Switch MCB Isolator Switch
BYG1-125 Main Switch MCB Isolator Switch BYVP1-63 100A Single Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
BYVP1-63 100A Single Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector BYVP2-63 40A 63A Adjustable Dual Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
BYVP2-63 40A 63A Adjustable Dual Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector BYX2 6-95A AC Contactor
BYX2 6-95A AC Contactor BY08 1+2-7 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 50KA Surge Protective Device
BY08 1+2-7 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 50KA Surge Protective Device BY08 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 60KA Surge Protective Device
BY08 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 60KA Surge Protective Device BY08II-40 SPD Class T2 Imax 40KA Surge Protective Device
BY08II-40 SPD Class T2 Imax 40KA Surge Protective Device BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch
BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch
LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch BYF-63 RCD 10KA Type B AC+A+Smoothing DC Residual Current Device
BYF-63 RCD 10KA Type B AC+A+Smoothing DC Residual Current Device BY08DC 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device
BY08DC 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device BY08IIDC-40 SPD Class T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device
BY08IIDC-40 SPD Class T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device BYPV-63 1500VDC 50A Fuse Holder with 10x85mm 14x85mm Fuse Link
BYPV-63 1500VDC 50A Fuse Holder with 10x85mm 14x85mm Fuse Link BYPV-30 1000VDC 32A Fuse Holder with 10x38mm Fuse Link
BYPV-30 1000VDC 32A Fuse Holder with 10x38mm Fuse Link BYPV-ELR2 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version
BYPV-ELR2 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version BYPV-ELR1 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version
BYPV-ELR1 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version BYPV-NL1/T PV Isolator Switch with Ultra-thin Lever Handle
BYPV-NL1/T PV Isolator Switch with Ultra-thin Lever Handle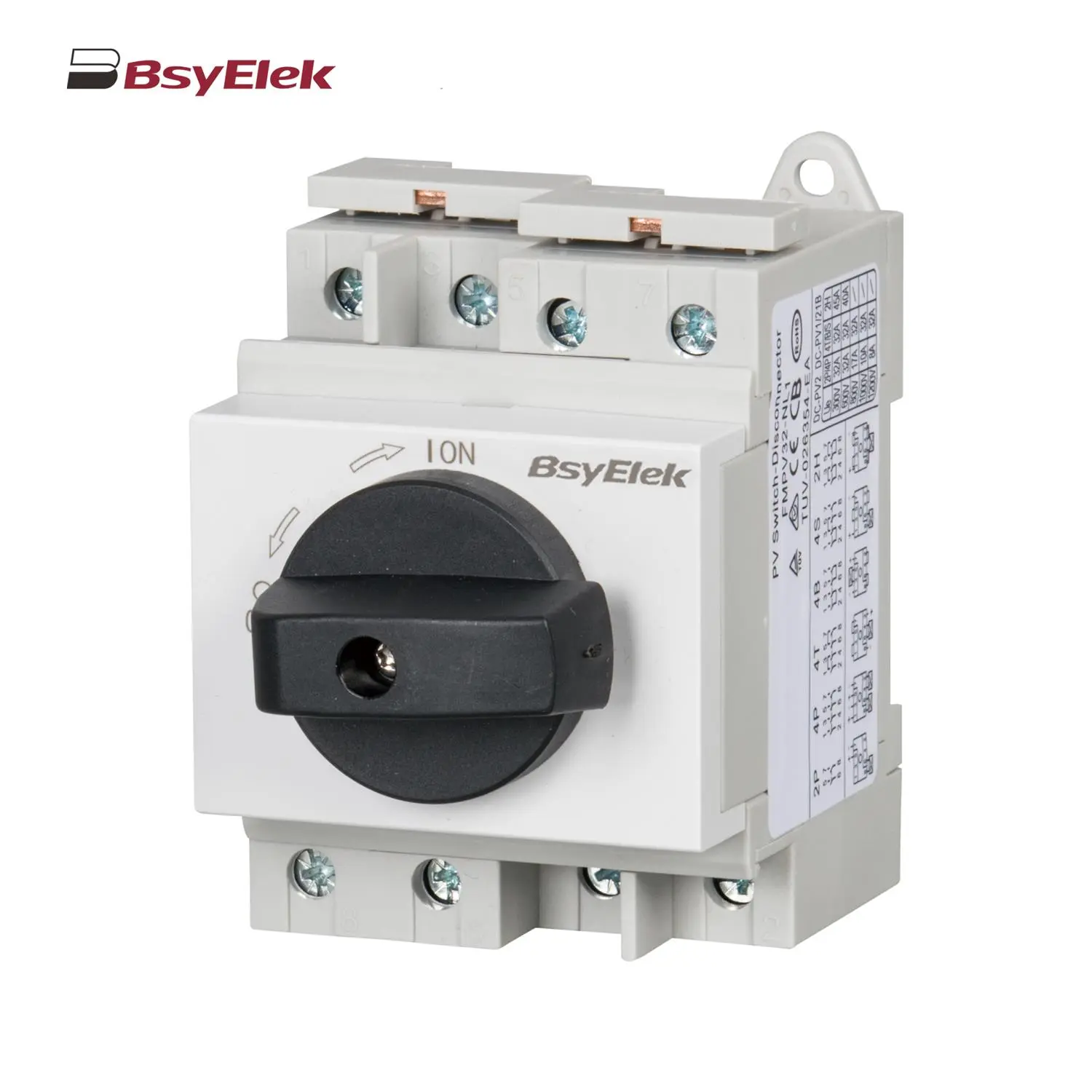 BYPV-NL1 PV Isolator Switch with Lever Handle
BYPV-NL1 PV Isolator Switch with Lever Handle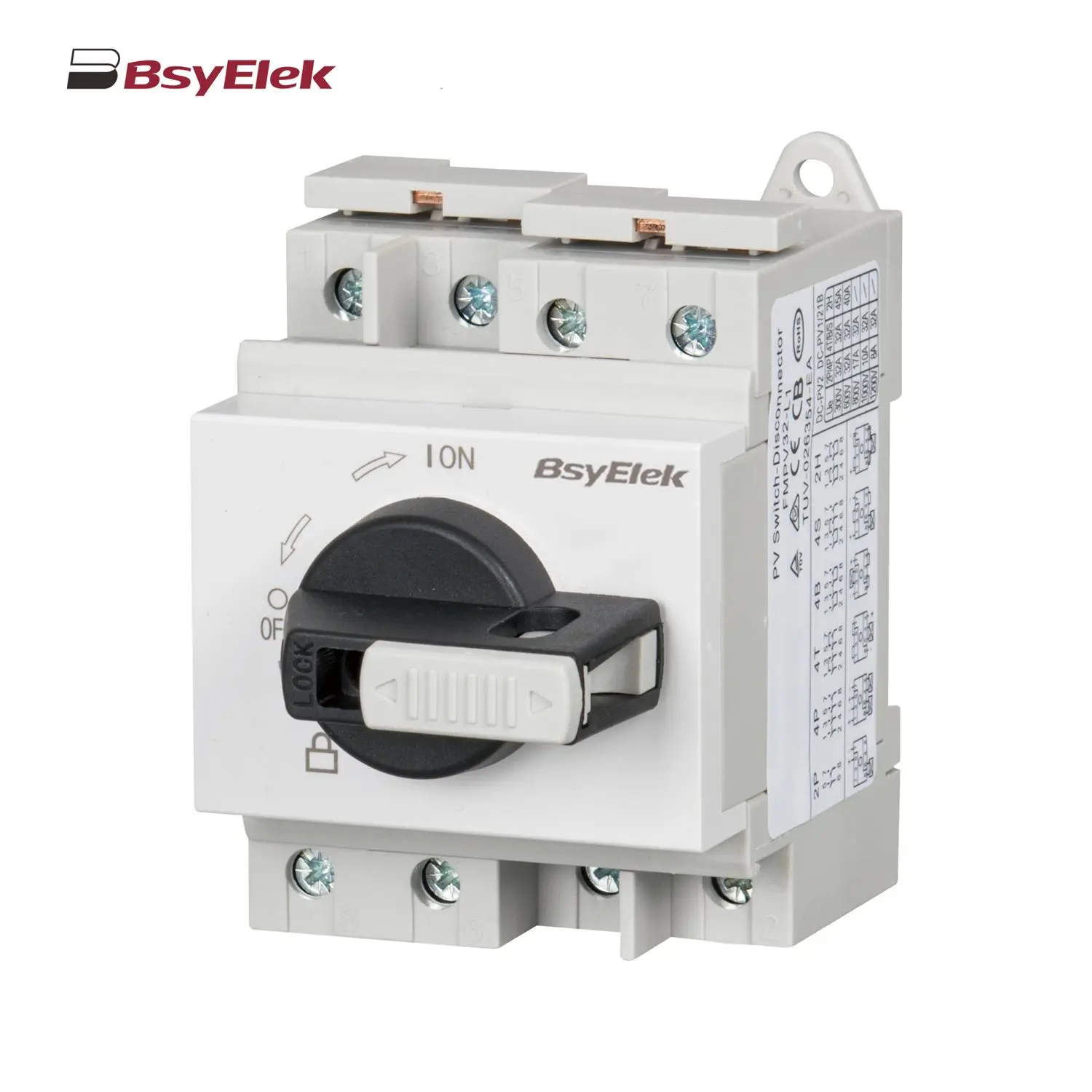 BYPV-L1/L2 PV Isolator Switch with Lockable Lever Handle
BYPV-L1/L2 PV Isolator Switch with Lockable Lever Handle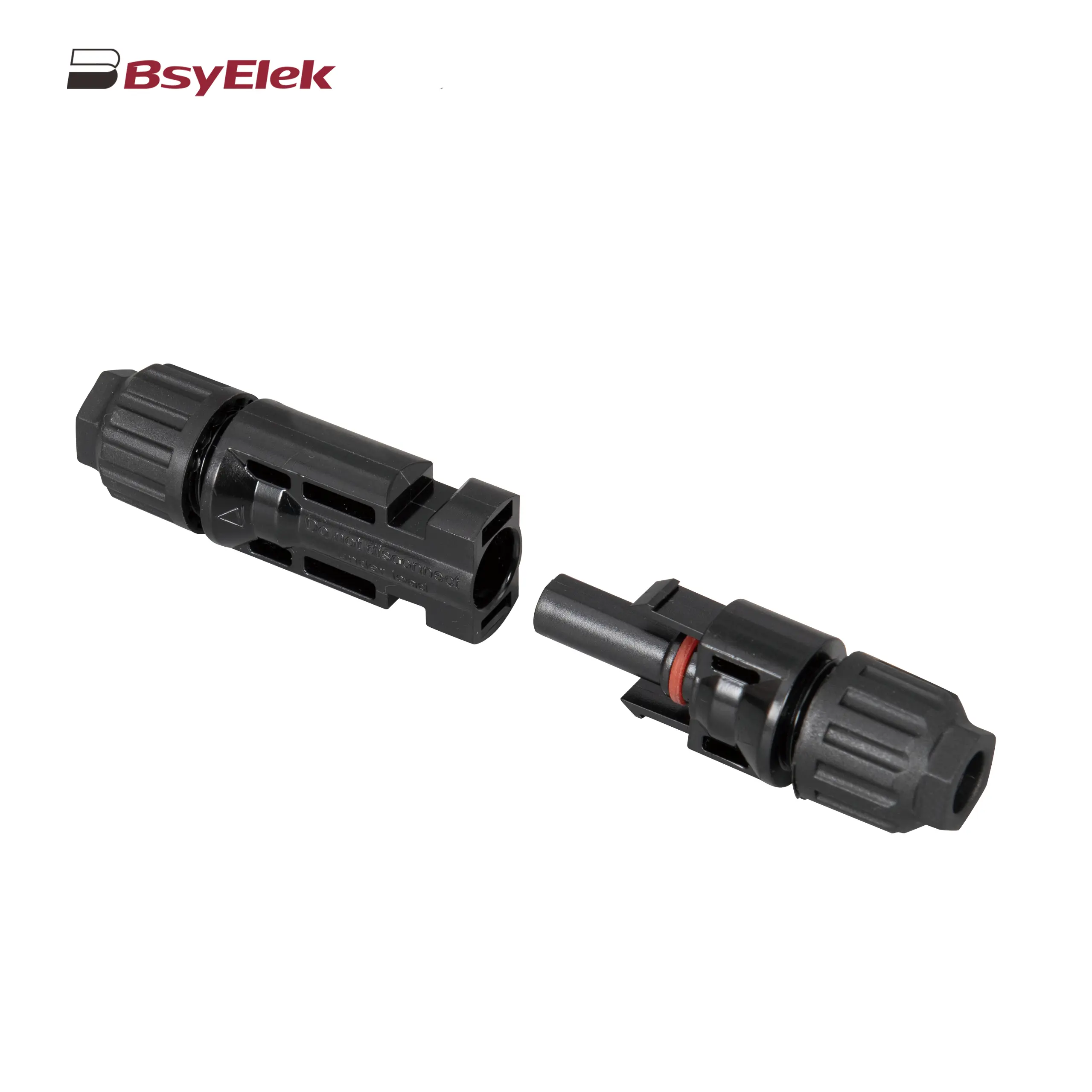 PV-BY-01 30A/50A 1000V Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-01 30A/50A 1000V Photovoltaic Connector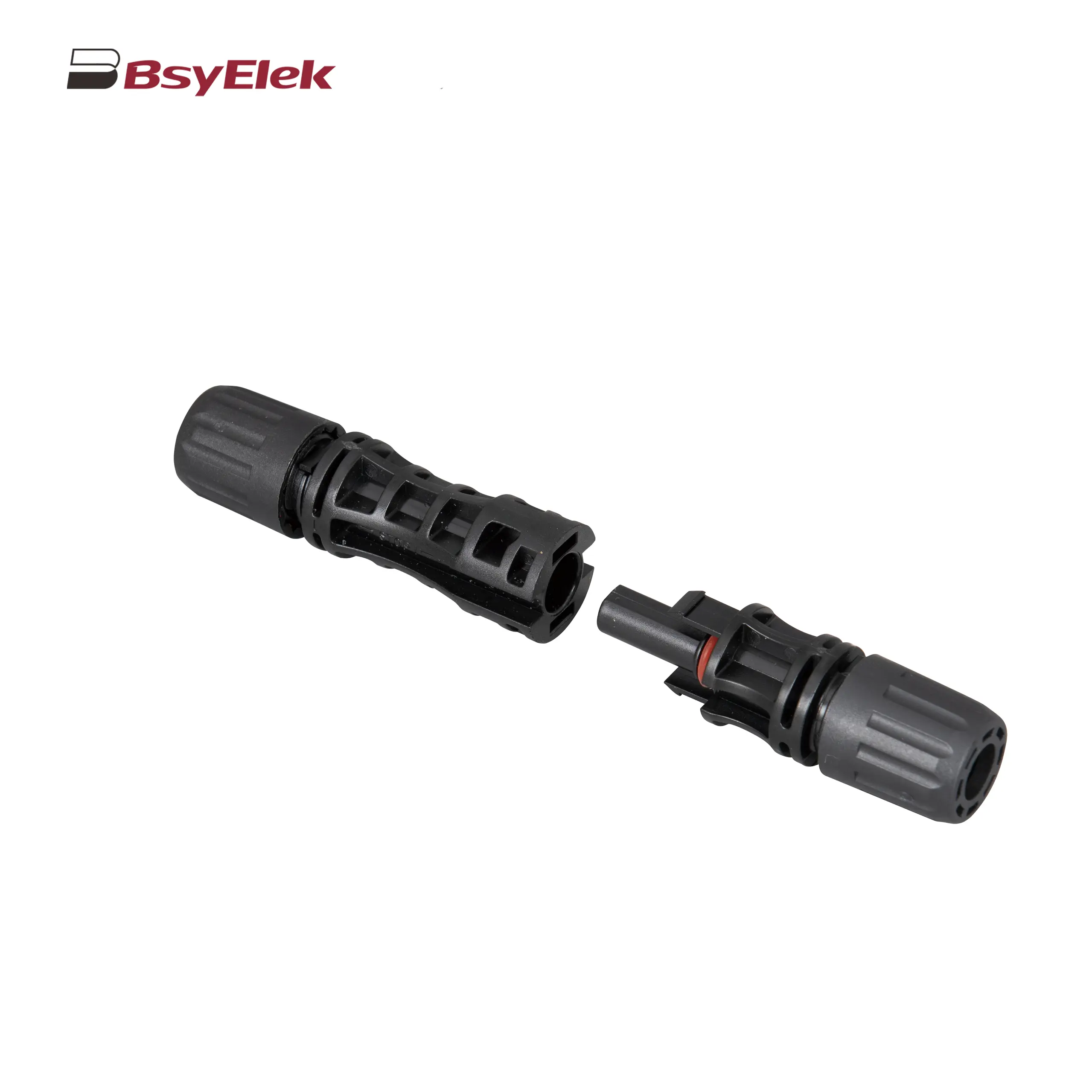 PV-BY-02 30A/50A 1500V Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-02 30A/50A 1500V Photovoltaic Connector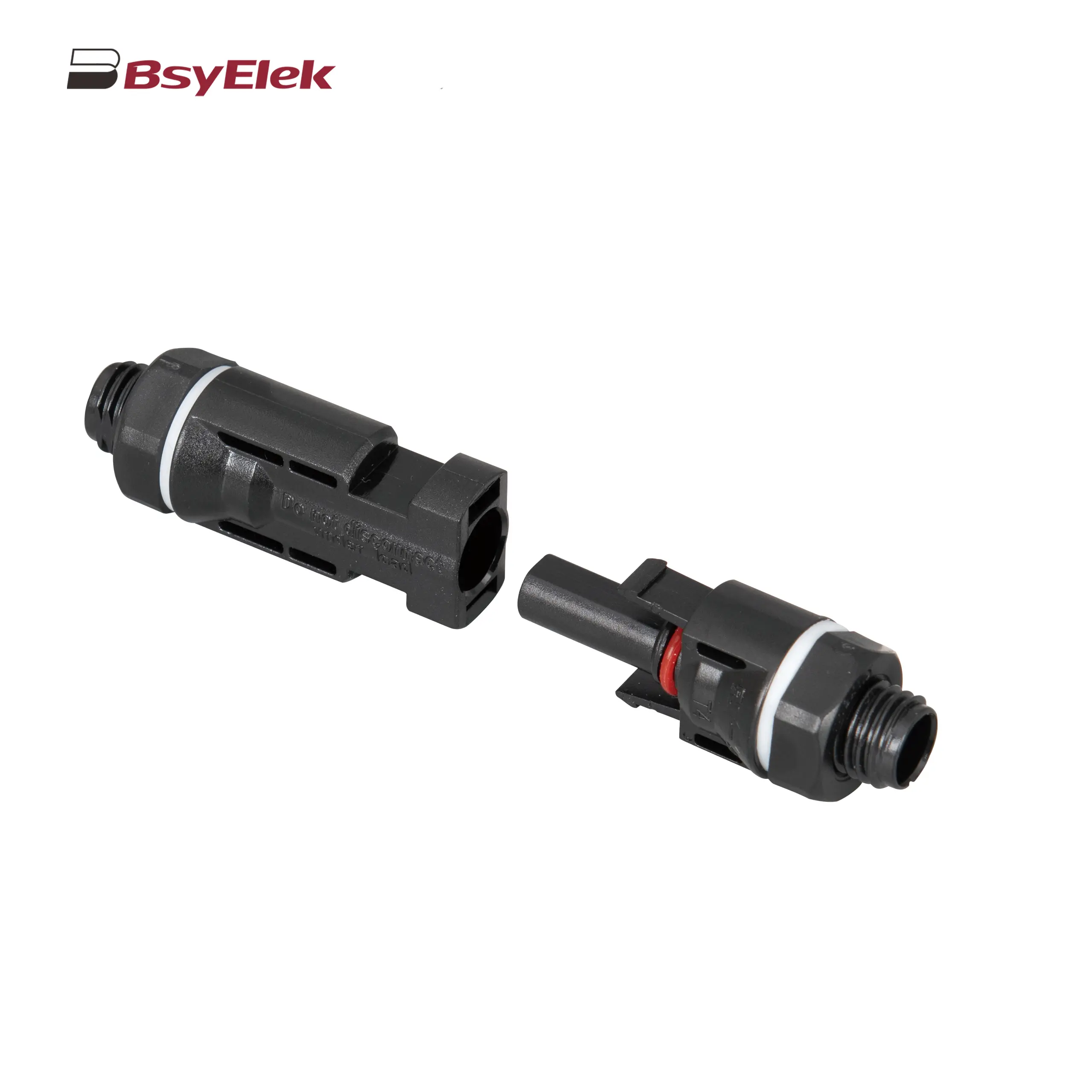 PV-BY-03 30A/50A 1000V Panel Mount Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-03 30A/50A 1000V Panel Mount Photovoltaic Connector PV-BY-F01 30A 1500V Diode/Fuse Type Connector
PV-BY-F01 30A 1500V Diode/Fuse Type Connector PV-BY-T 50A 1500V T Type Branch Connector
PV-BY-T 50A 1500V T Type Branch Connector PV-BY-Y 30A 1500V Y Type Branch Connector
PV-BY-Y 30A 1500V Y Type Branch Connector PG Waterproof Cable Gland with Washer
PG Waterproof Cable Gland with Washer Photovoltaic Cable
Photovoltaic Cable HD11N Photovoltaic Knife Switch
HD11N Photovoltaic Knife Switch BYM3DC MCCB Photovoltaic DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM3DC MCCB Photovoltaic DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker BYM1DC MCCB 1000VDC Thermal Magnetic Type DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1DC MCCB 1000VDC Thermal Magnetic Type DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker BYM1E MCCB Electronic Type Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1E MCCB Electronic Type Molded Case Circuit Breaker BYM1 MCCB Thermal Magnetic AC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1 MCCB Thermal Magnetic AC Molded Case Circuit Breaker BYW1 ACB Intelligent Universal Air Circuit Breaker
BYW1 ACB Intelligent Universal Air Circuit Breaker BYQ1 ATS Isolated Type PC Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Isolated Type PC Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch BYQ1 ATS Intelligent Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Intelligent Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch BYQ1 ATS End Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS End Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch BYQ1 ATS Mini Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Mini Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch Stainless Steel Hinge Type Electrical Box
Stainless Steel Hinge Type Electrical Box HA Waterproof Distribution Box
HA Waterproof Distribution Box HT Waterproof Distribution Box
HT Waterproof Distribution Box BS Definite Purpose Magnetic AC Contactor
BS Definite Purpose Magnetic AC Contactor