-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
Terminal Power Distribution Electric
-
AC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
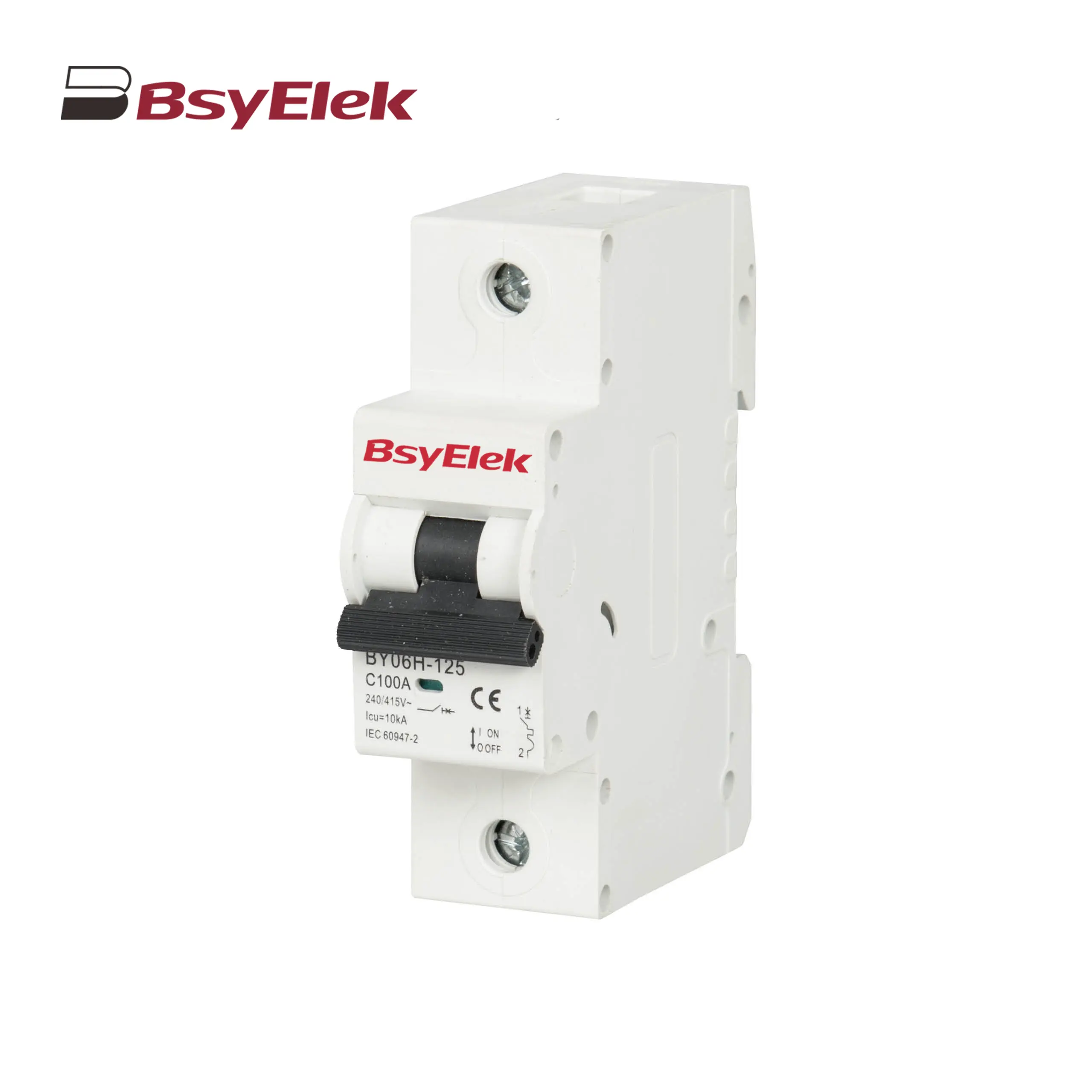 BY06H-125 MCB 10-15KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06H-125 MCB 10-15KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
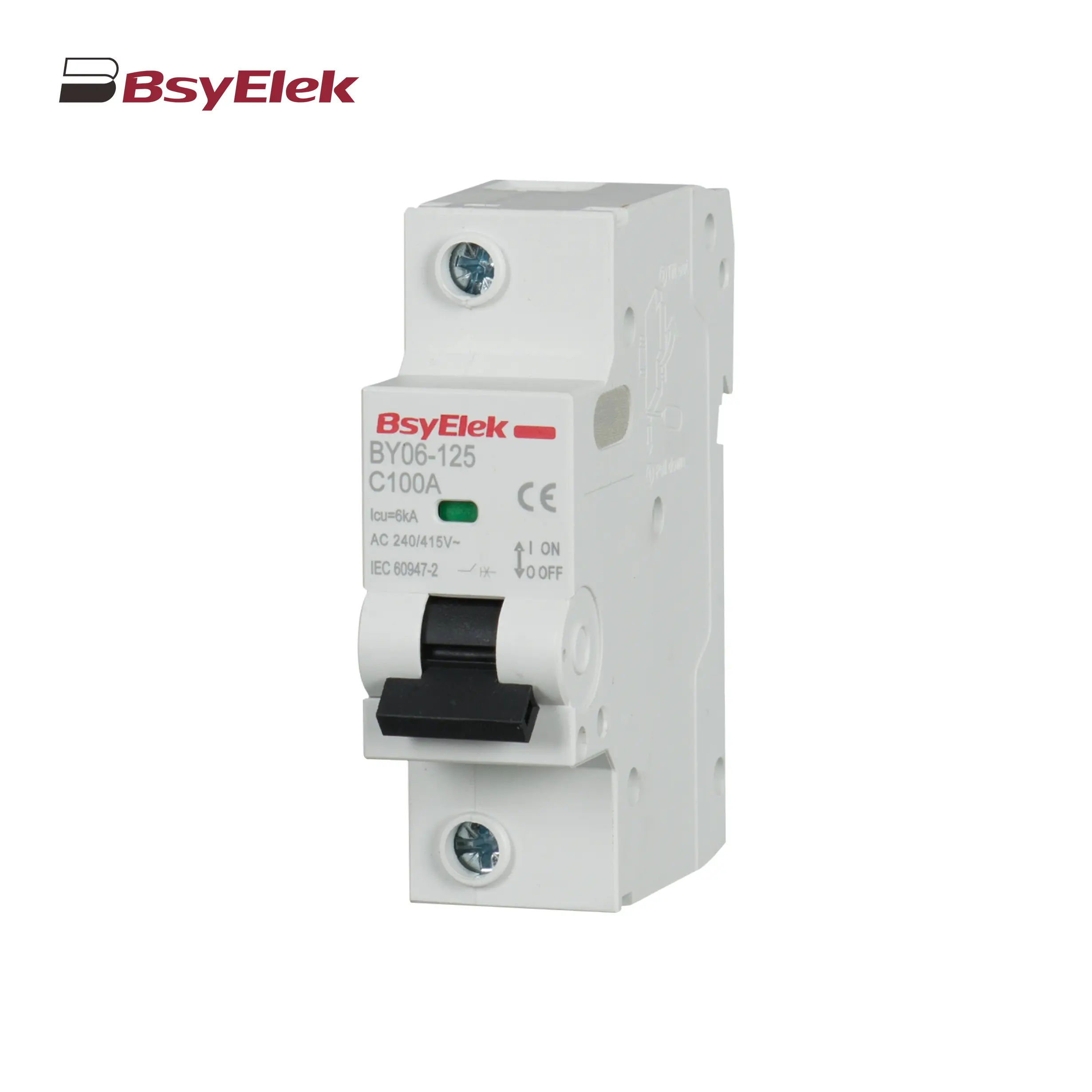 BY06-125 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06-125 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
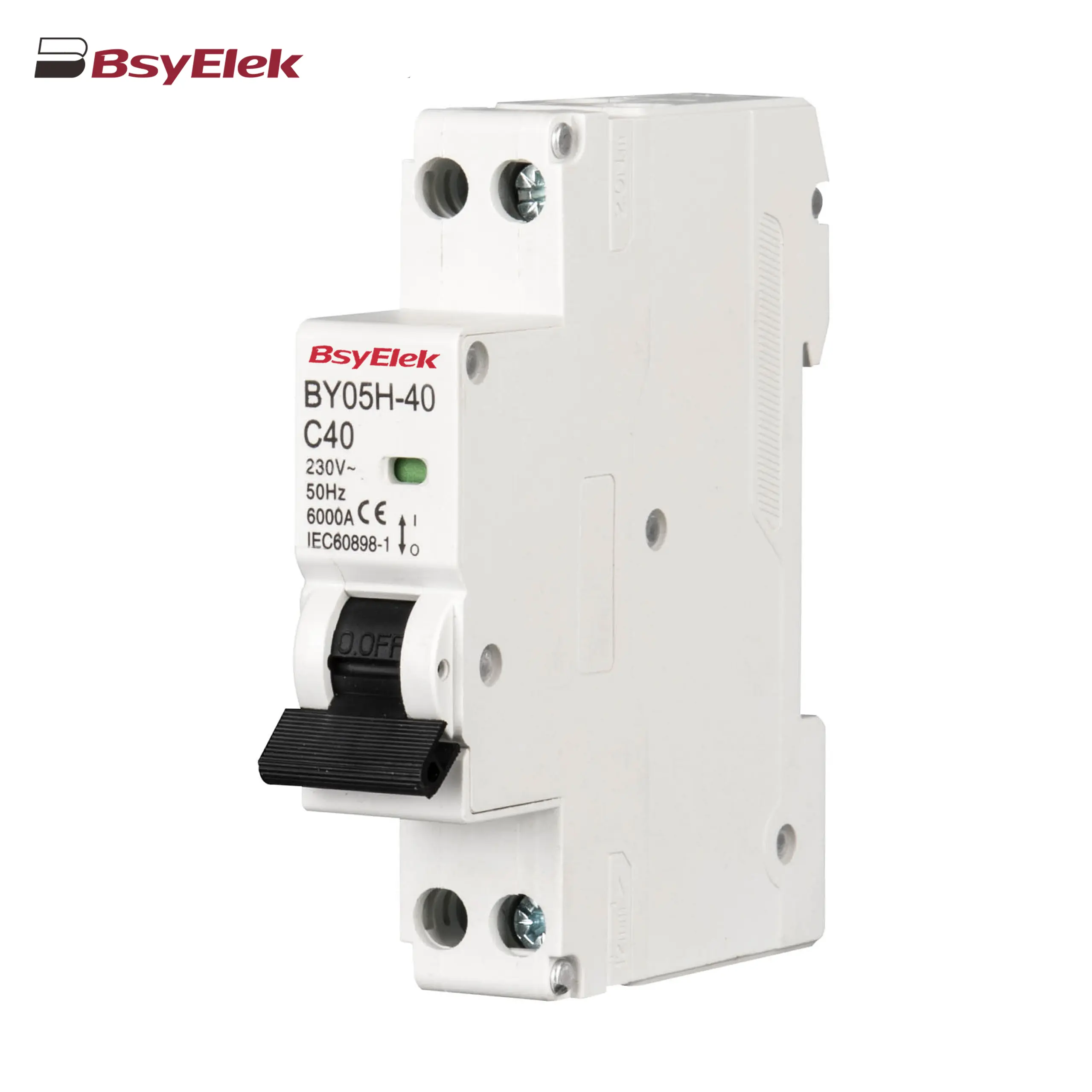 BY05H-40 MCB Single Modular 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY05H-40 MCB Single Modular 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
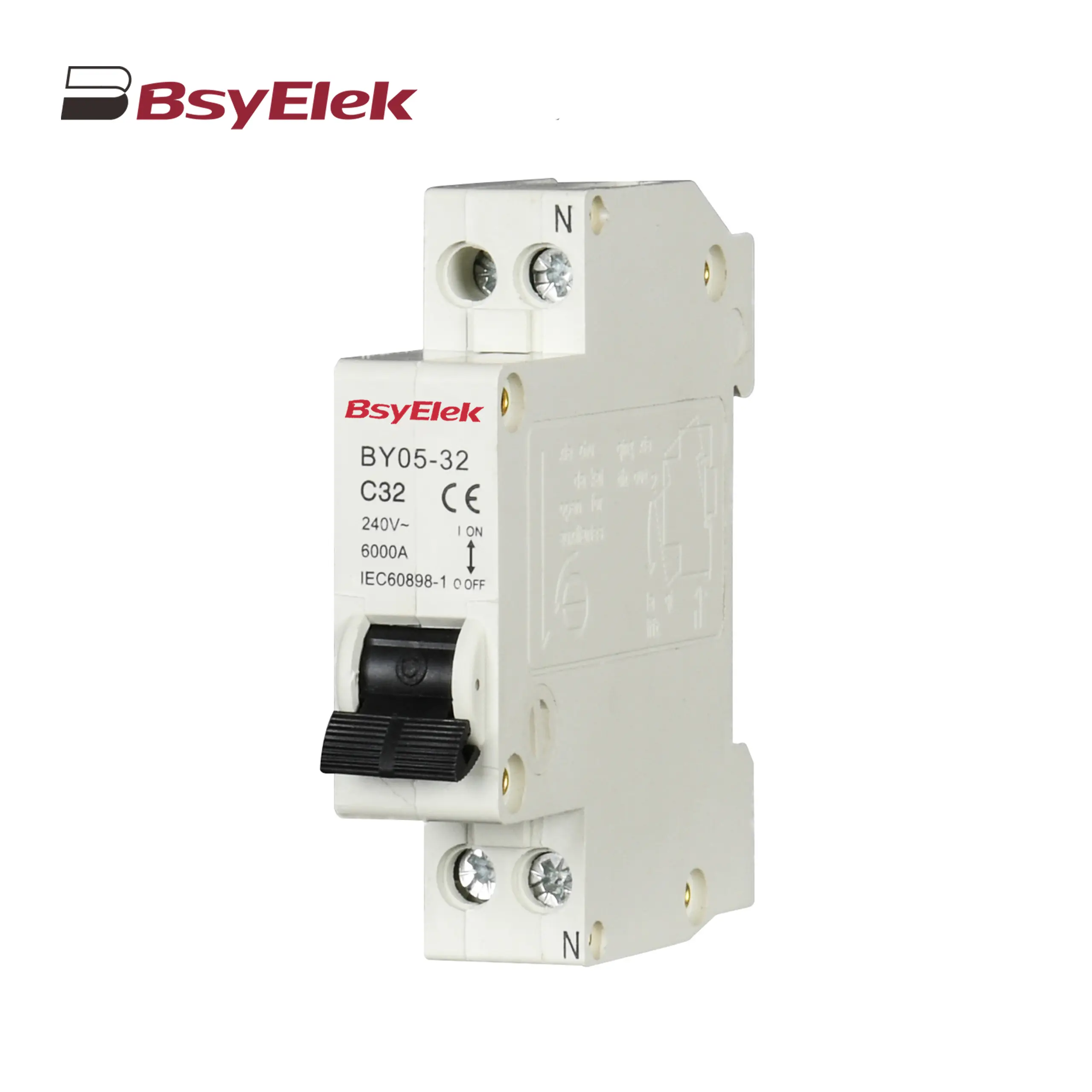 BY05-32 MCB Single Modular 3KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY05-32 MCB Single Modular 3KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
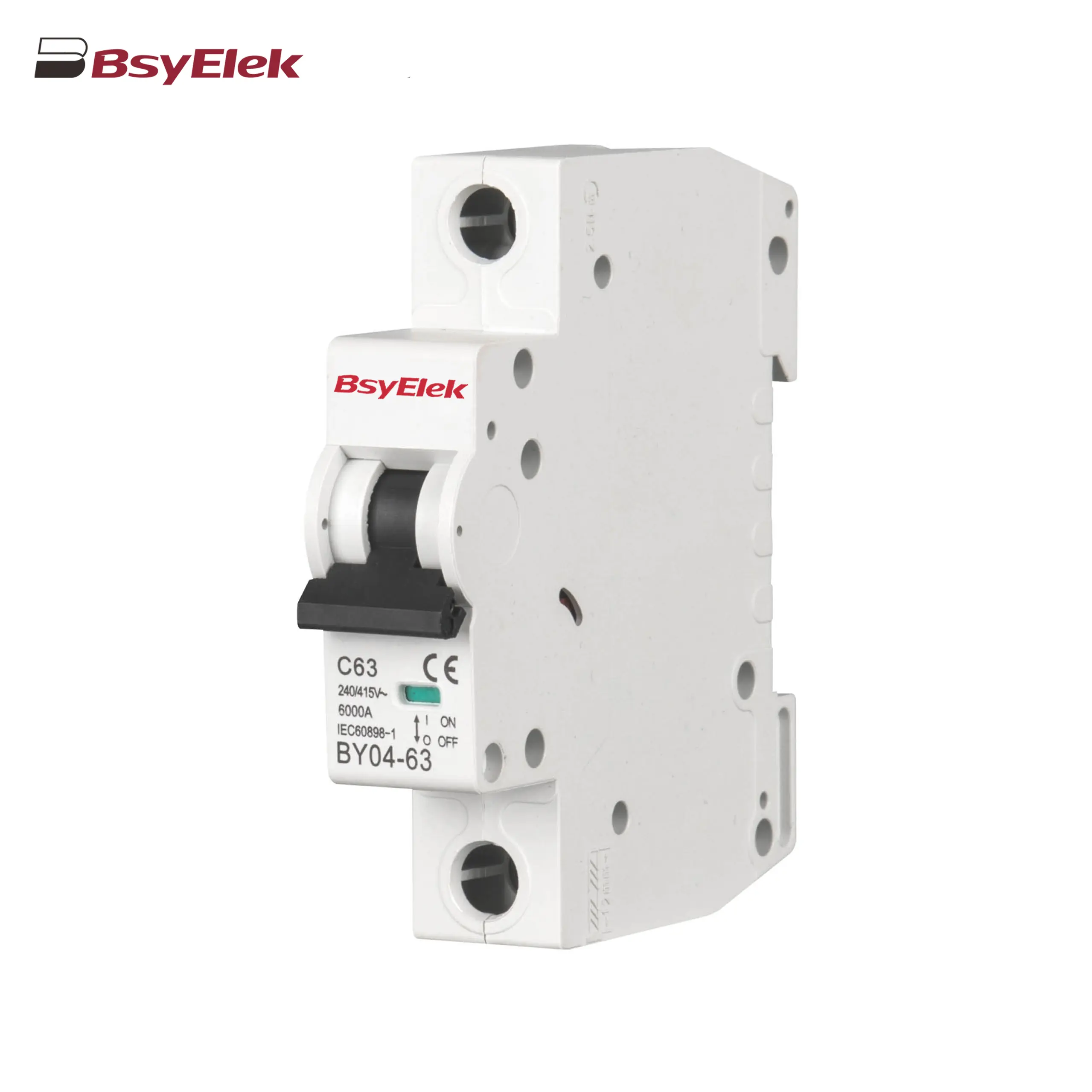 BY04-63 MCB 6-10KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY04-63 MCB 6-10KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
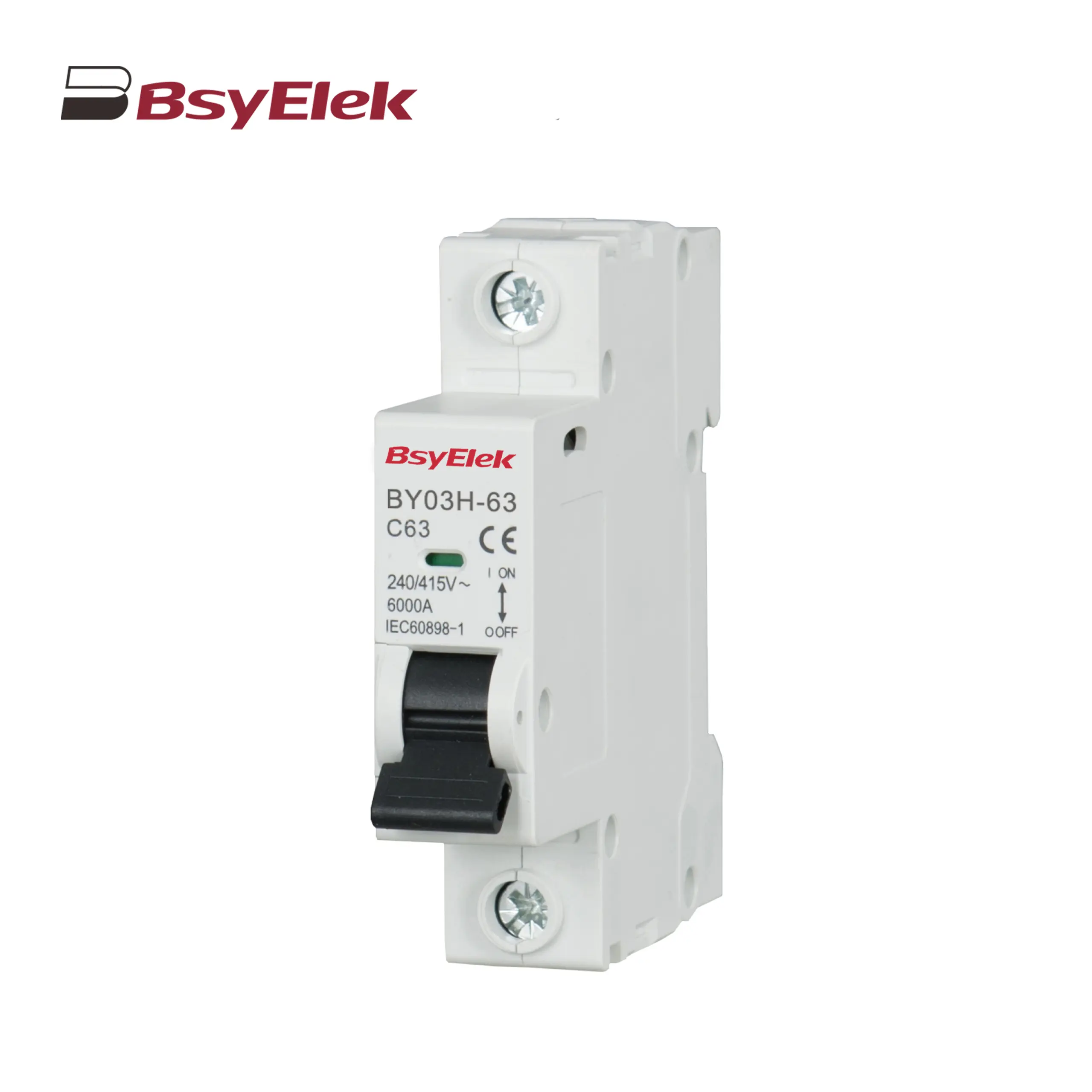 BY03H-63 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03H-63 MCB 6KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
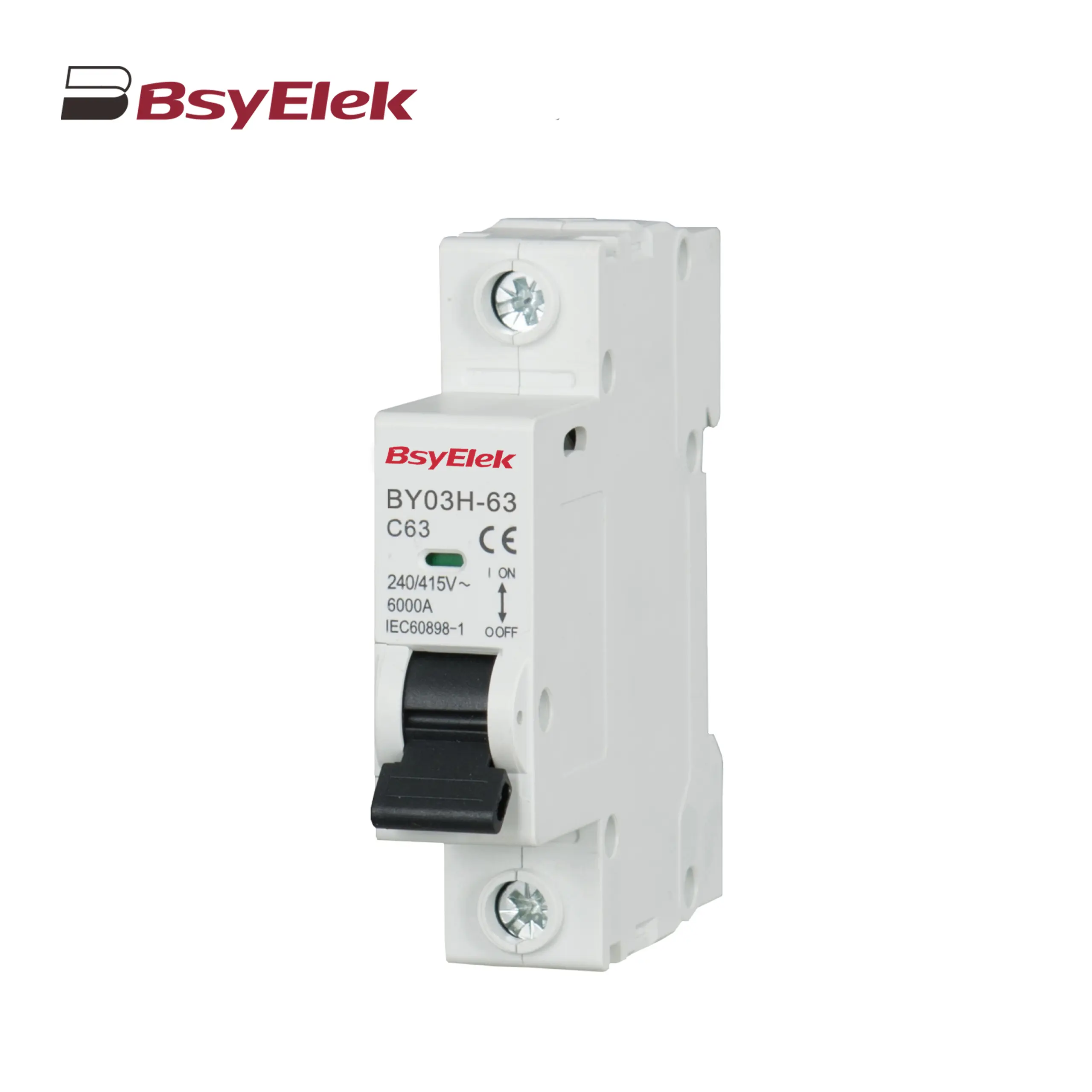 BY03-63 MCB 4.5KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03-63 MCB 4.5KA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
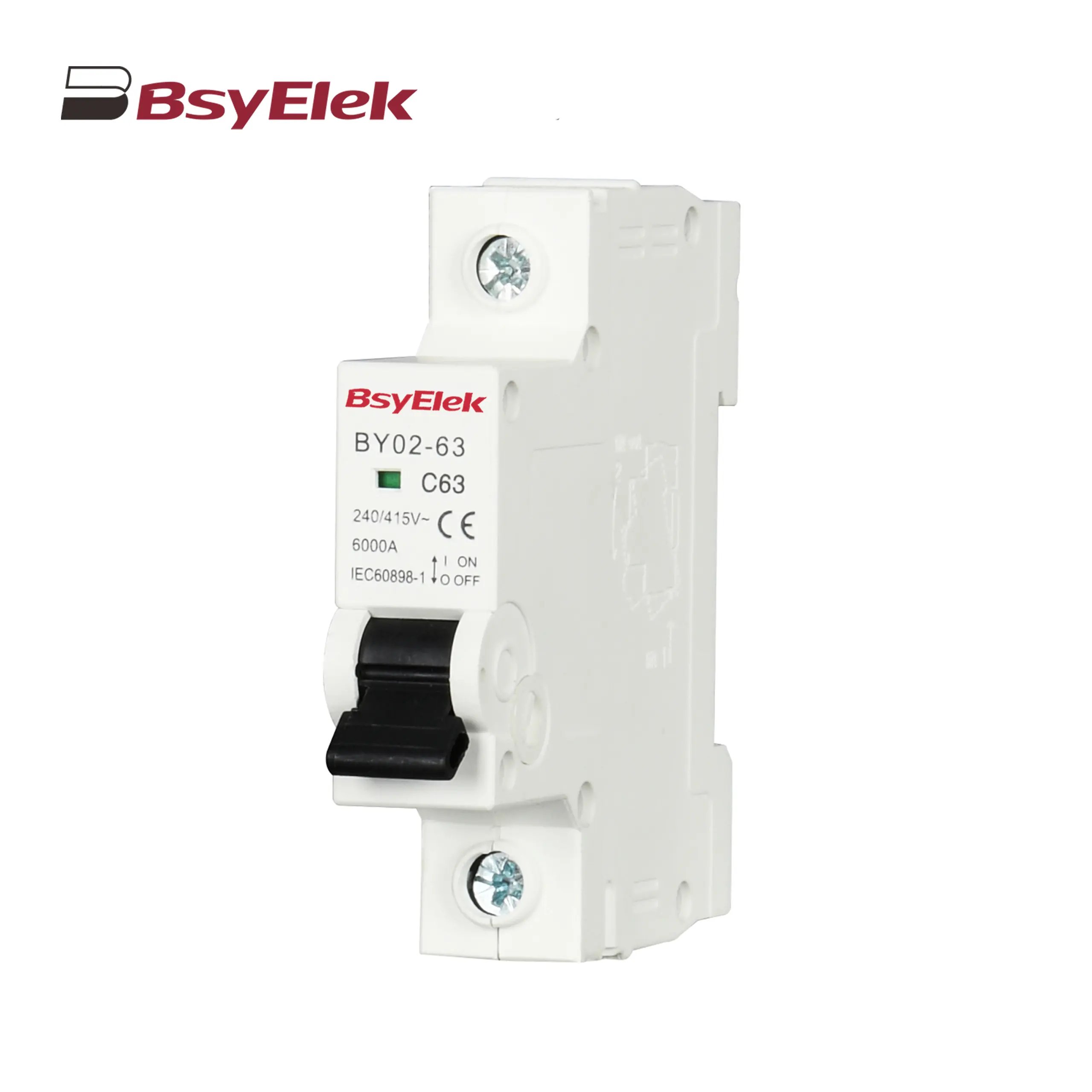 BY02-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY02-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
 BY01-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY01-63 MCB 3kA Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
-
MCB Accessories
-
Main Switch
-
RCBO RCCB
-
 BY07L-63 RCCB 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker
BY07L-63 RCCB 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker
-
 BY05HL-40 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY05HL-40 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
 BY05L-32 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY05L-32 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
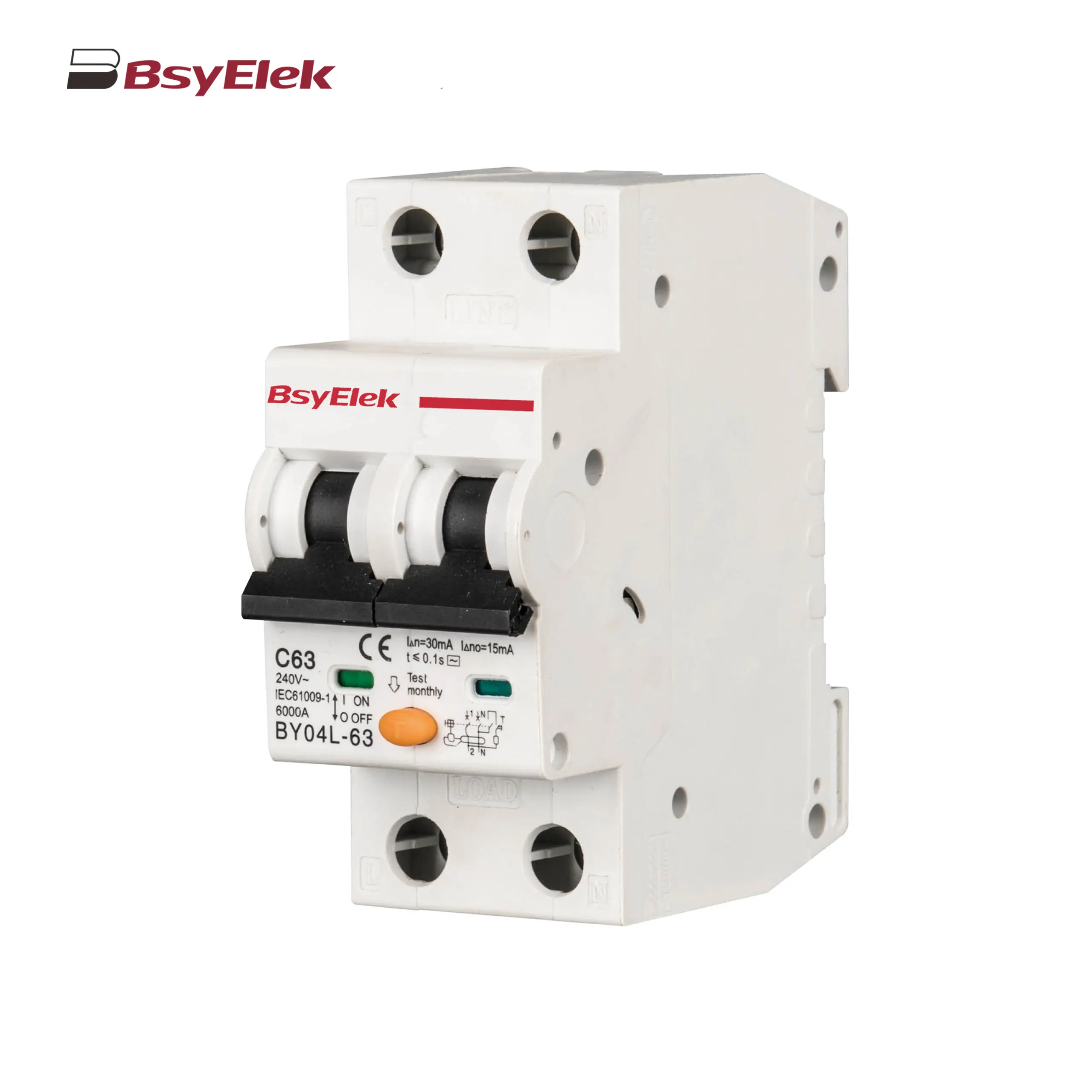 BY04L-63 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY04L-63 RCBO 6KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
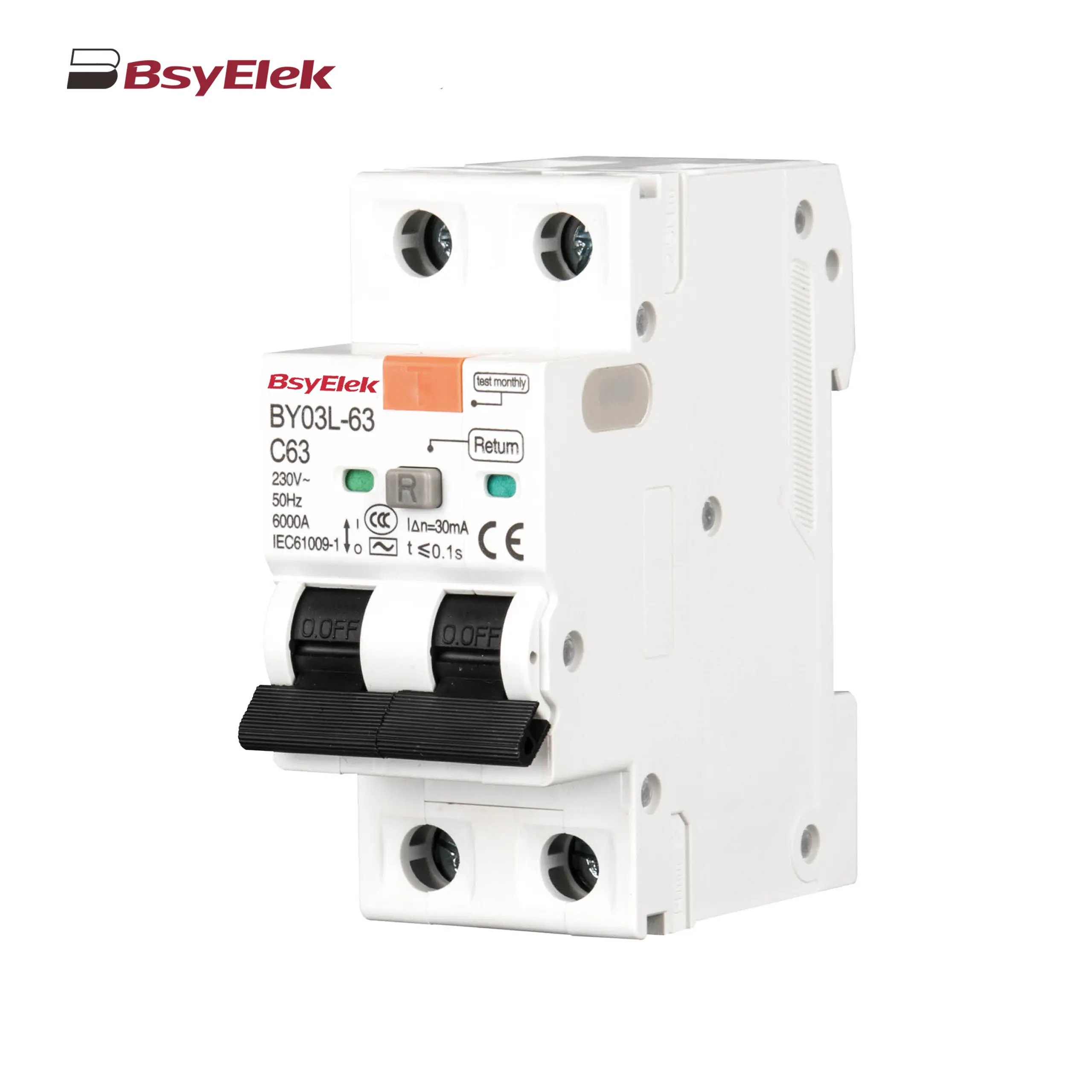 BY03L-63 RCBO 4.5KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY03L-63 RCBO 4.5KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
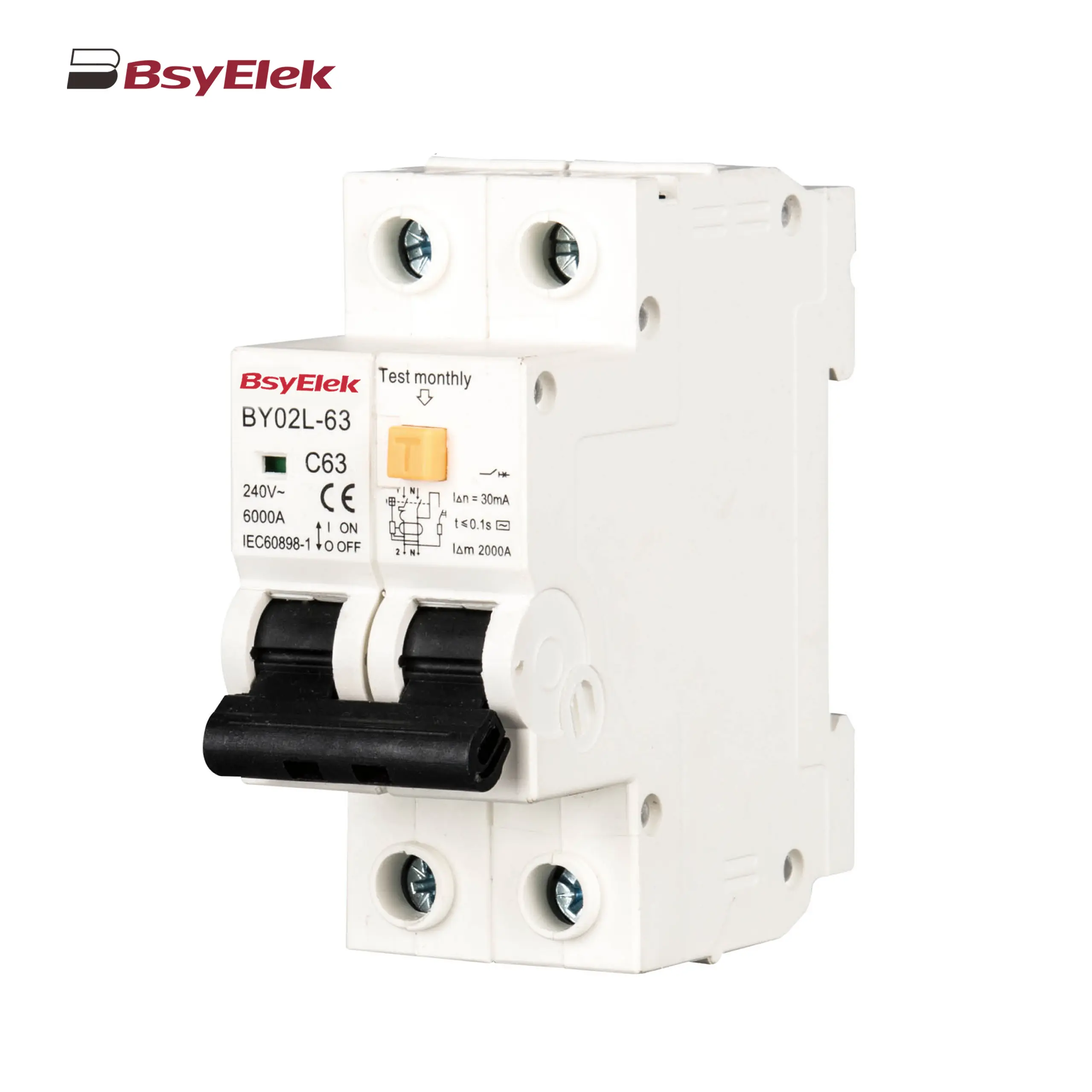 BY02L-63 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY02L-63 RCBO 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
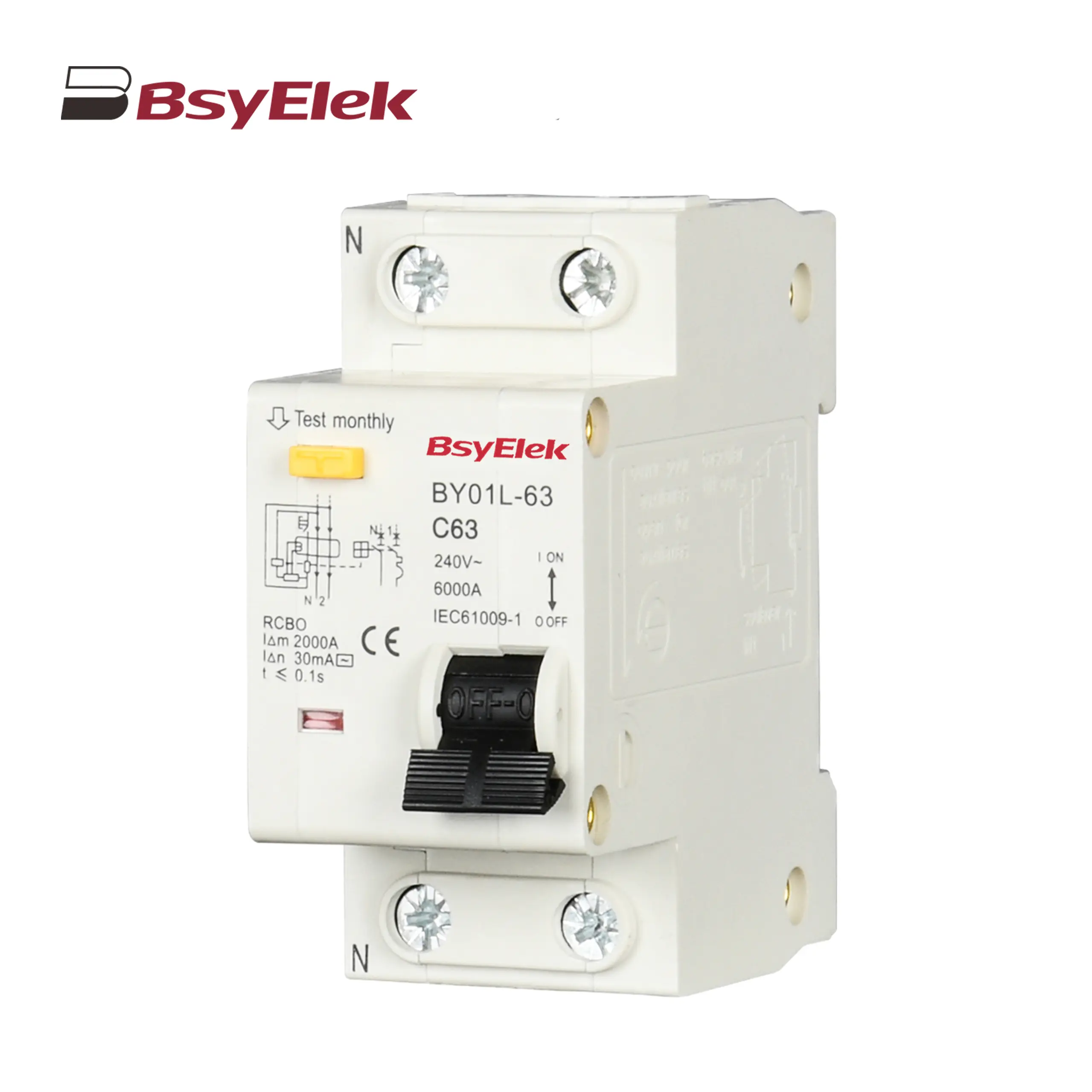 BY01L-63 RCBO 1P+N 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
BY01L-63 RCBO 1P+N 3KA Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Over-current Protection
-
-
Resettable Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
-
AC Contactor
-
AC Surge Protective Device
-
Changeover Switch
-
-
Photovoltaic System Protection
-
DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
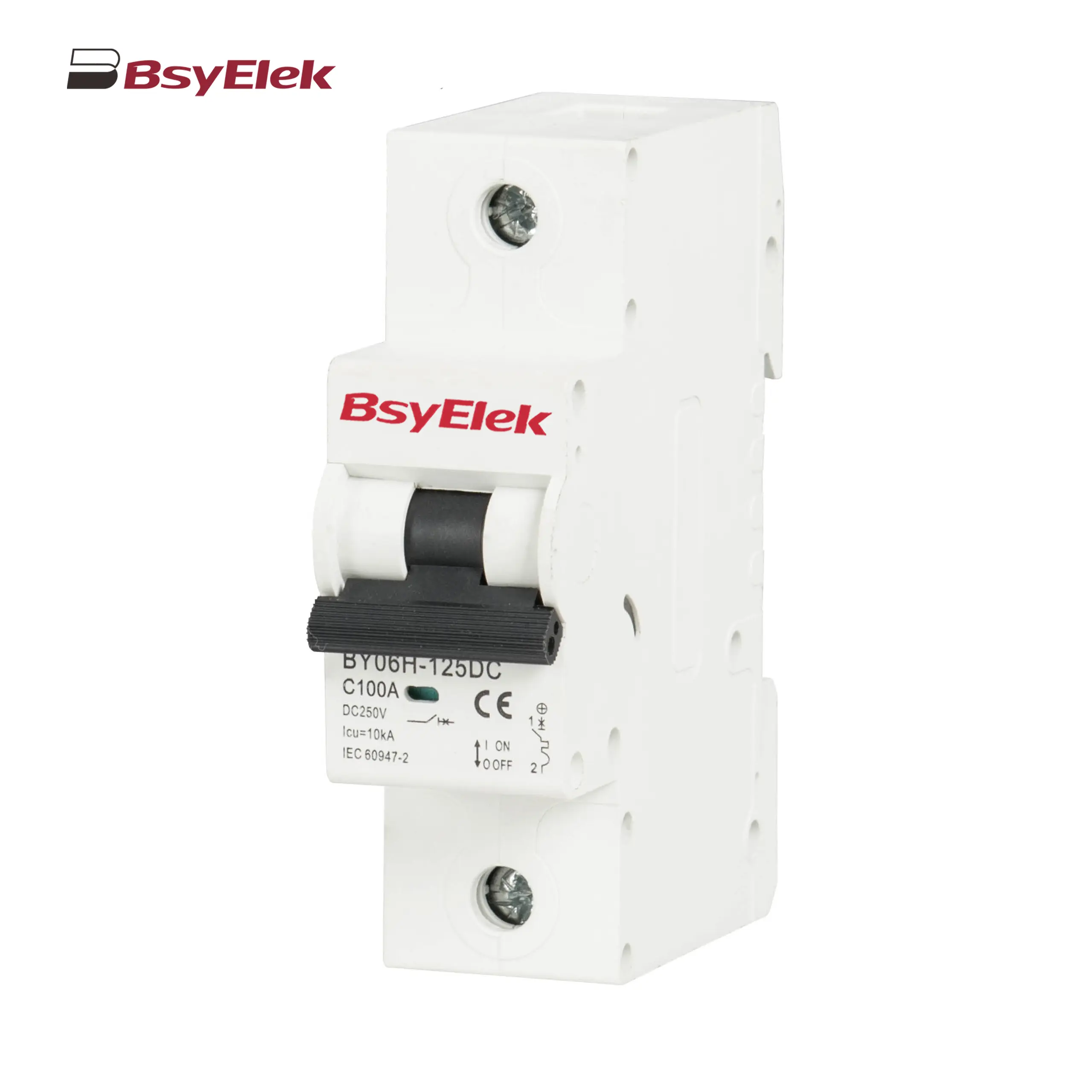 BY06H-125DC MCB 10-15kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06H-125DC MCB 10-15kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
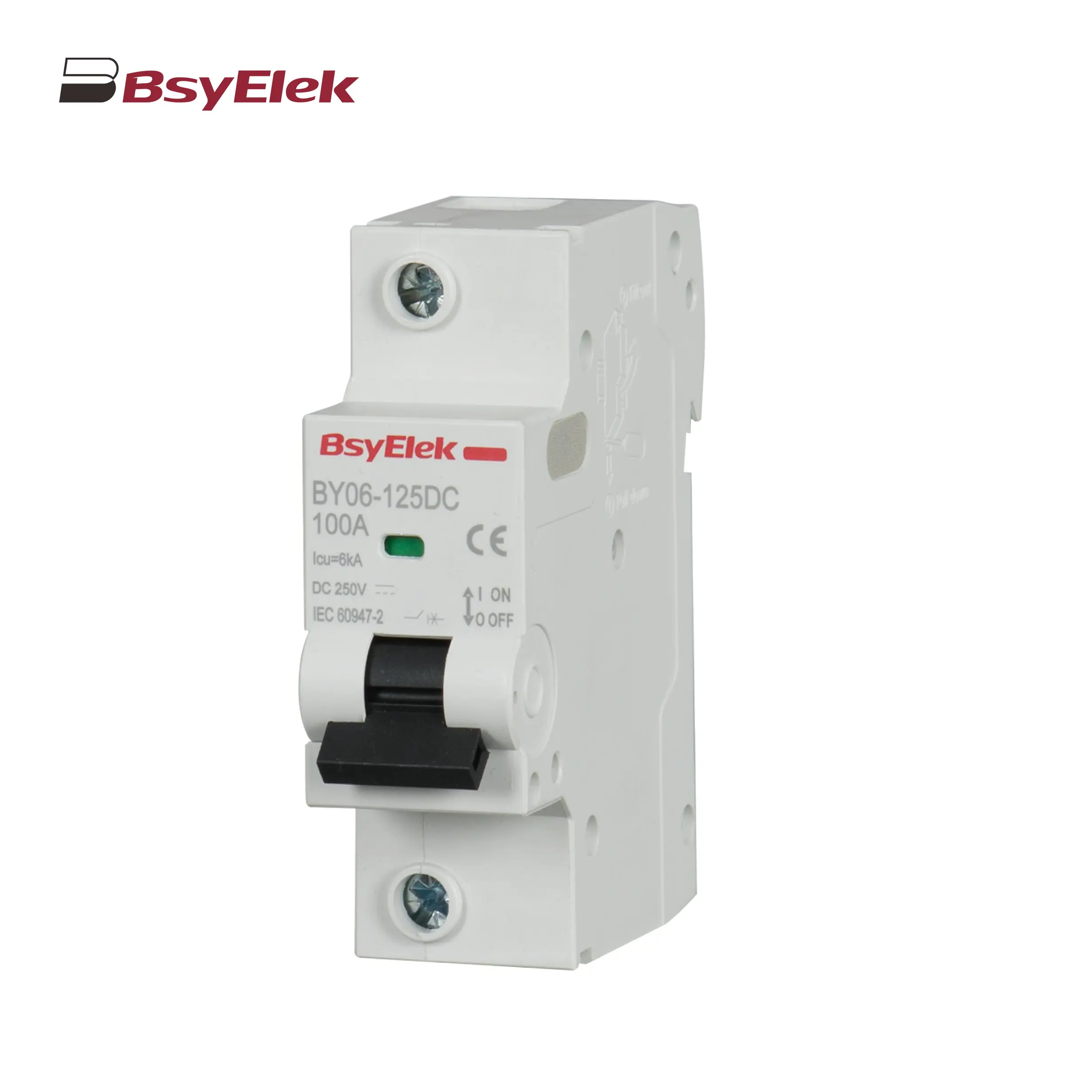 BY06-125DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY06-125DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
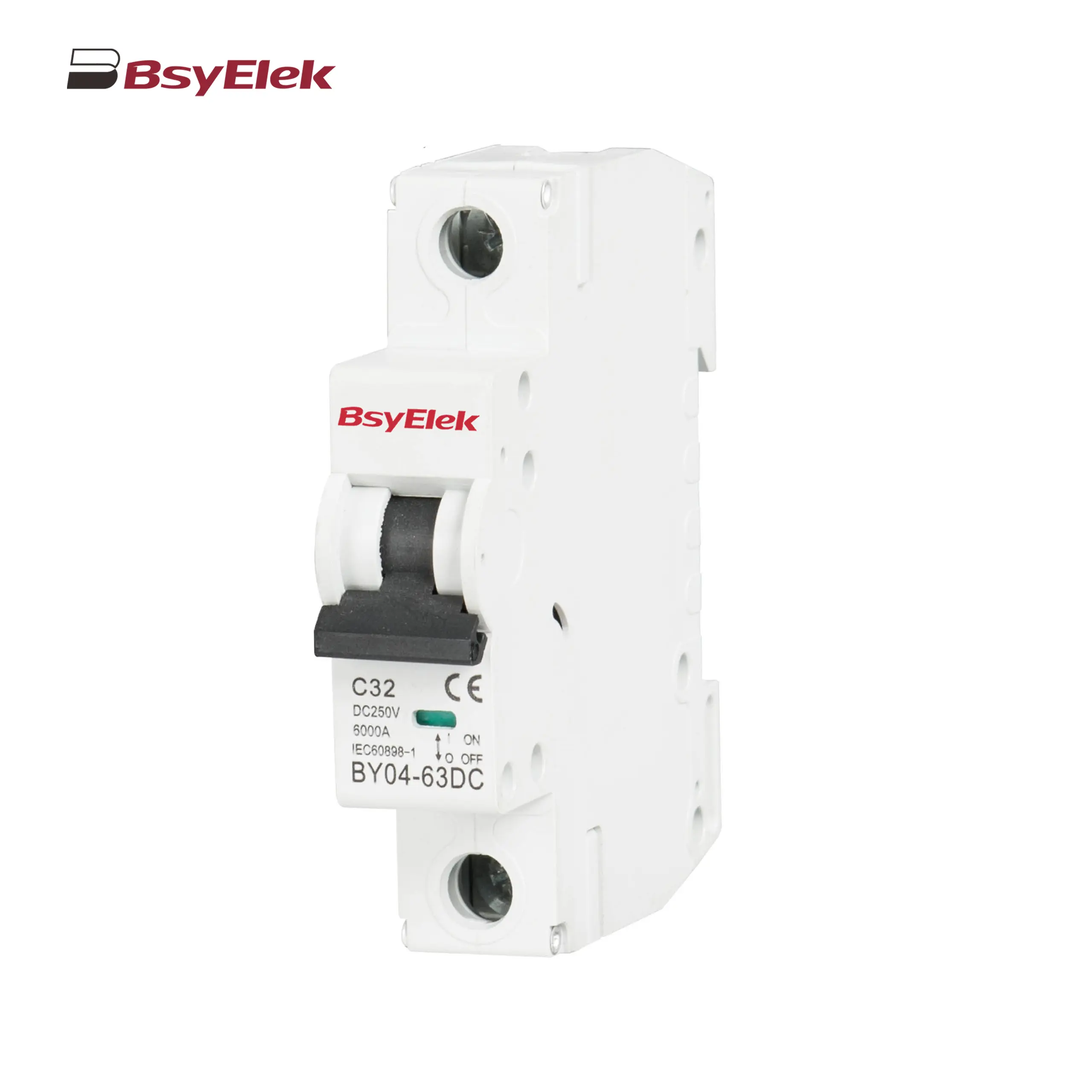 BY04-63DC MCB 6-10kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY04-63DC MCB 6-10kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
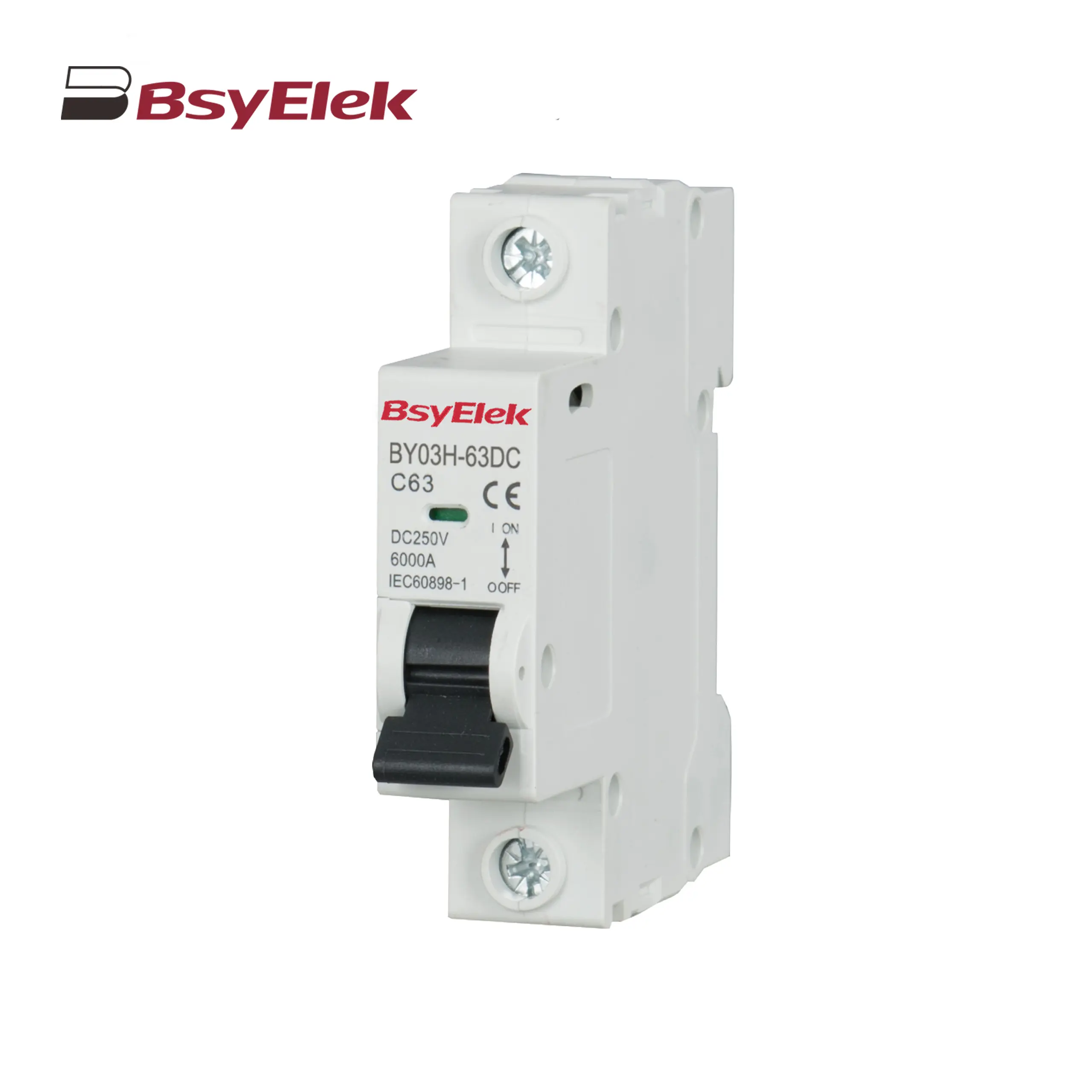 BY03H-63DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03H-63DC MCB 6kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
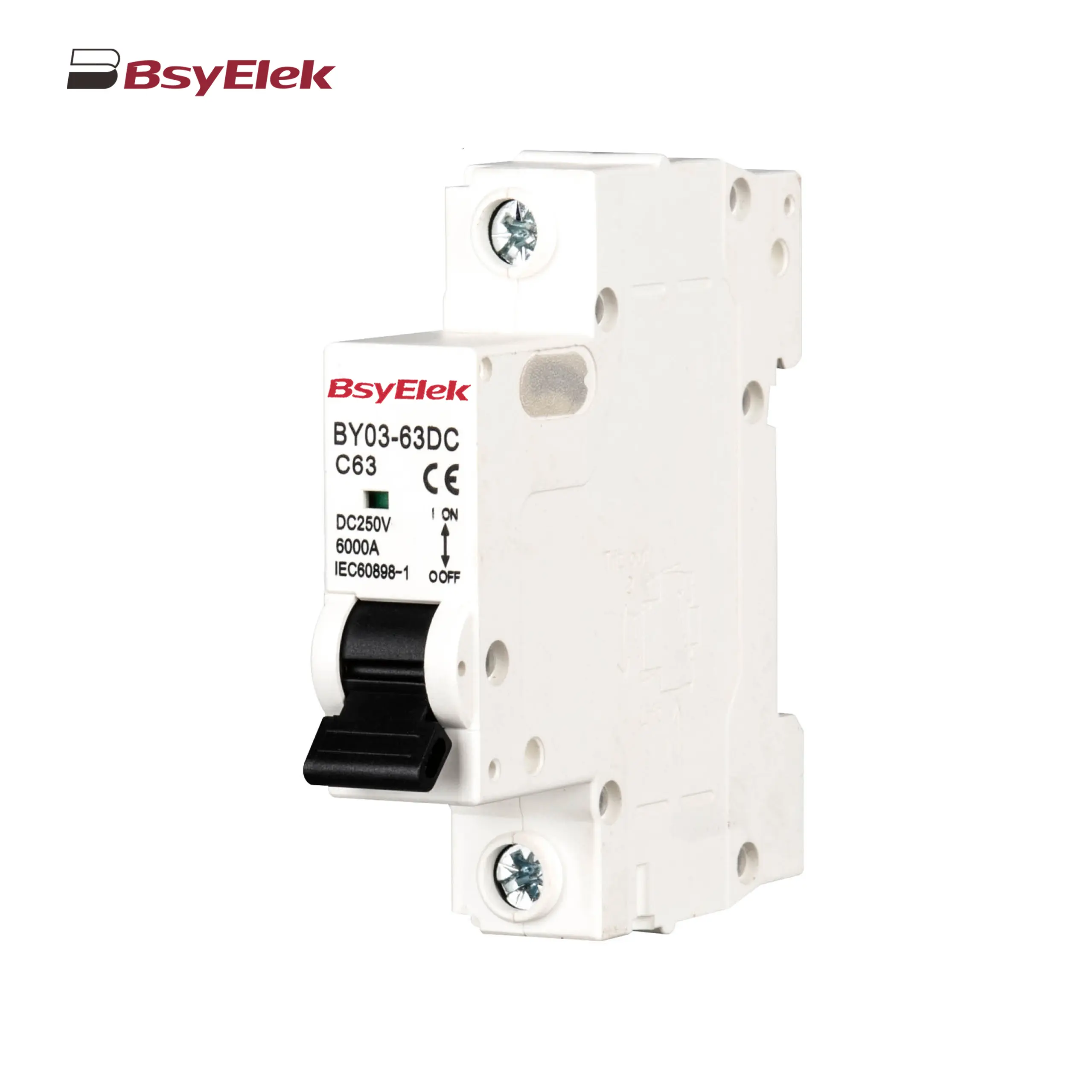 BY03-63DC MCB 4.5kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY03-63DC MCB 4.5kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
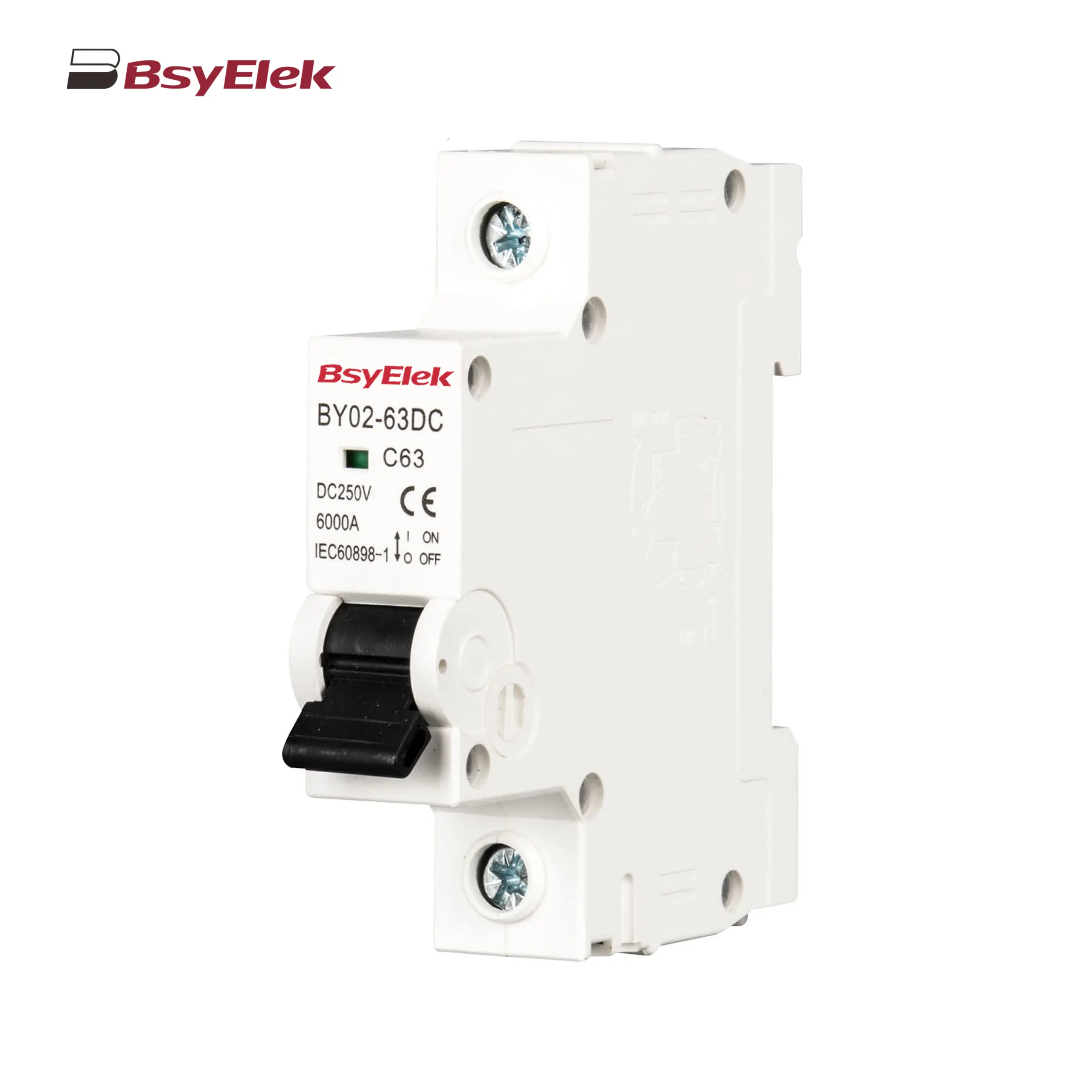 BY02-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY02-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
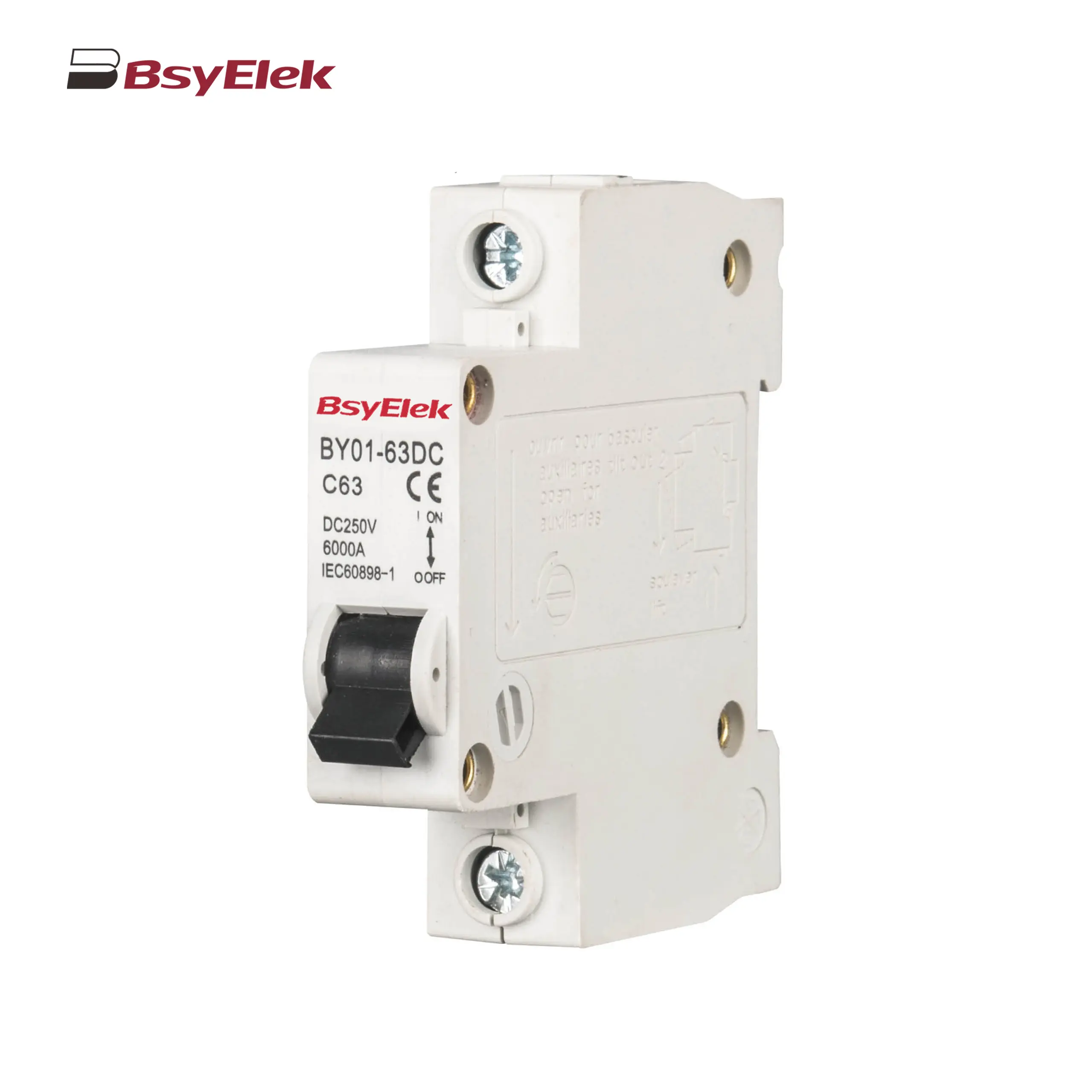 BY01-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
BY01-63DC MCB 3kA DC Miniature Circuit Breaker
-
-
RCD
-
DC Surge Protective Device
-
DC Fuse
-
PV Isolator Switch
-
PV Connector
-
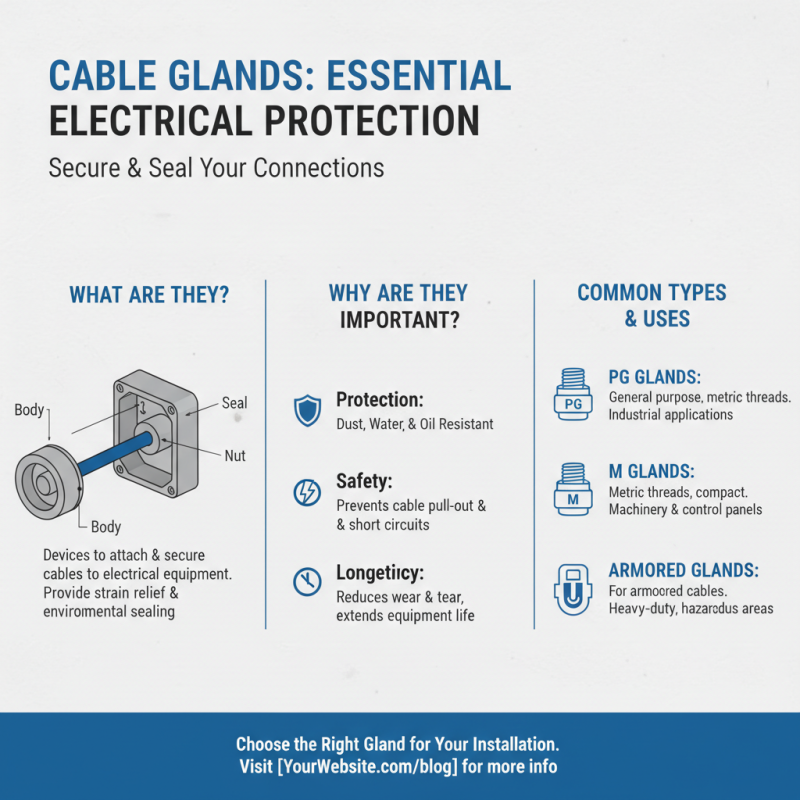
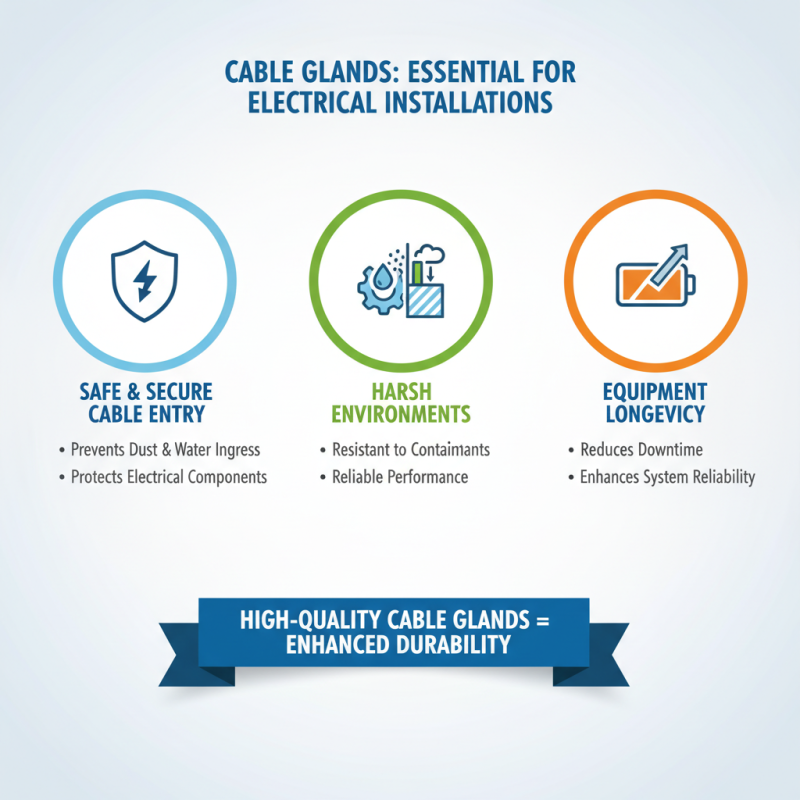
Cable Gland
-
PV Cable
-
PV Knife Switch
-
DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
-
-
Industrial Power Distribution Electric
-
Distribution Box
-
Air Conditioning System
-
Definite Purpose Magnetic Contactor
-
Condensate Pump
-
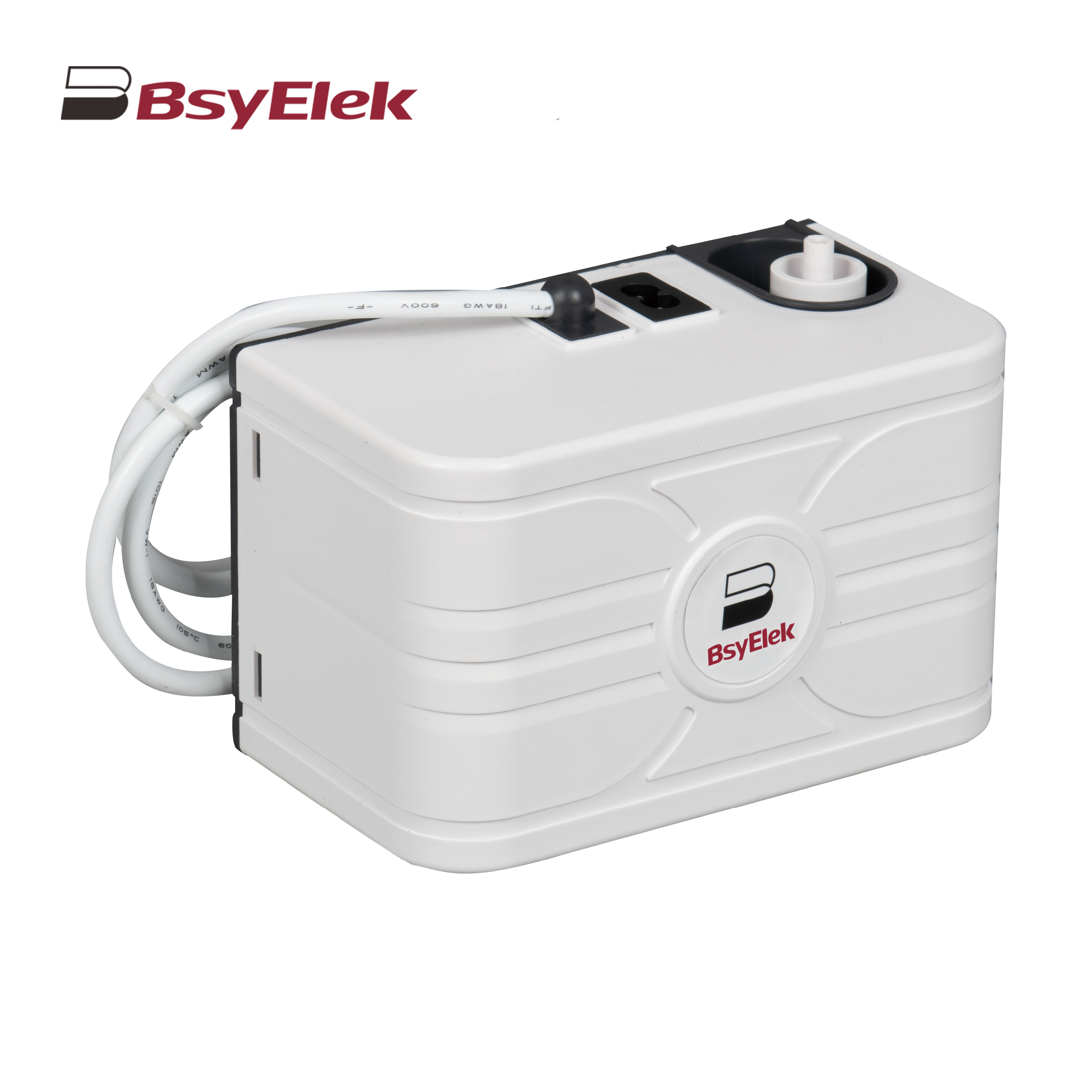 BY-5018 1.8M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-5018 1.8M Engineering Drainage Pump
-
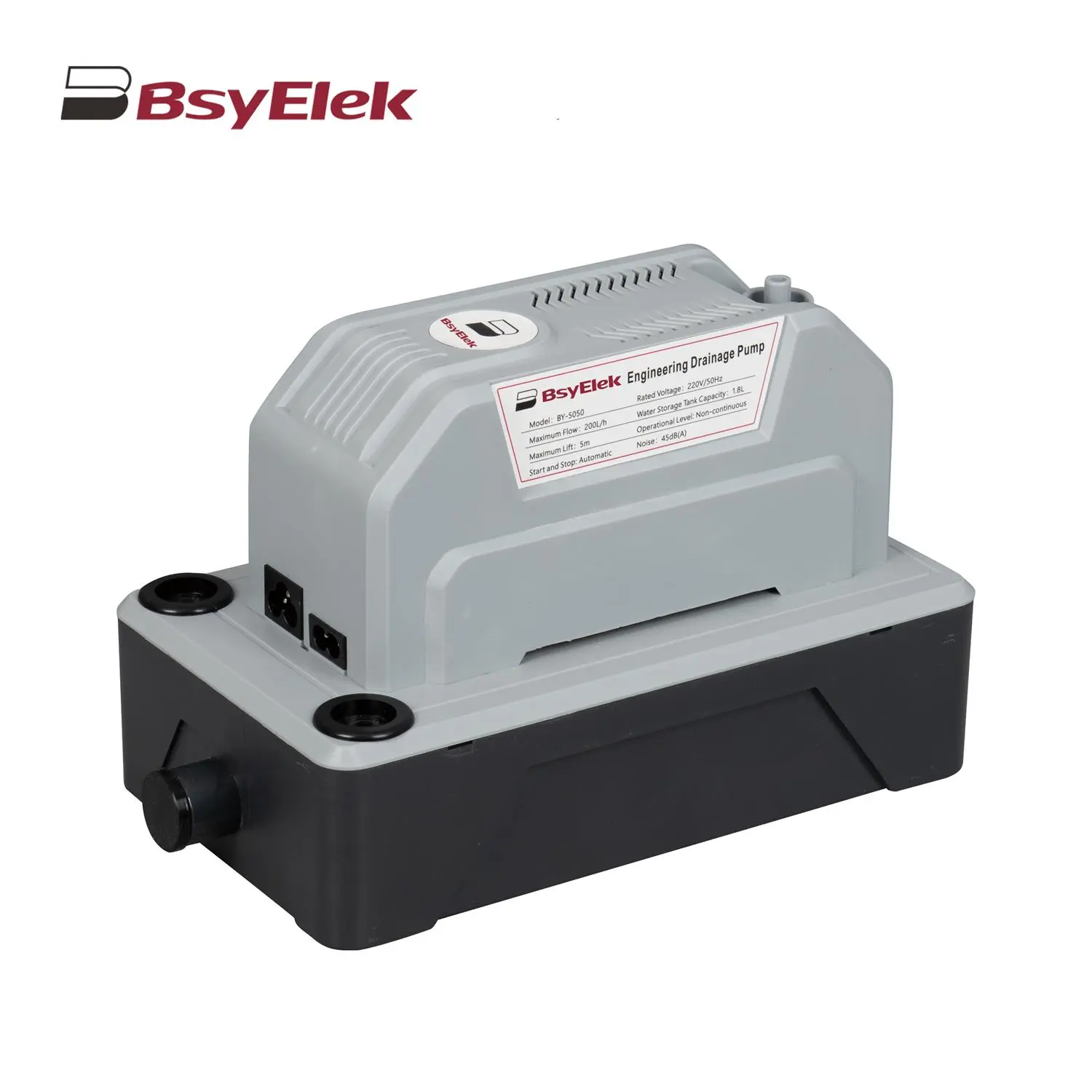 BY-5050 5M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-5050 5M Engineering Drainage Pump
-
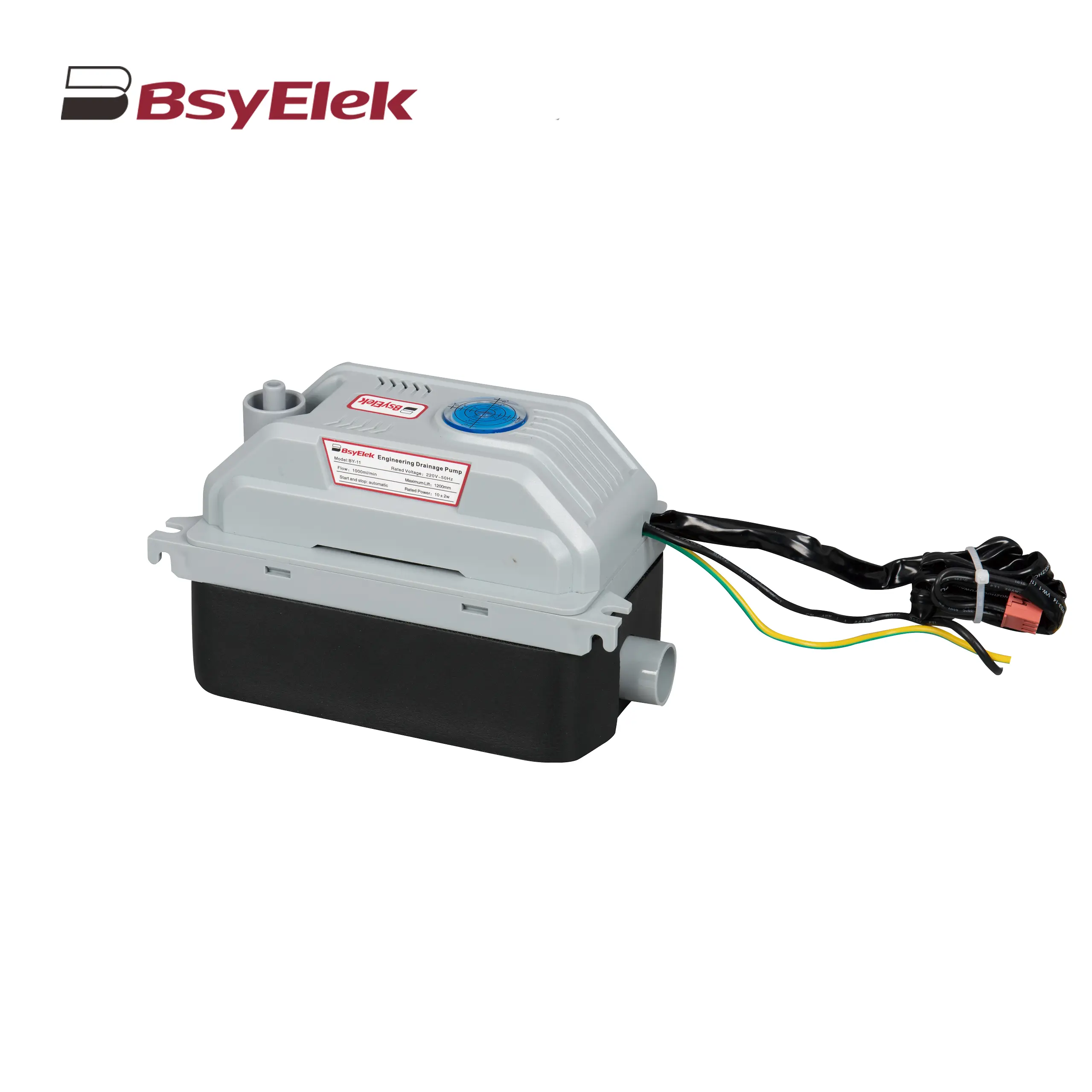 BY-11 1.2M Engineering Drainage Pump
BY-11 1.2M Engineering Drainage Pump
-
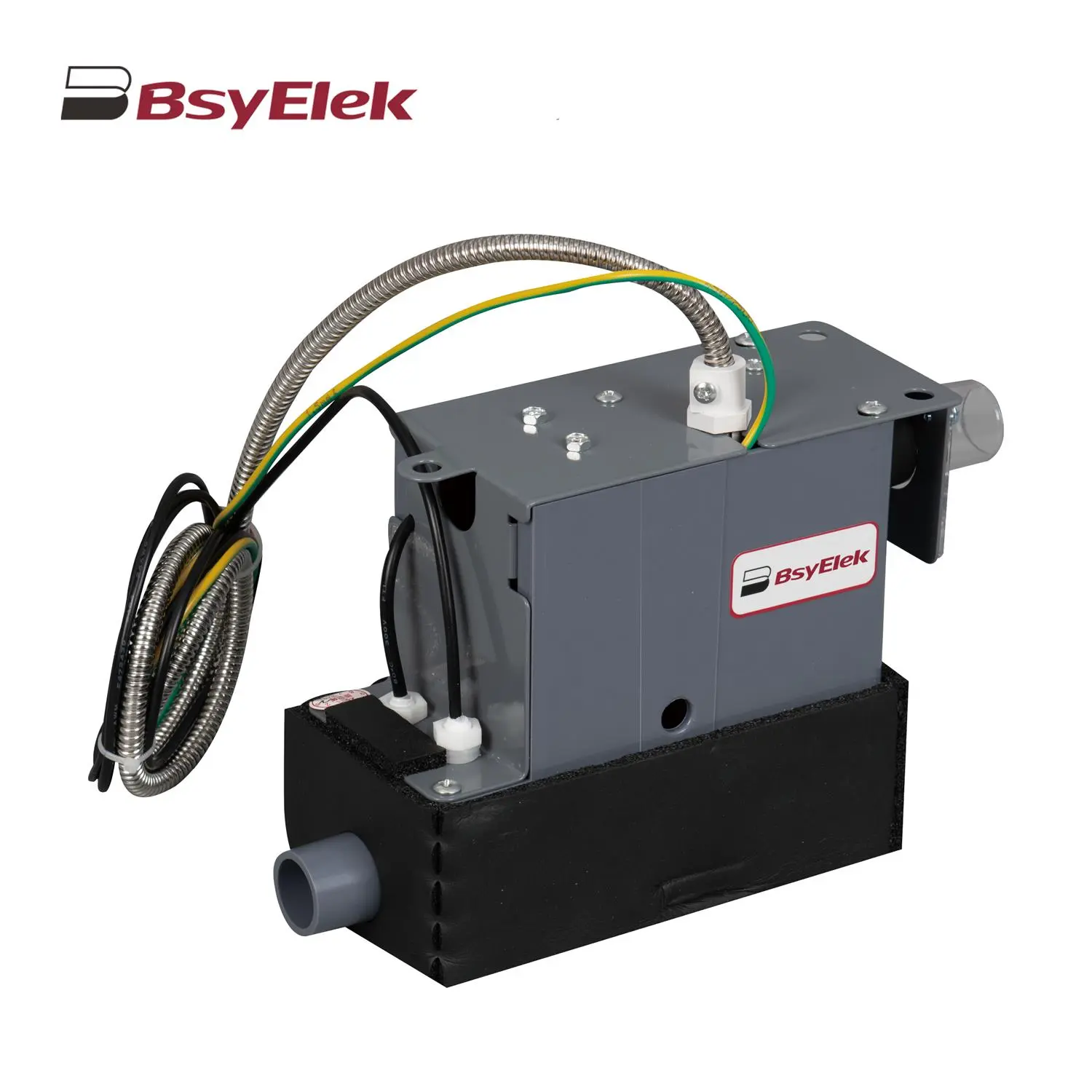 SBH-05 0.7M Original Drainage Pump of Duct Type Air Conditioner
SBH-05 0.7M Original Drainage Pump of Duct Type Air Conditioner
-
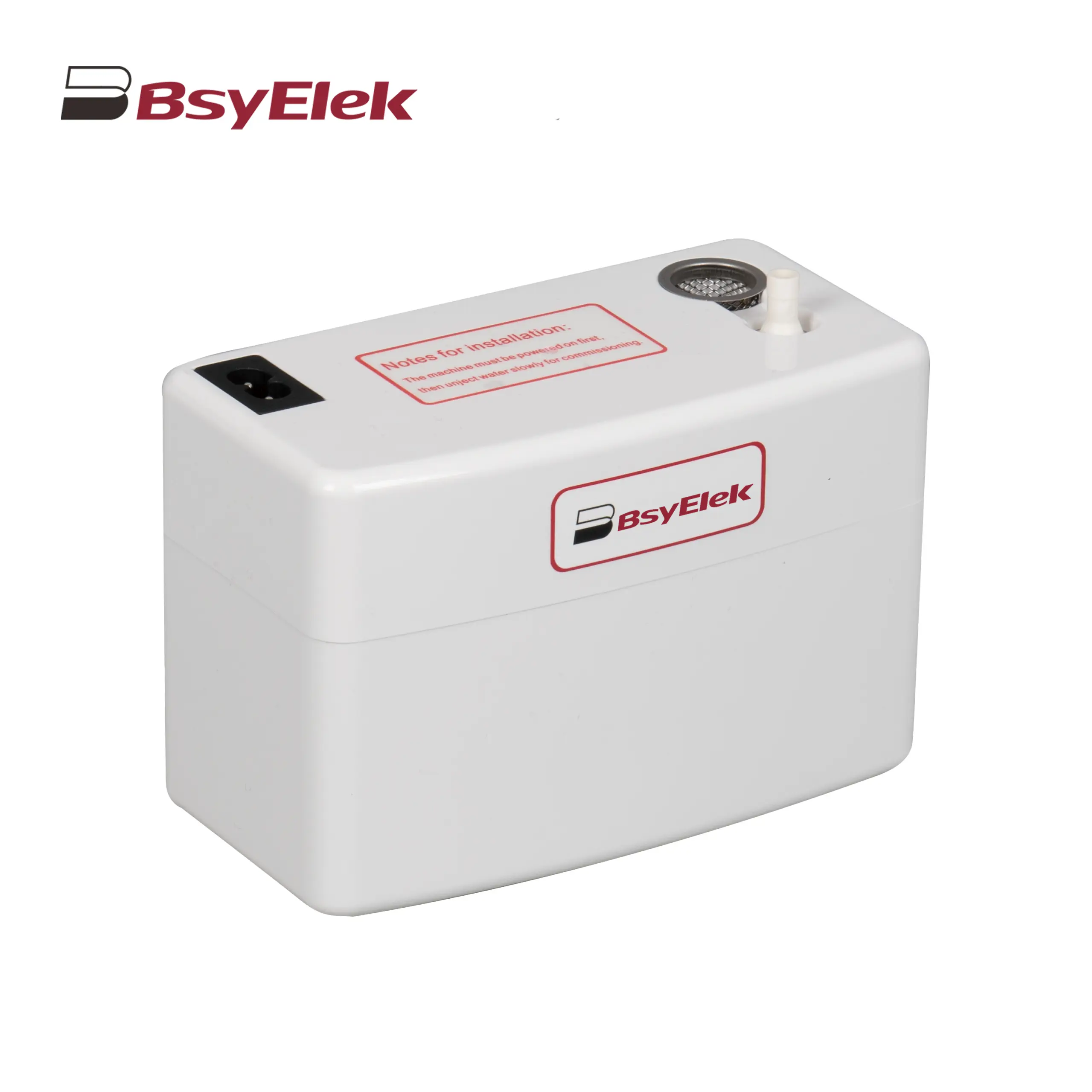 BY-24A/40A 10M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-24A/40A 10M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
-
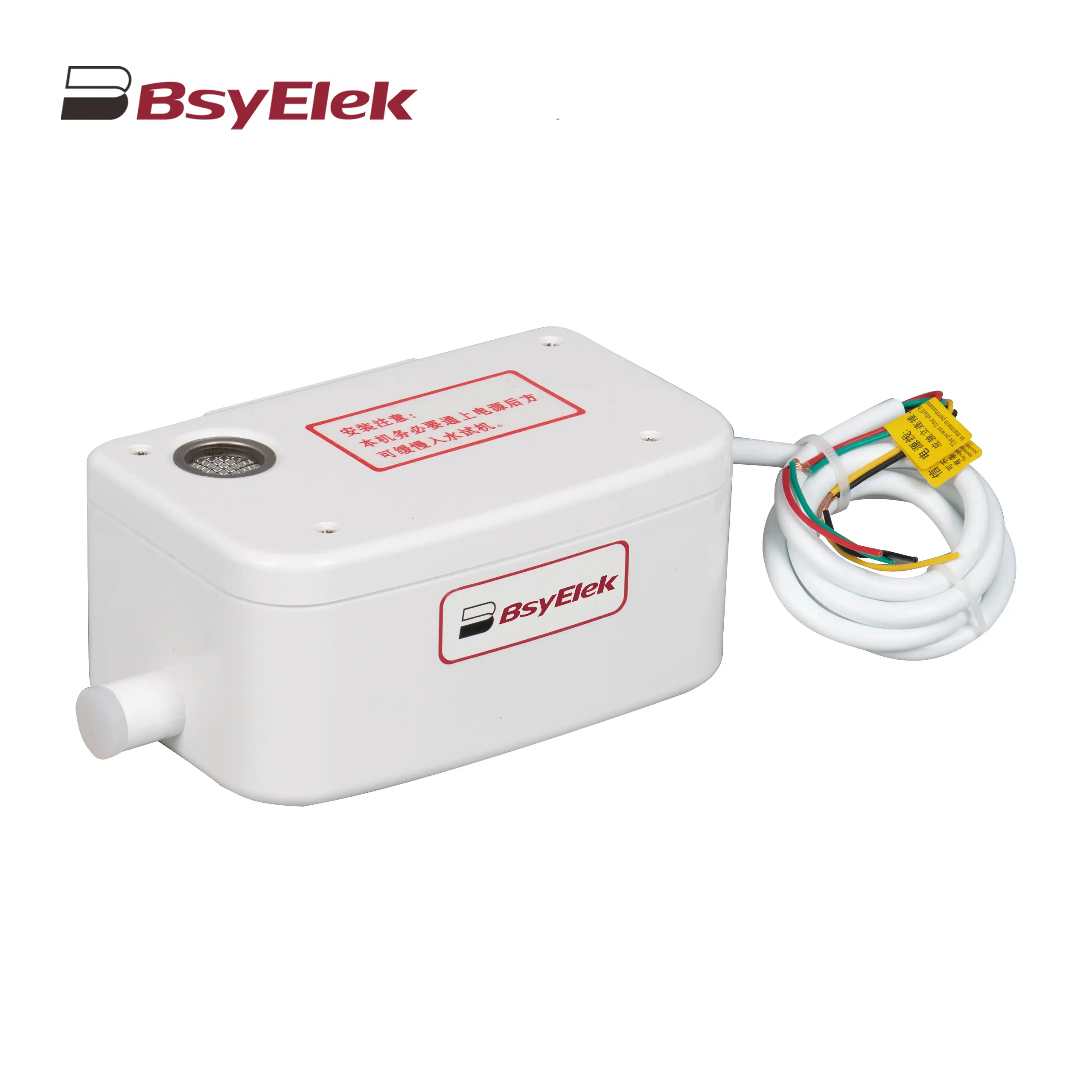 BY-50A 12M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-50A 12M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
-
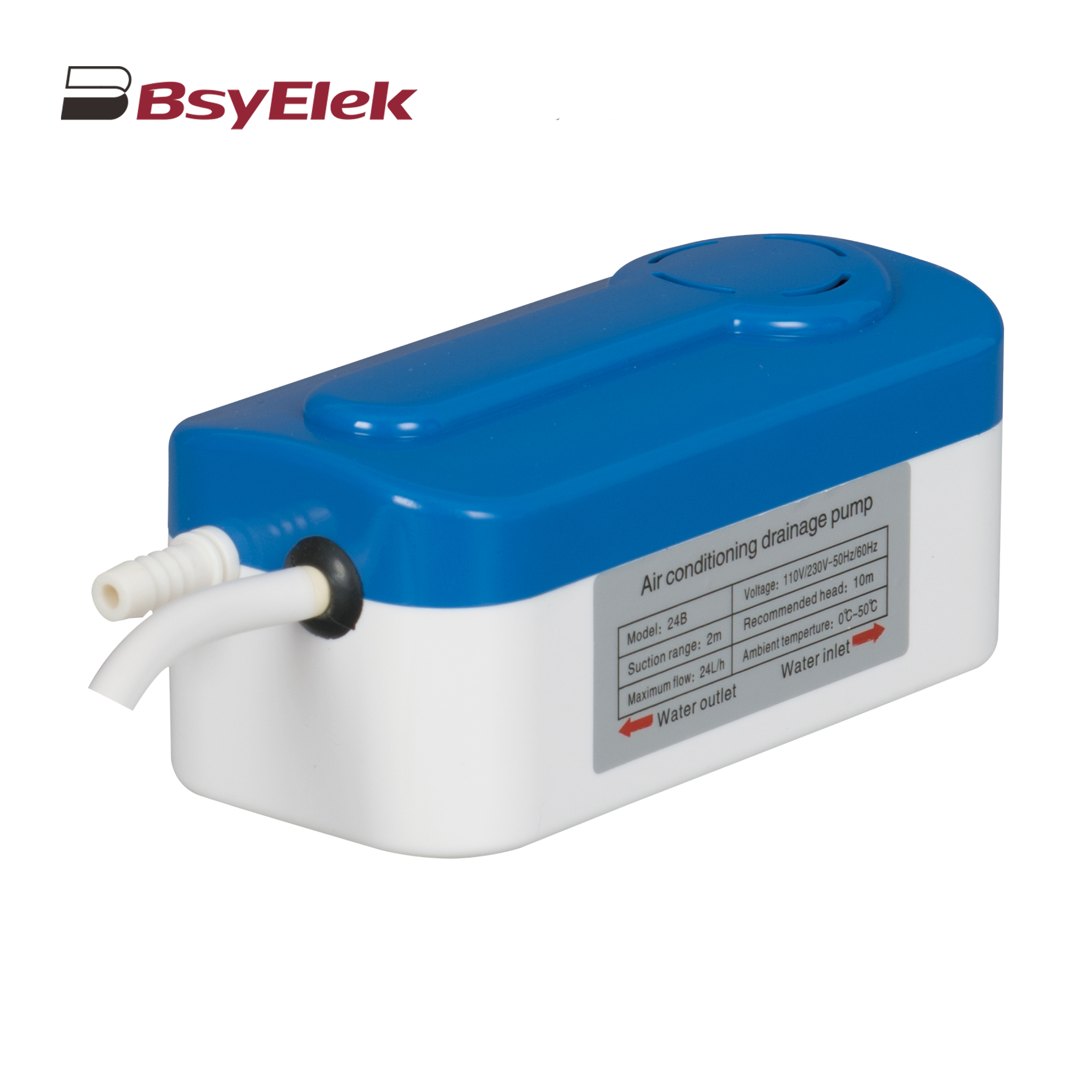 BY-24B/40B 10M Split Type Drainage Pump
BY-24B/40B 10M Split Type Drainage Pump
-
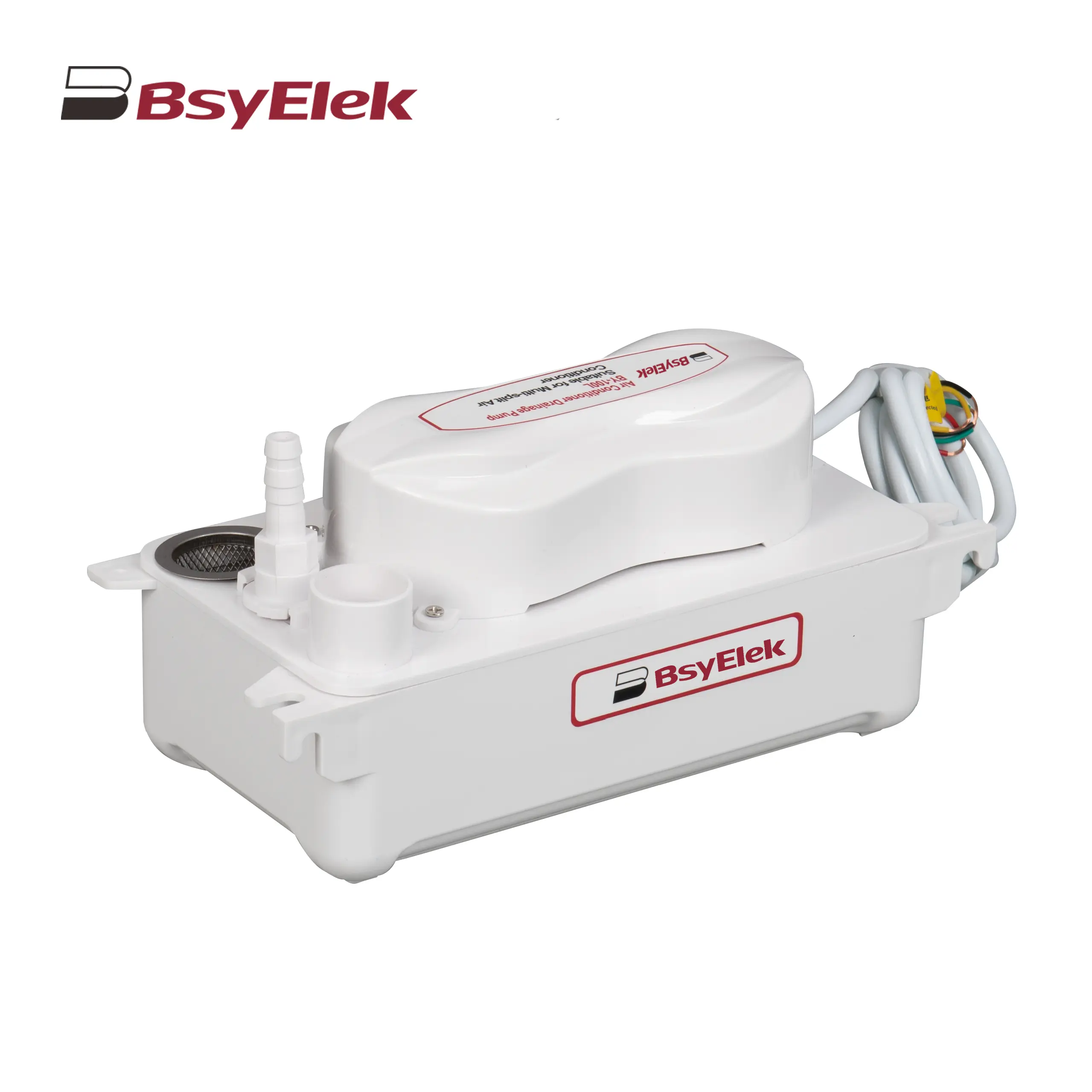 BY-100L 2M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
BY-100L 2M Drainage Pump of Air Conditioner
-
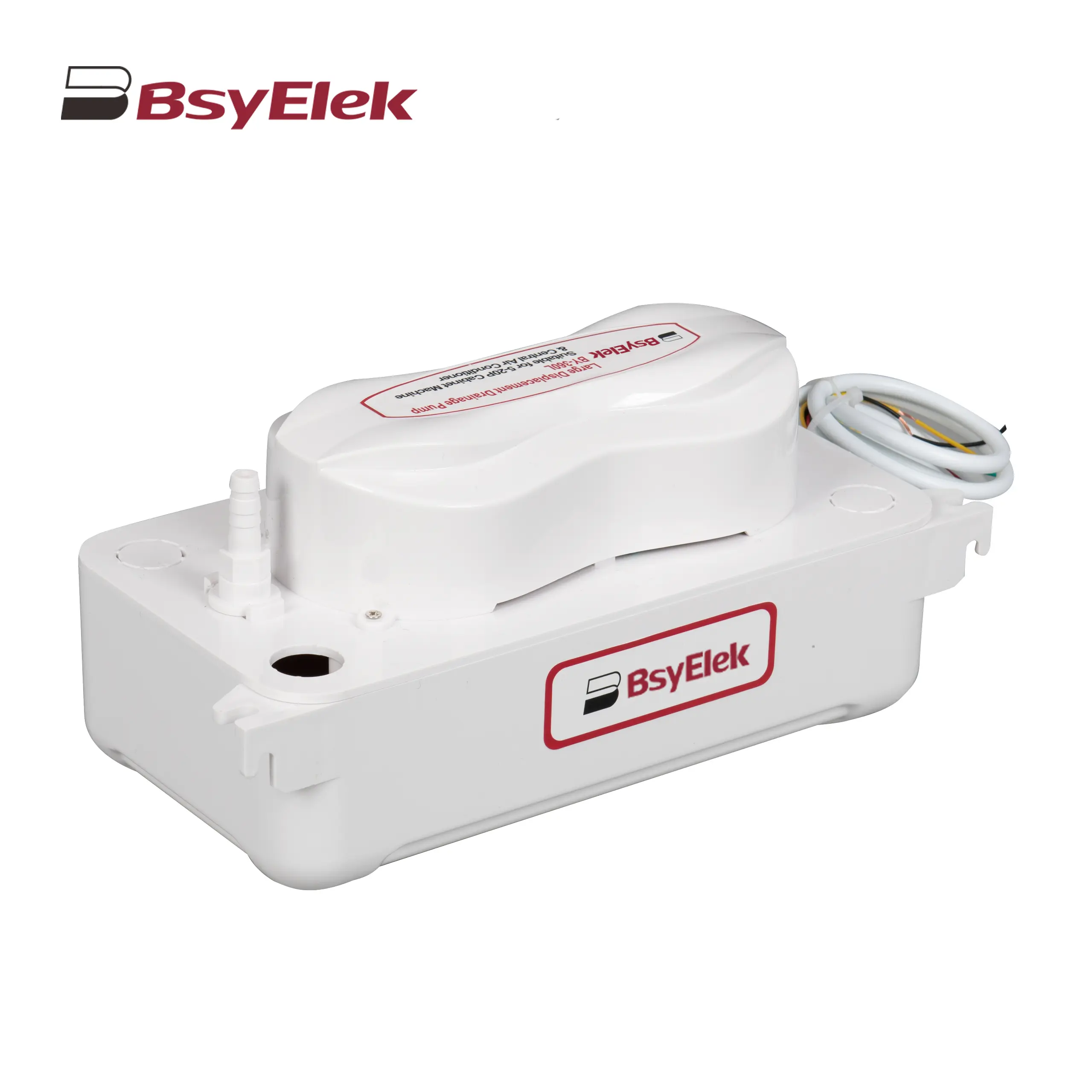 BY-360L 6M Large Displacement Drainage Pump
BY-360L 6M Large Displacement Drainage Pump
-
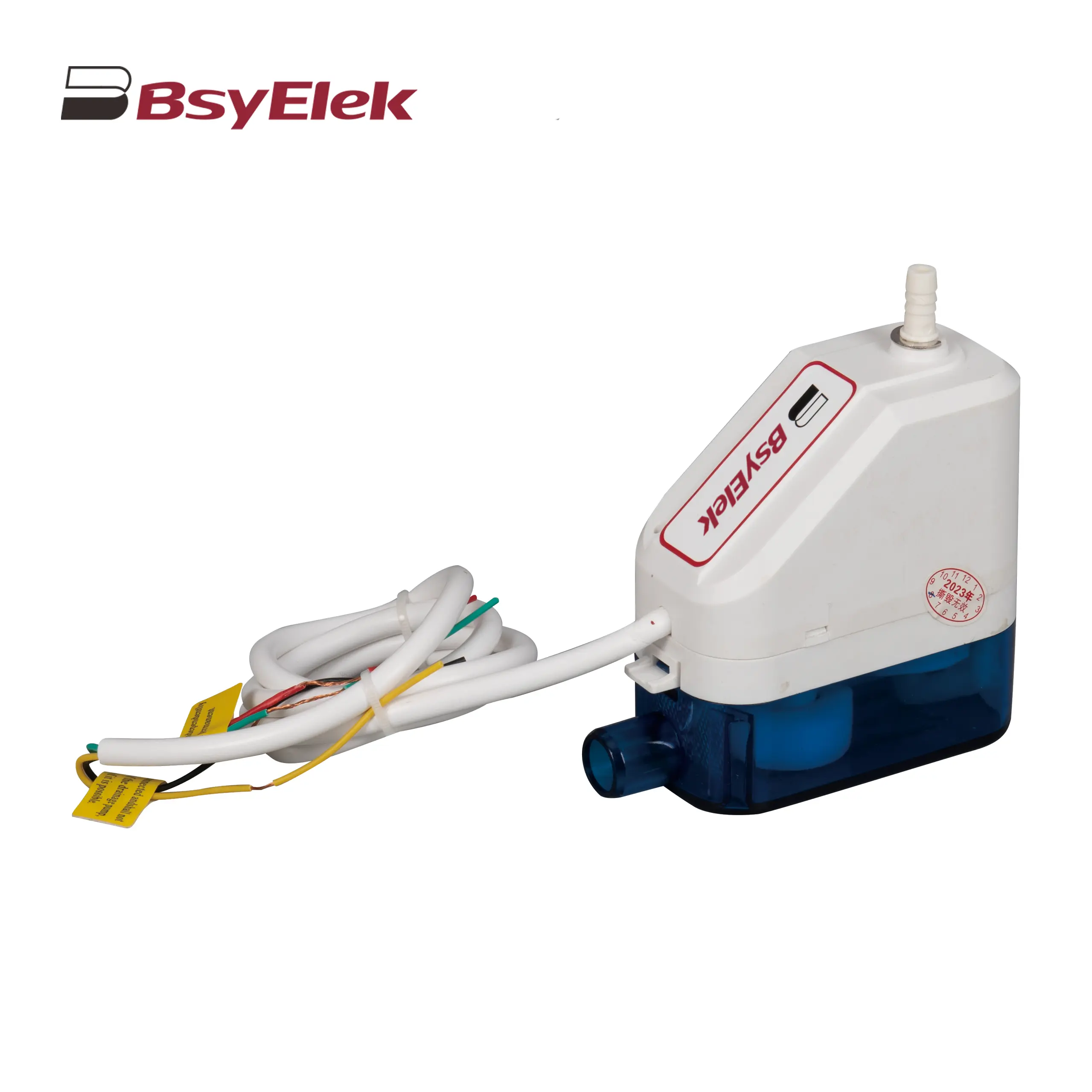 BY-24C/40C 10M Corner Drainage Pump
BY-24C/40C 10M Corner Drainage Pump
-
-
-
-
News
-
Top Blog
-
Company News
-
Industry Dynamics
-
What is a miniature circuit breaker (MCB)?
-
PG Series Waterproof Cable Glands with Washer for Harsh Environments
-
LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch ensures reliable power transfer
-
BYX2 AC contactor series: reliable power control for modern electrical systems
-
High-performance 1000V DC fuse holder optimizes solar photovoltaic system protection
-
BY07L-63 Residual Current Circuit Breaker Ensures Global Electrical Safety
-
BYQ5 ATS Isolation Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
-
BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch: Features and Benefits
-
-
-
Support
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message
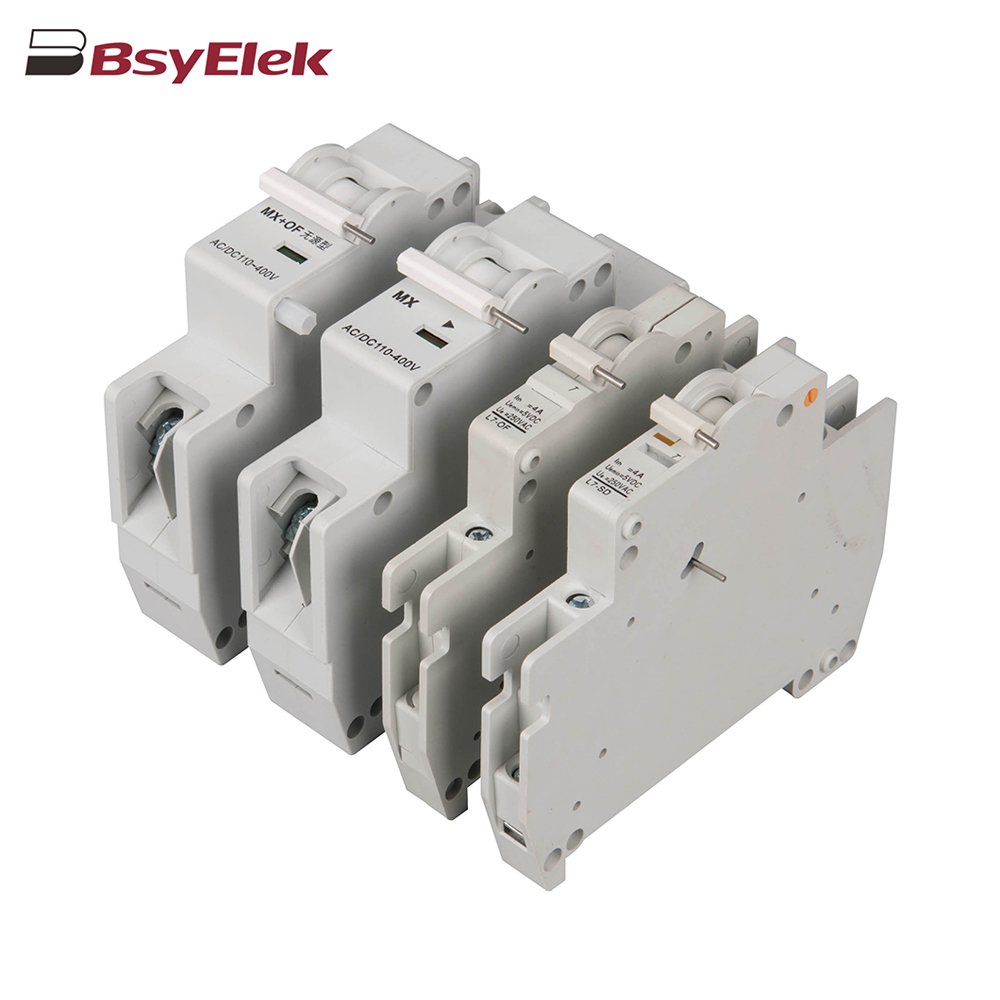




 OF SD MX OF MCB Miniature Circuit Breaker Accessories
OF SD MX OF MCB Miniature Circuit Breaker Accessories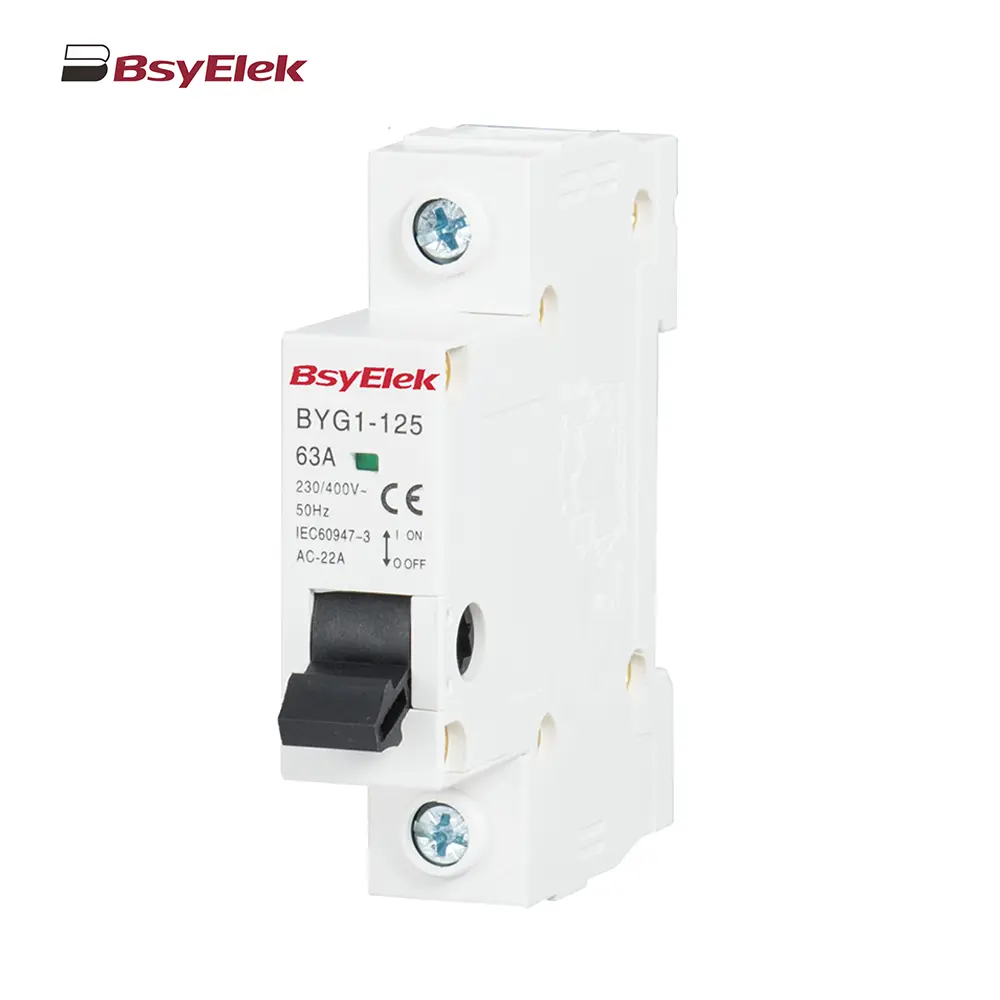 BYG1-125 Main Switch MCB Isolator Switch
BYG1-125 Main Switch MCB Isolator Switch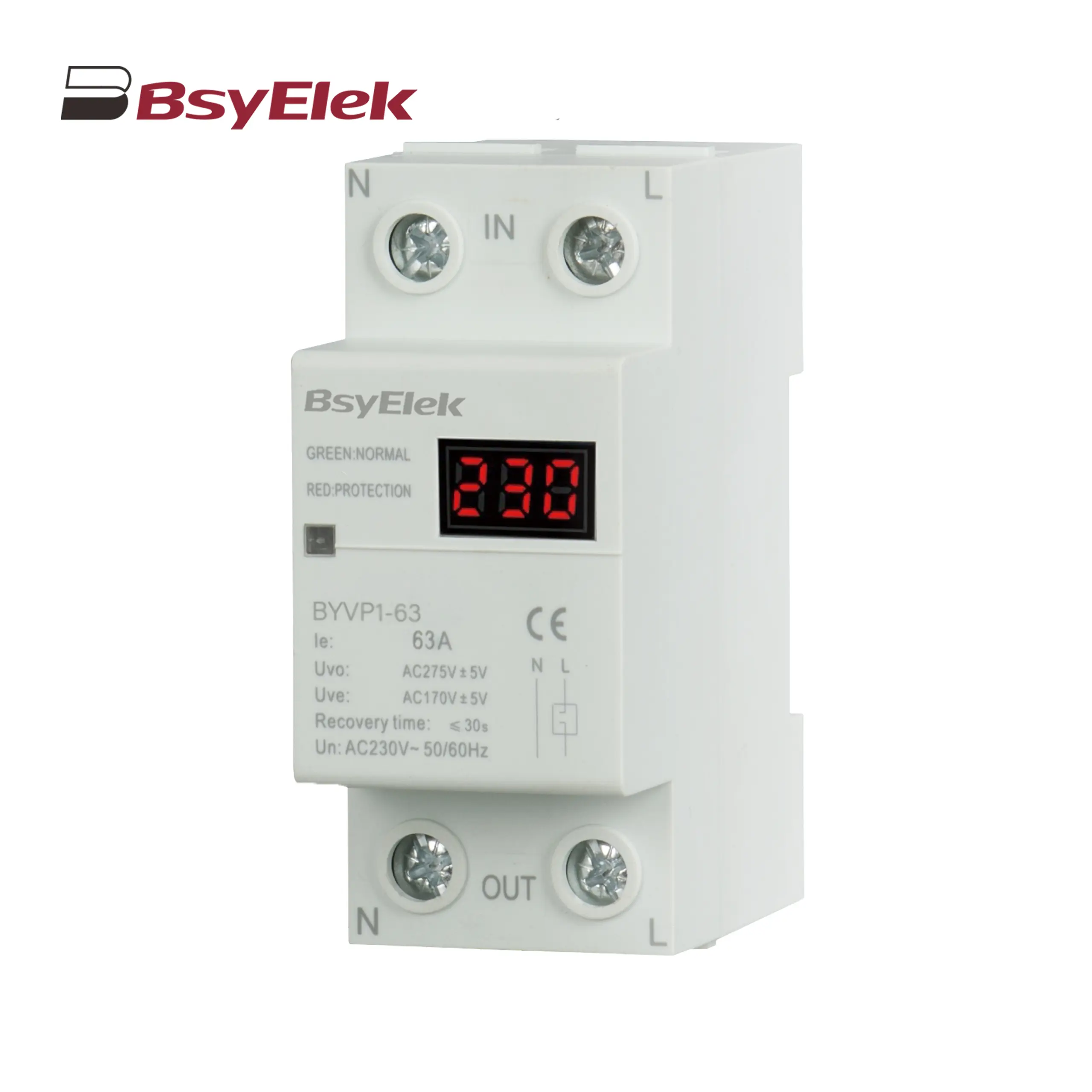 BYVP1-63 100A Single Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
BYVP1-63 100A Single Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector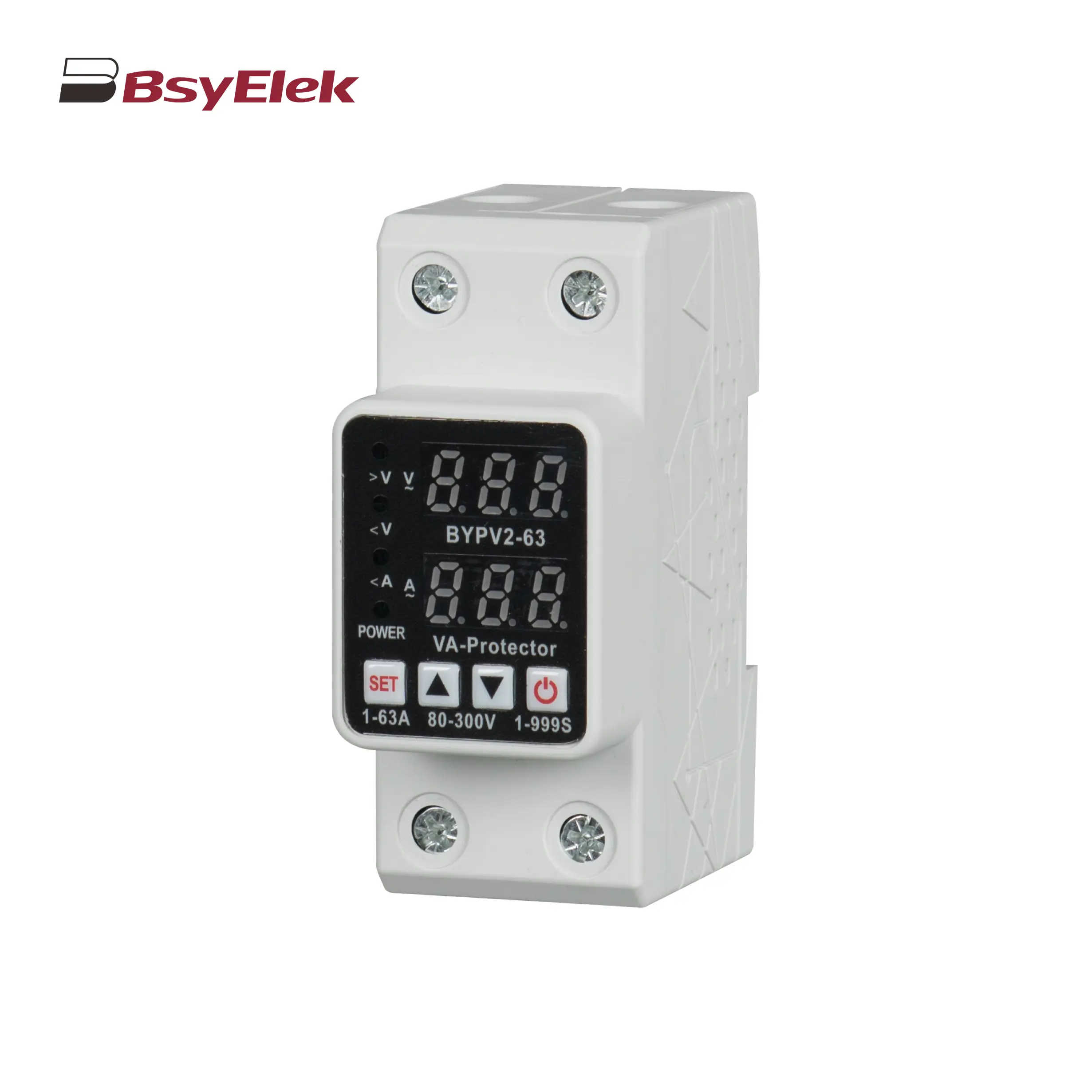 BYVP2-63 40A 63A Adjustable Dual Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector
BYVP2-63 40A 63A Adjustable Dual Display Overvoltage and Undervoltage Protector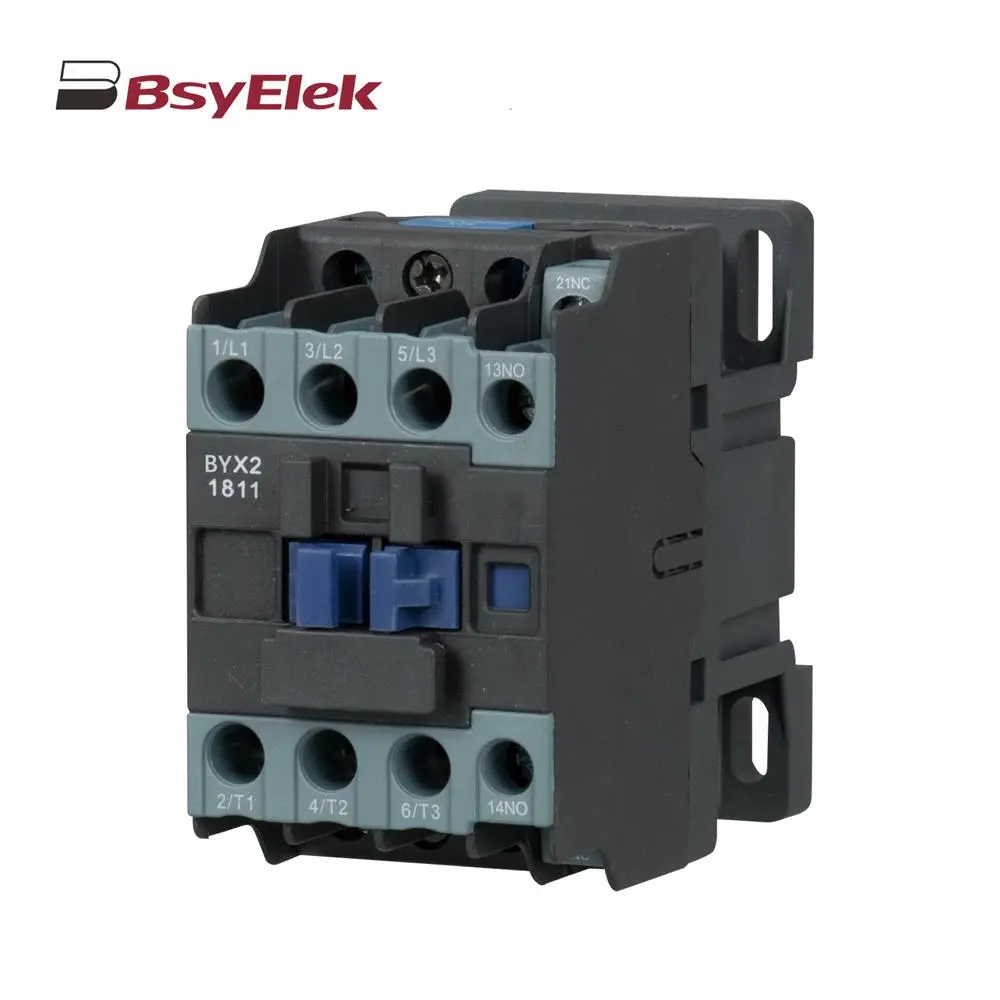 BYX2 6-95A AC Contactor
BYX2 6-95A AC Contactor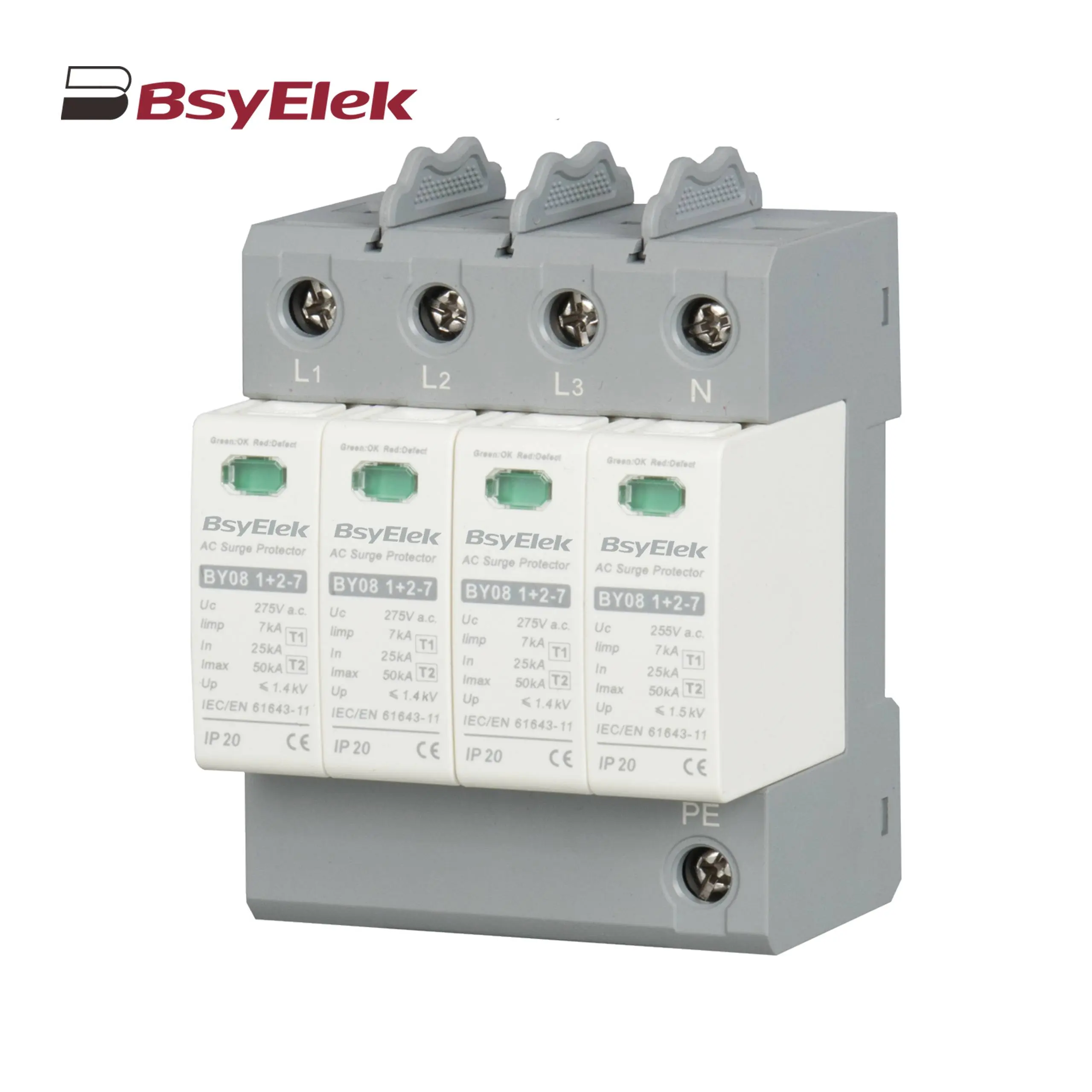 BY08 1+2-7 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 50KA Surge Protective Device
BY08 1+2-7 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 50KA Surge Protective Device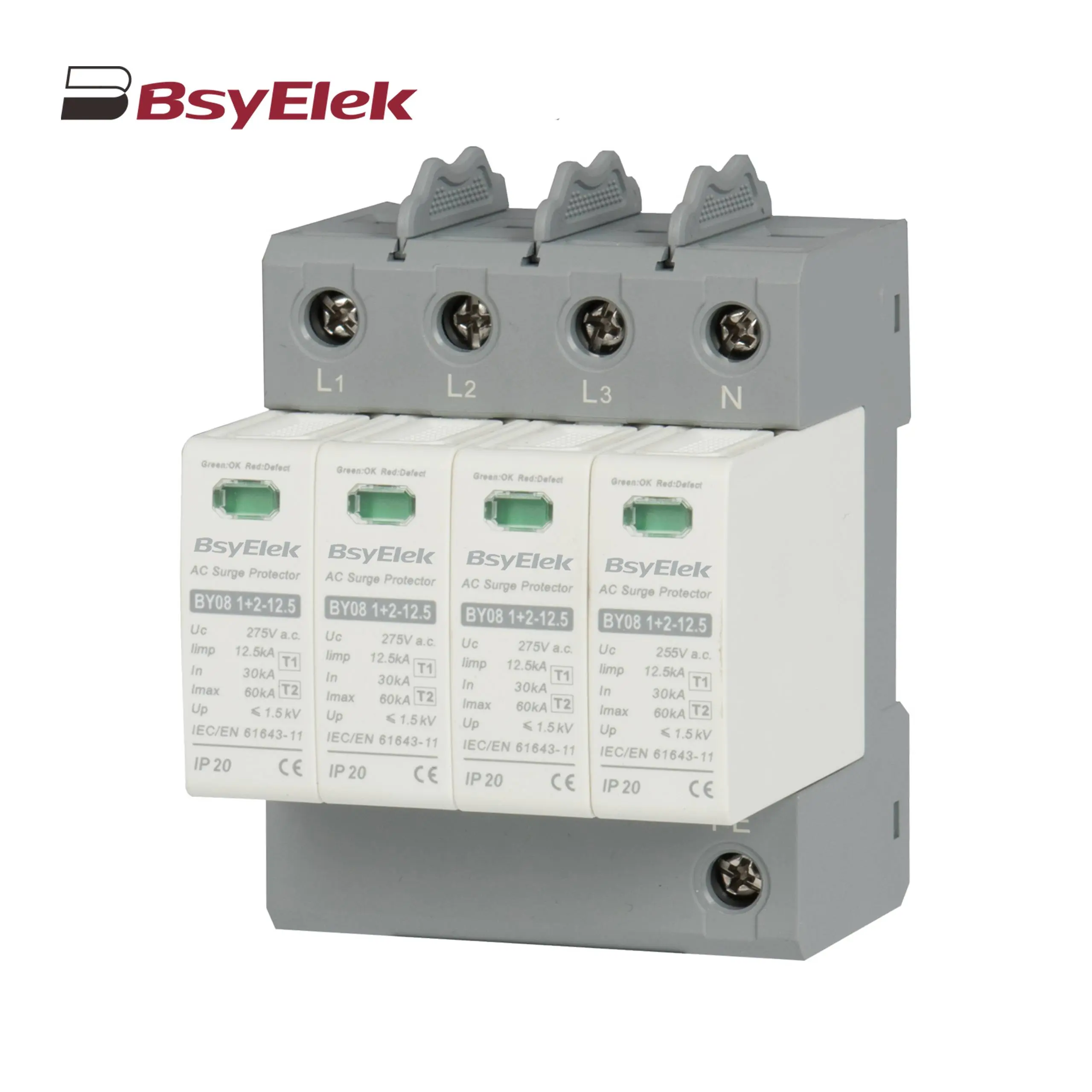 BY08 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 60KA Surge Protective Device
BY08 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 Imax 60KA Surge Protective Device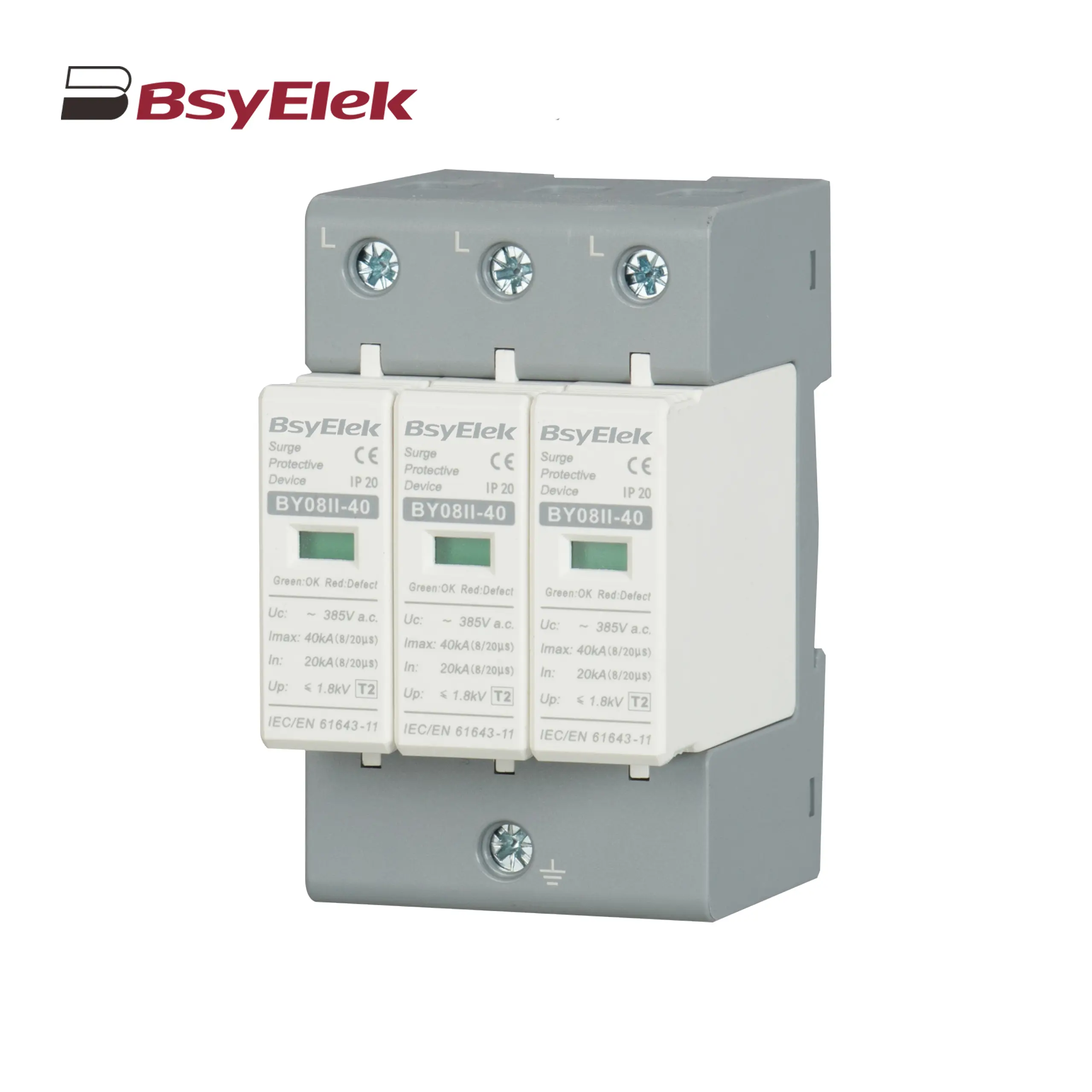 BY08II-40 SPD Class T2 Imax 40KA Surge Protective Device
BY08II-40 SPD Class T2 Imax 40KA Surge Protective Device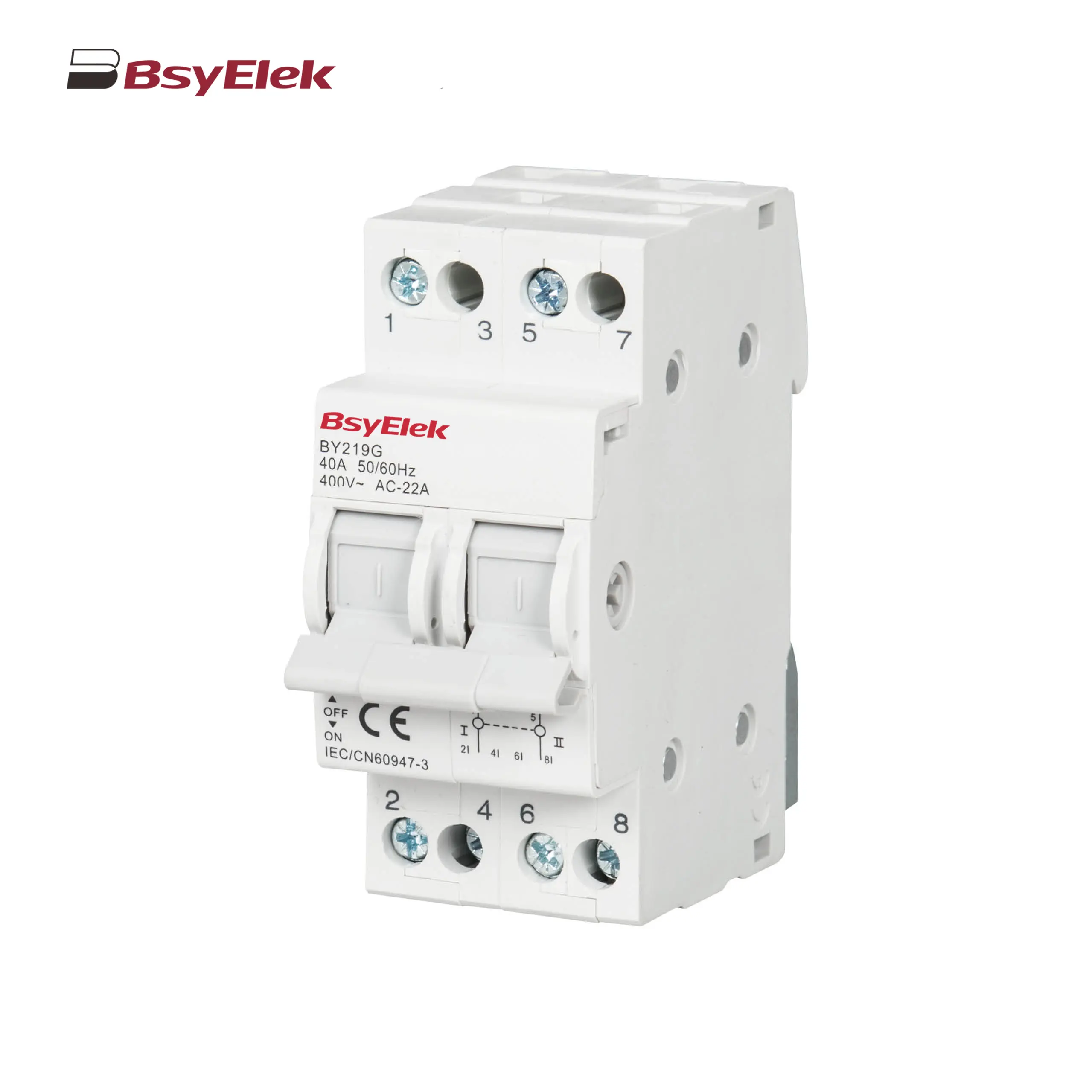 BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch
BY19G 63A Manual Changeover Switch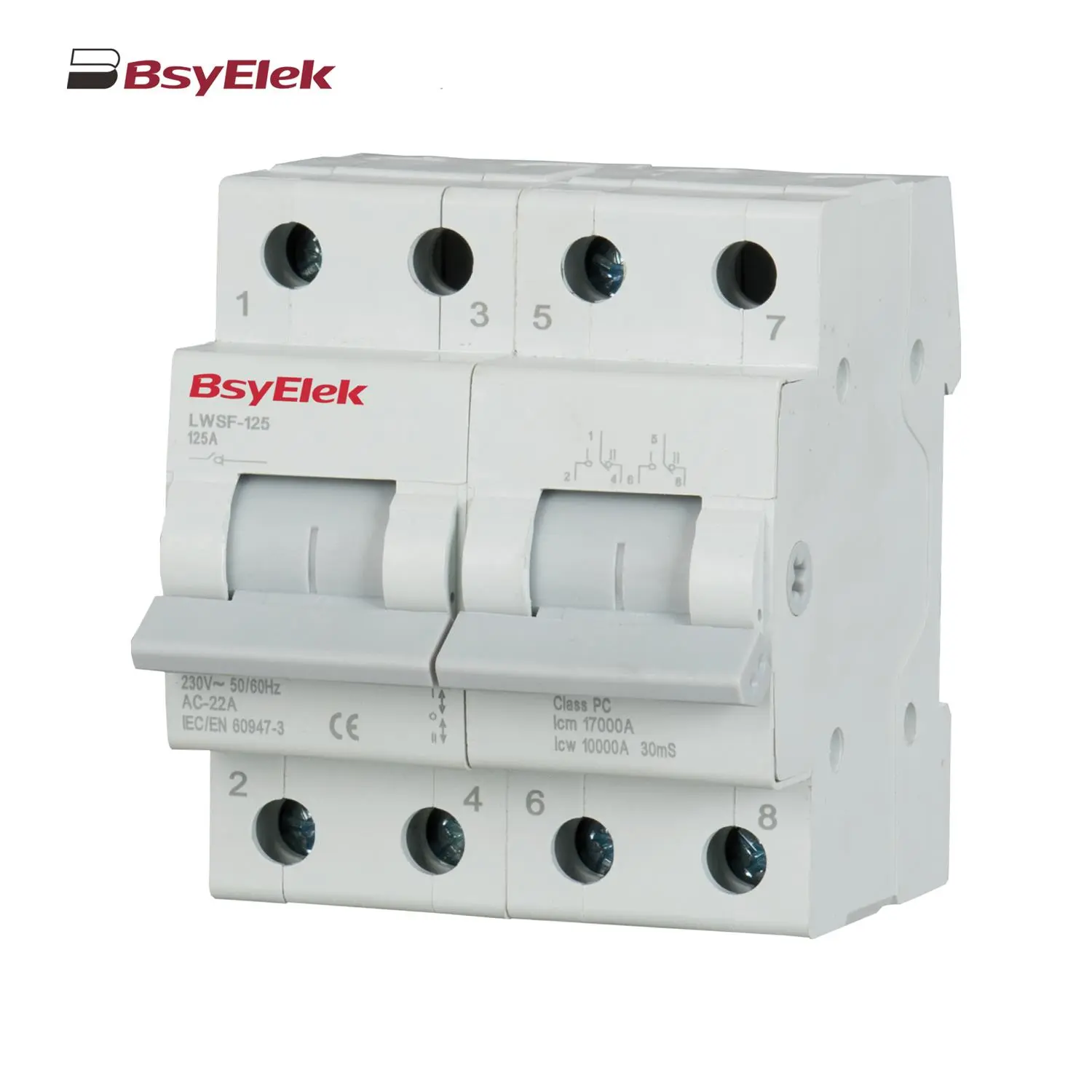 LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch
LWSF-125 125A Manual Changeover Switch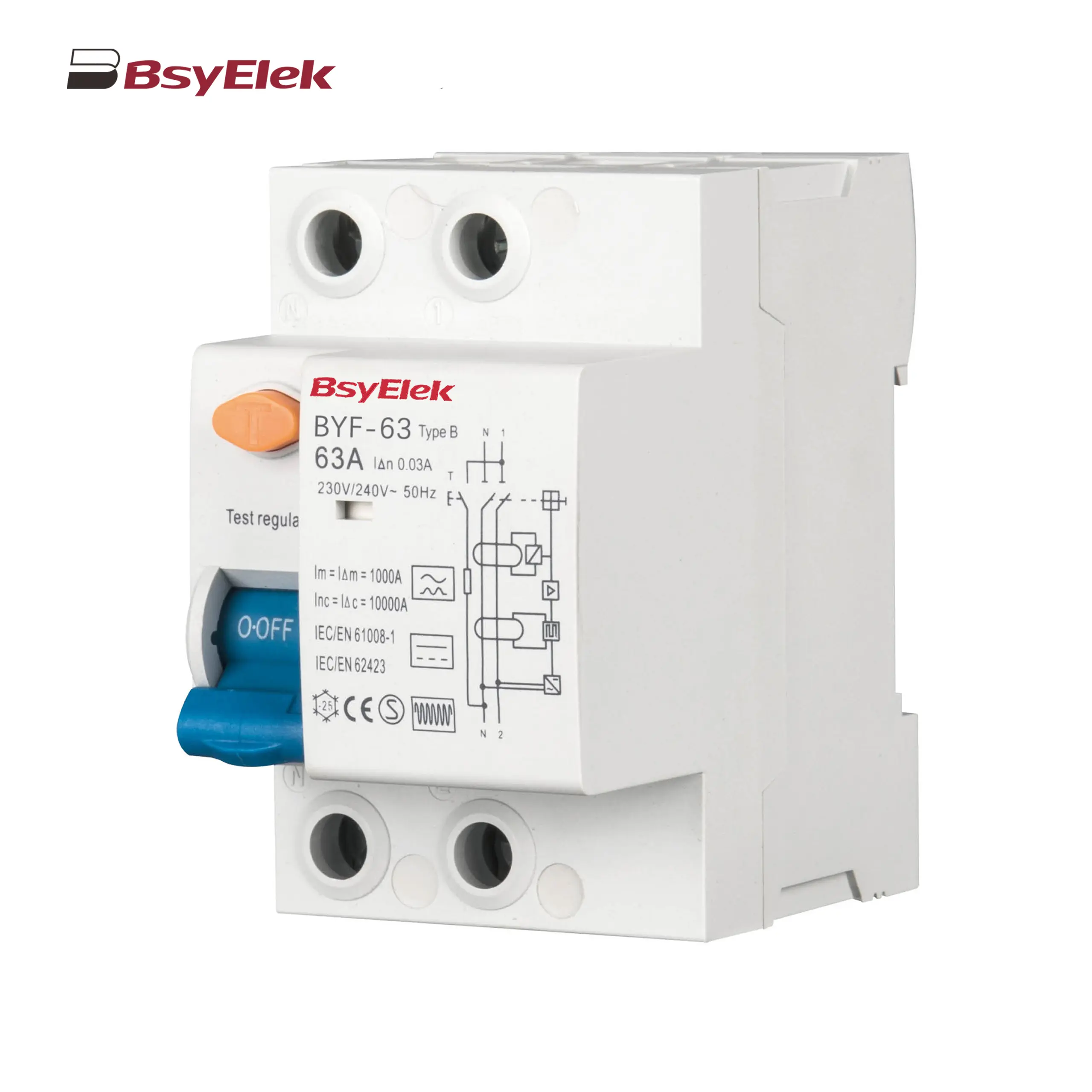 BYF-63 RCD 10KA Type B AC+A+Smoothing DC Residual Current Device
BYF-63 RCD 10KA Type B AC+A+Smoothing DC Residual Current Device BY08DC 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device
BY08DC 1+2-12.5 SPD Class T1+T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device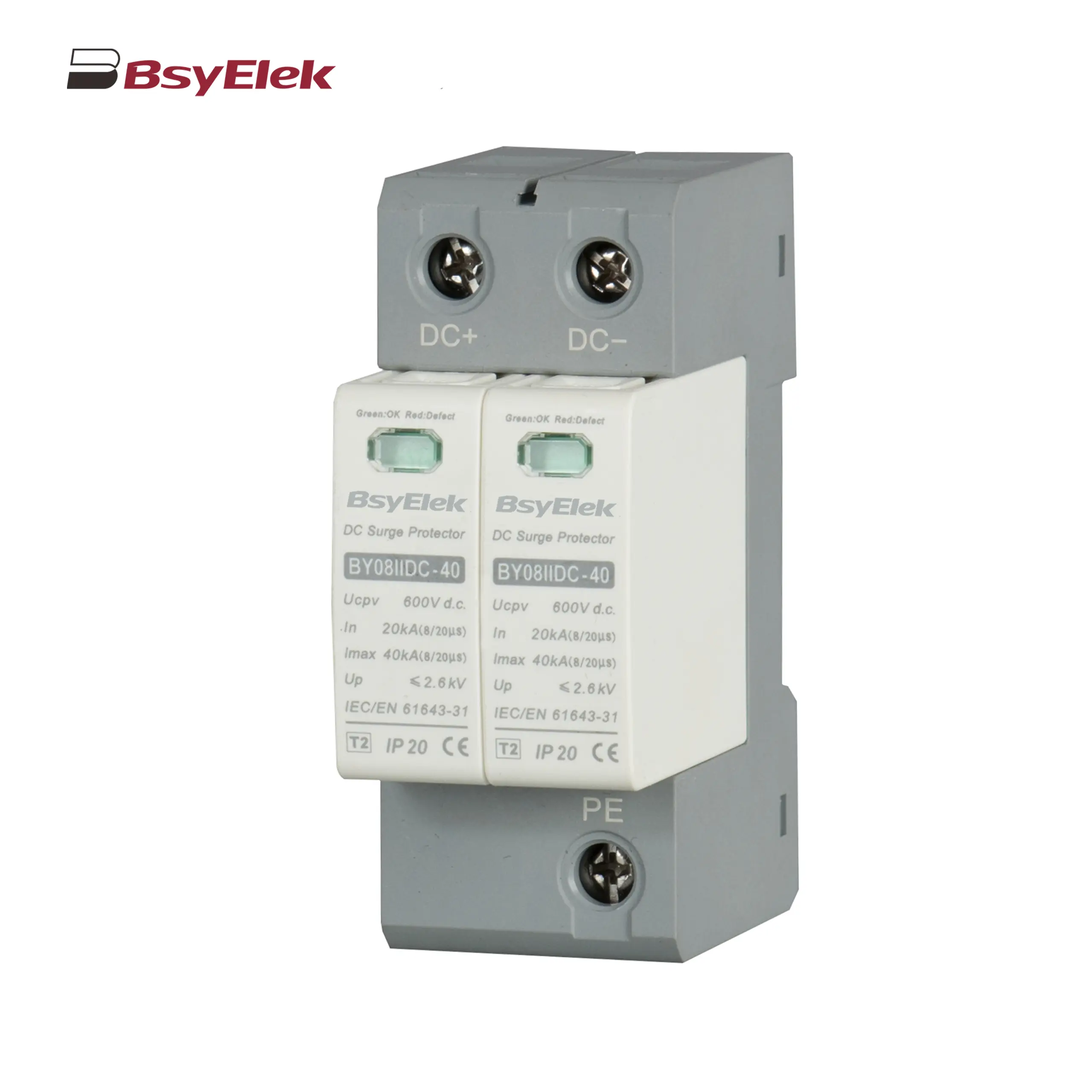 BY08IIDC-40 SPD Class T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device
BY08IIDC-40 SPD Class T2 40KA DC Surge Protective Device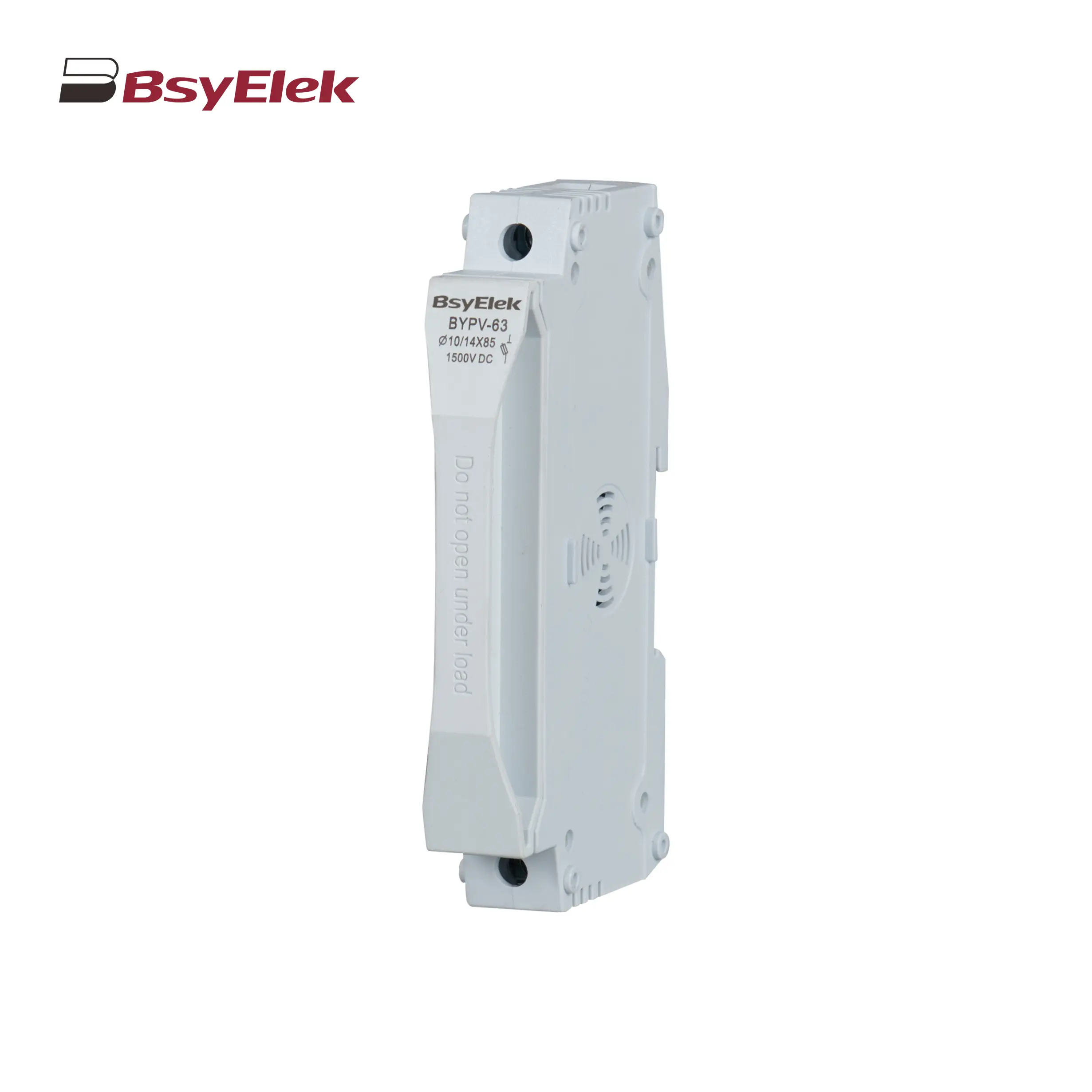 BYPV-63 1500VDC 50A Fuse Holder with 10x85mm 14x85mm Fuse Link
BYPV-63 1500VDC 50A Fuse Holder with 10x85mm 14x85mm Fuse Link BYPV-30 1000VDC 32A Fuse Holder with 10x38mm Fuse Link
BYPV-30 1000VDC 32A Fuse Holder with 10x38mm Fuse Link BYPV-ELR2 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version
BYPV-ELR2 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version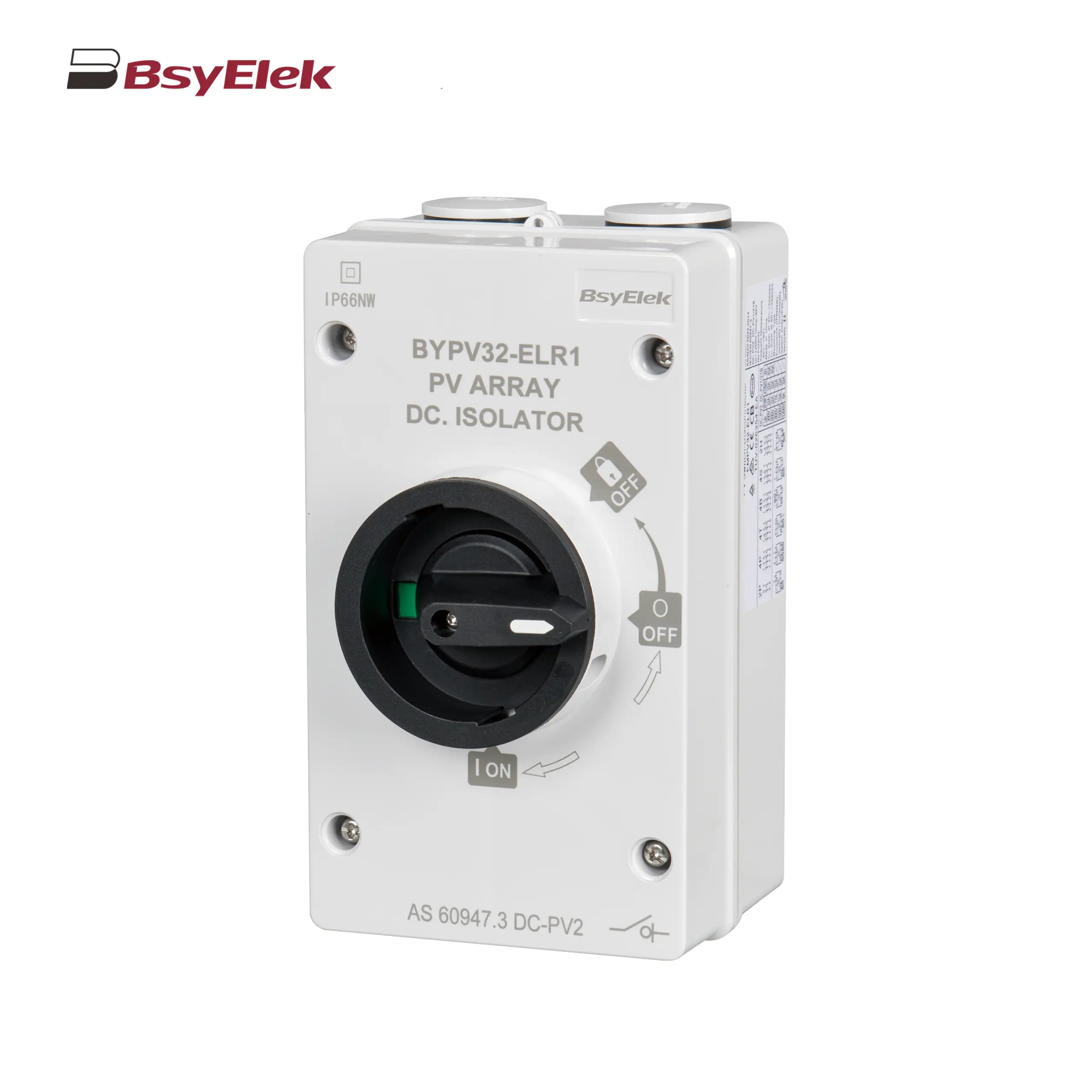 BYPV-ELR1 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version
BYPV-ELR1 PV Isolator Switch with Enclosed Version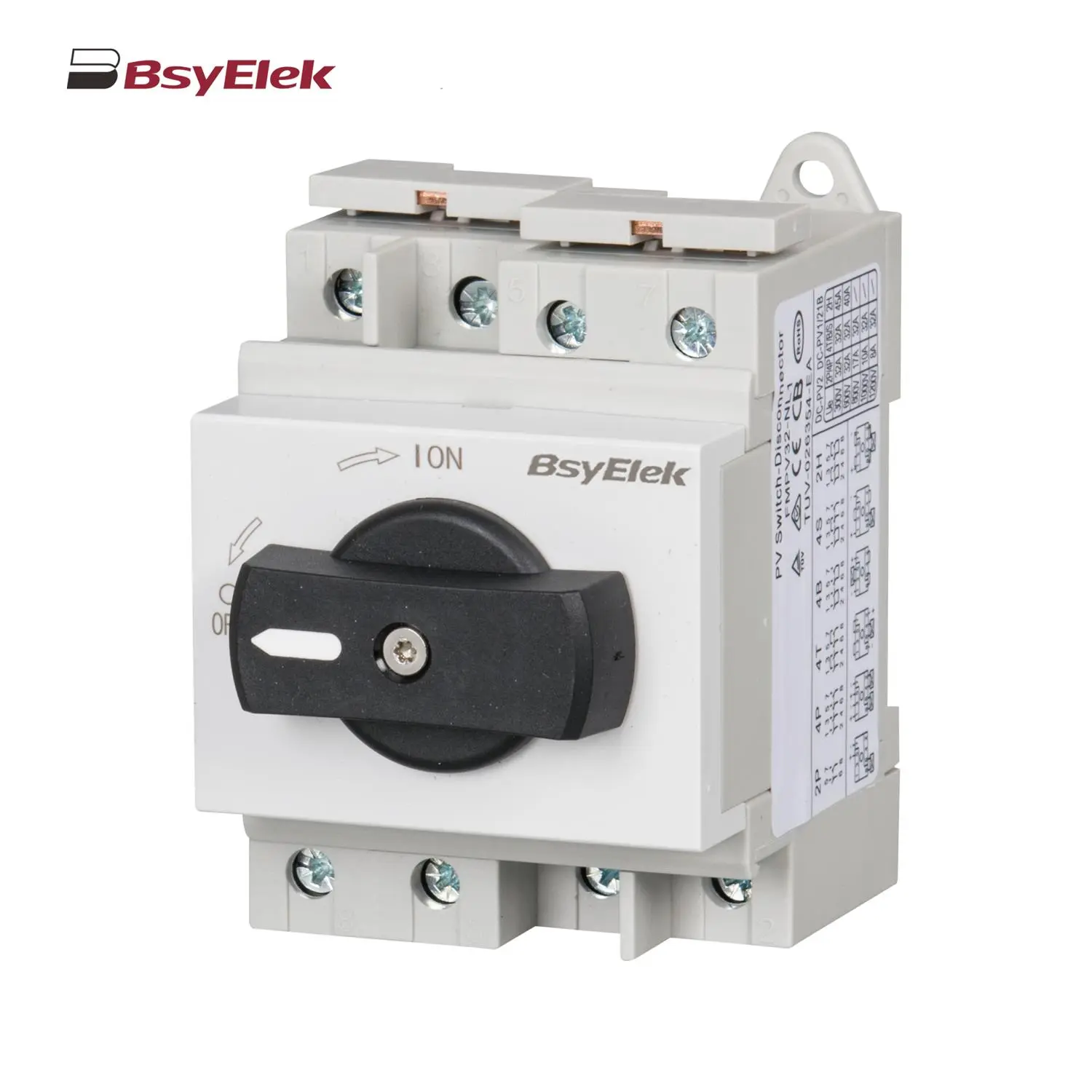 BYPV-NL1/T PV Isolator Switch with Ultra-thin Lever Handle
BYPV-NL1/T PV Isolator Switch with Ultra-thin Lever Handle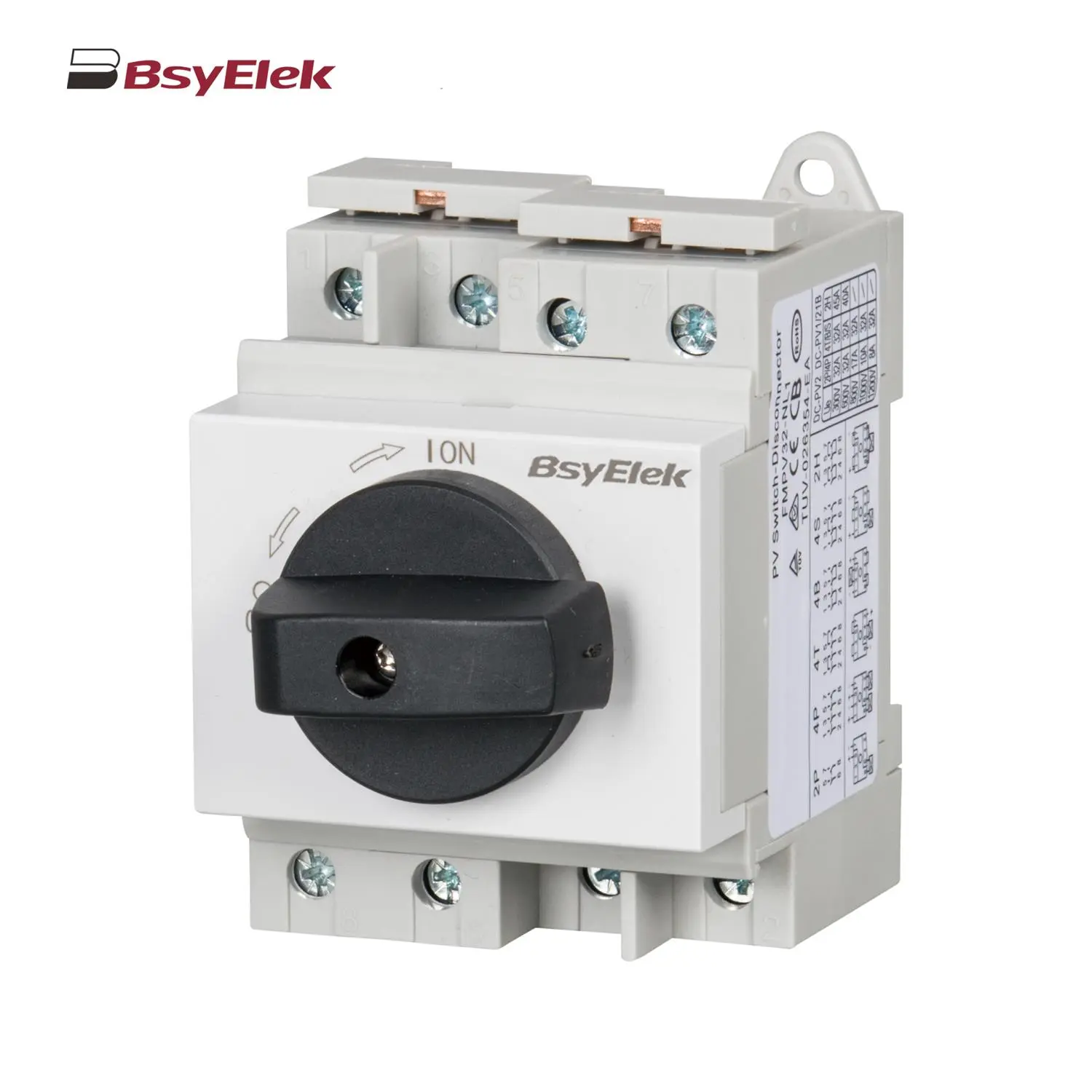 BYPV-NL1 PV Isolator Switch with Lever Handle
BYPV-NL1 PV Isolator Switch with Lever Handle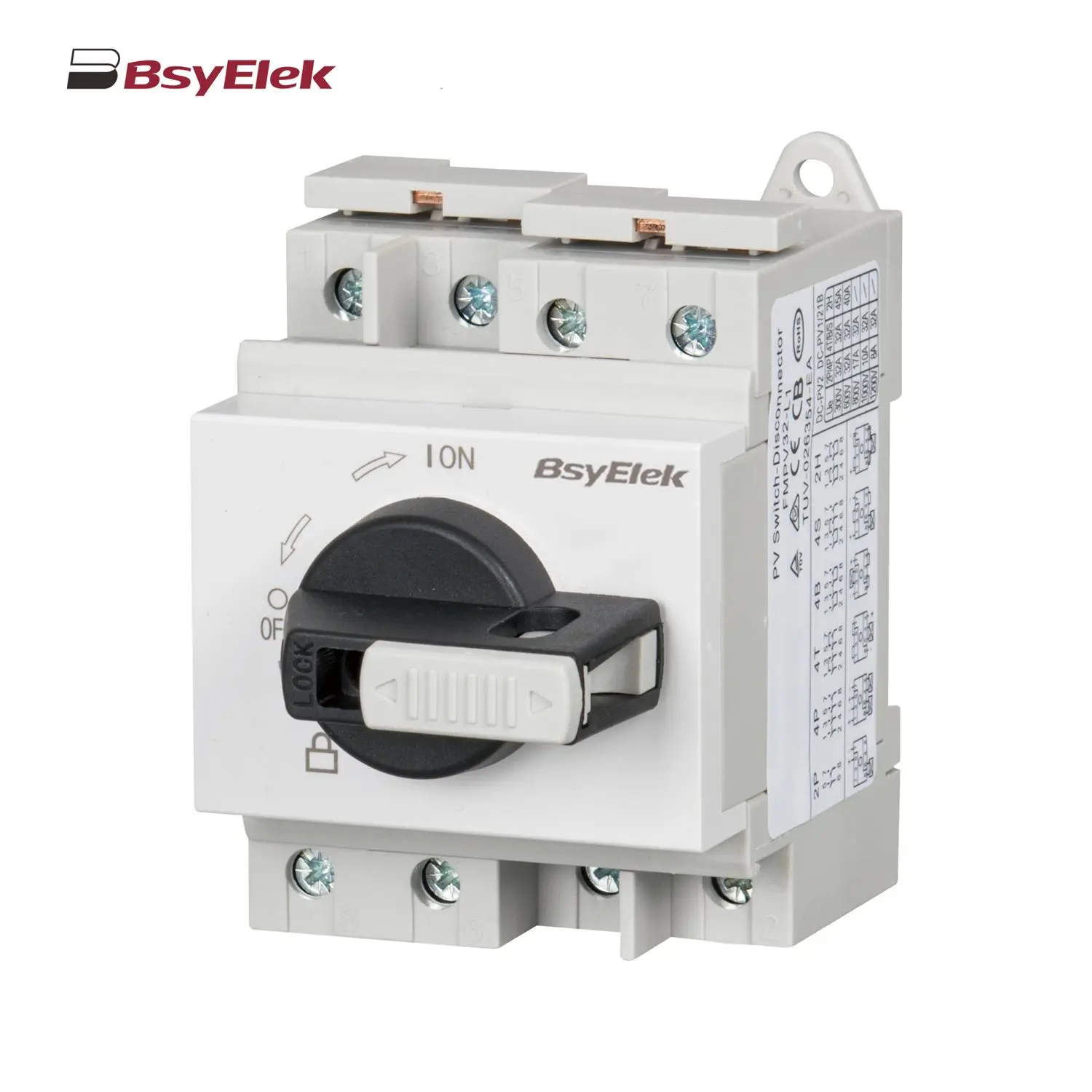 BYPV-L1/L2 PV Isolator Switch with Lockable Lever Handle
BYPV-L1/L2 PV Isolator Switch with Lockable Lever Handle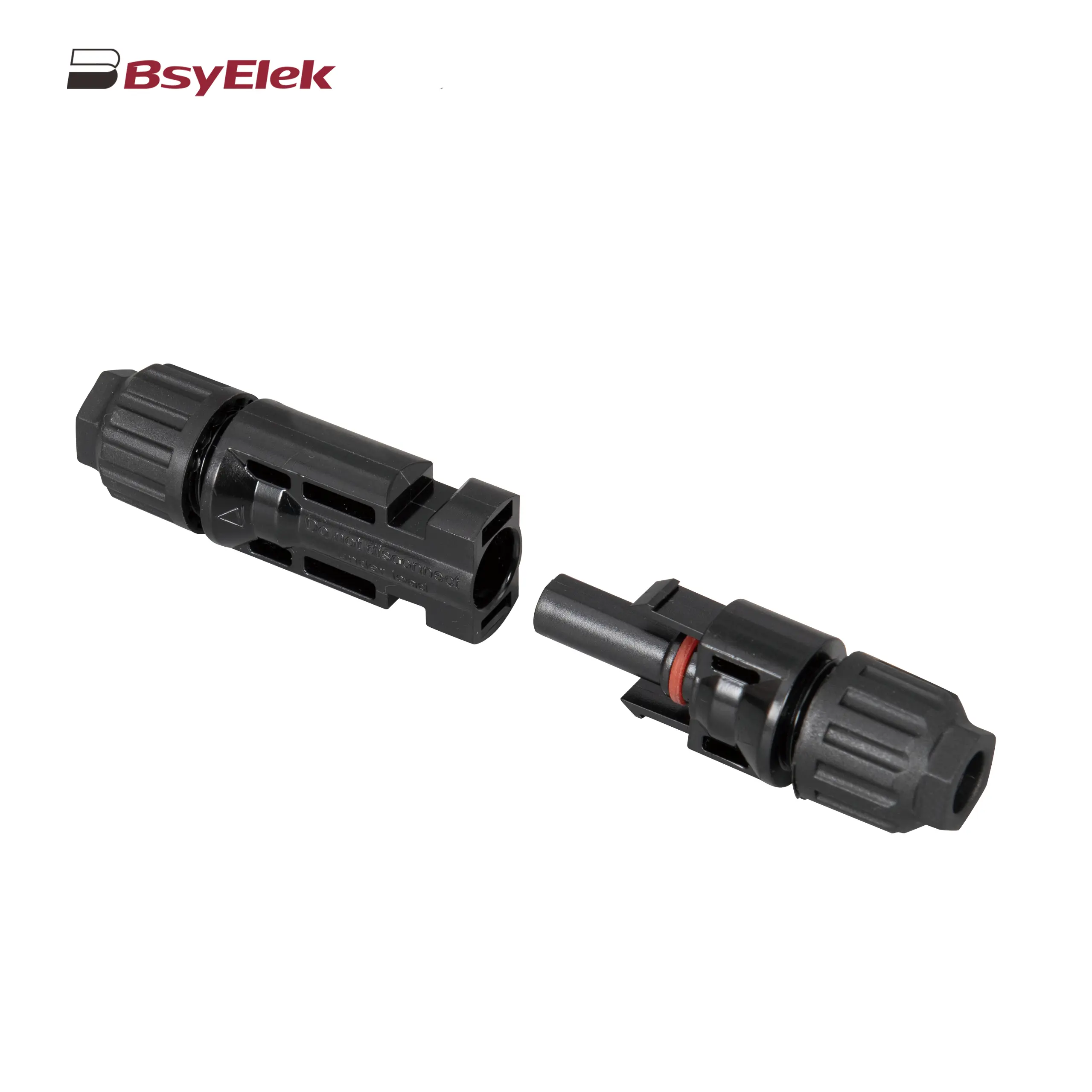 PV-BY-01 30A/50A 1000V Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-01 30A/50A 1000V Photovoltaic Connector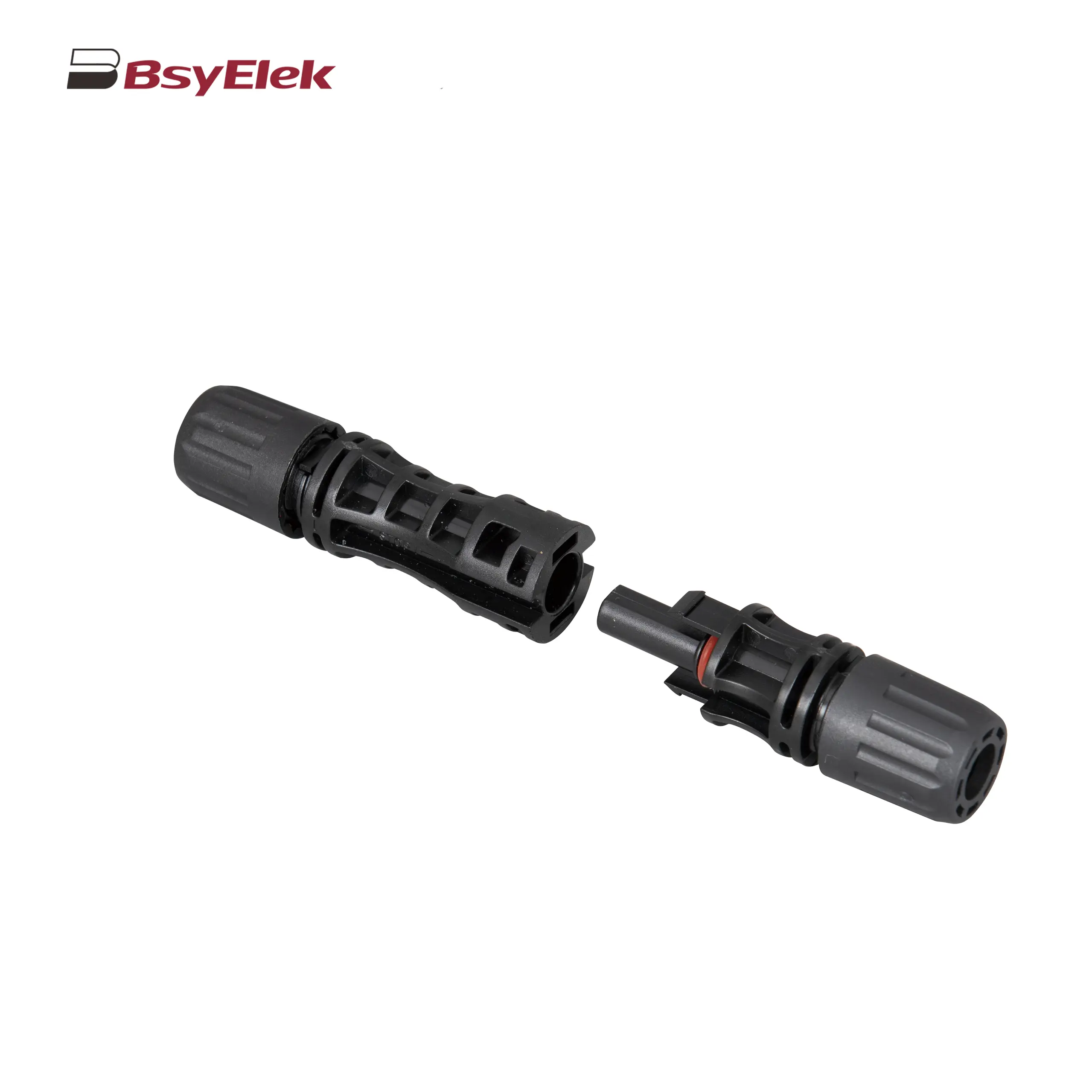 PV-BY-02 30A/50A 1500V Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-02 30A/50A 1500V Photovoltaic Connector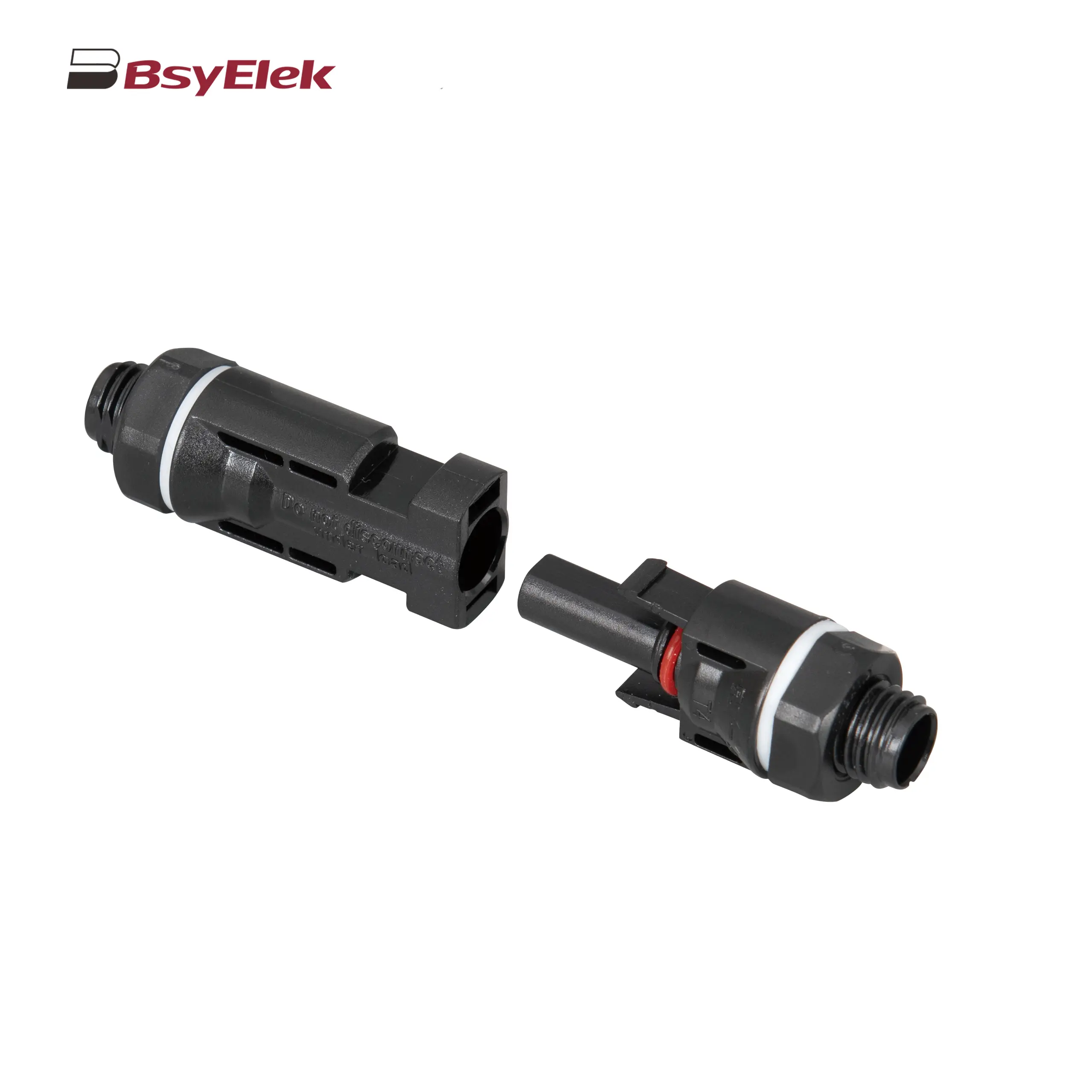 PV-BY-03 30A/50A 1000V Panel Mount Photovoltaic Connector
PV-BY-03 30A/50A 1000V Panel Mount Photovoltaic Connector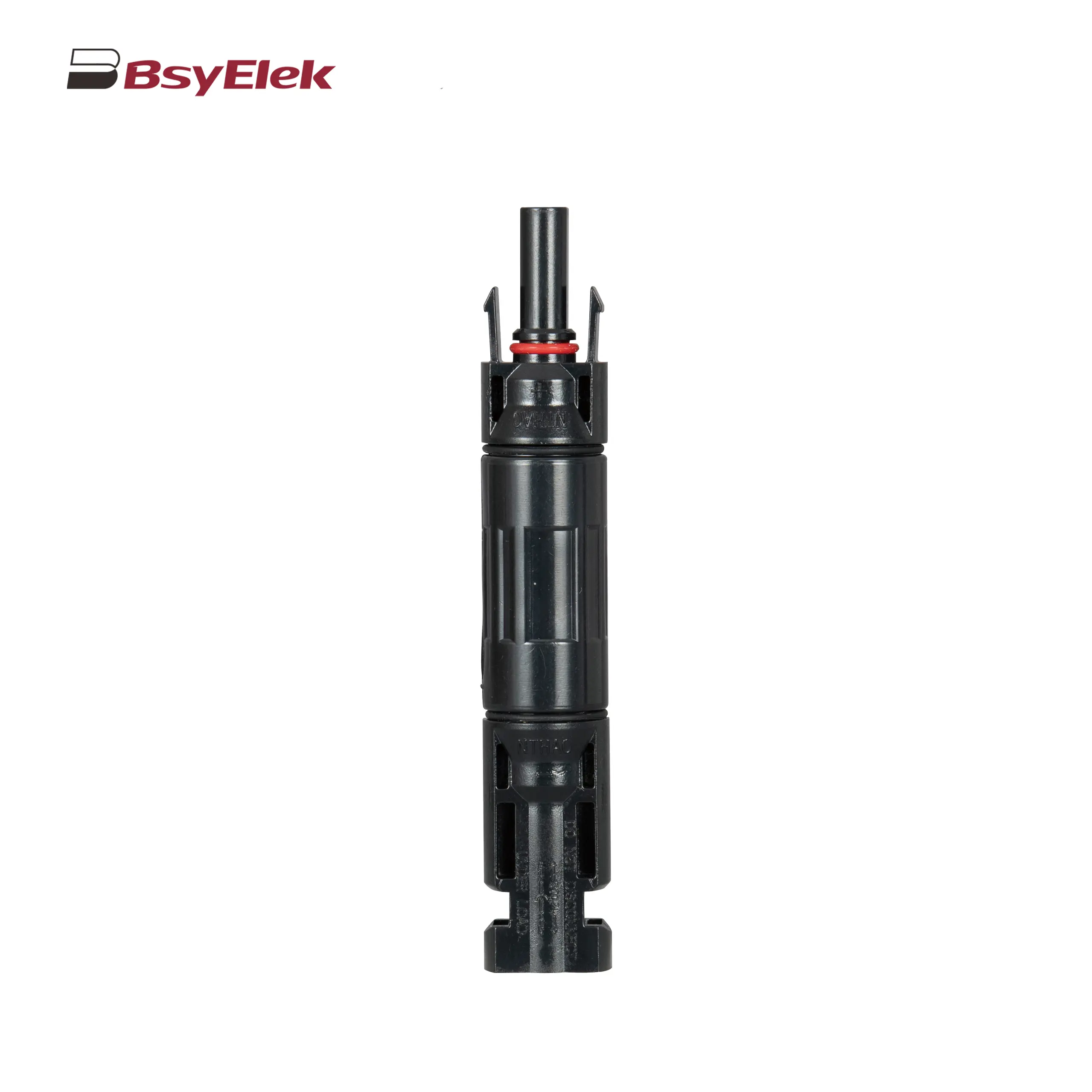 PV-BY-F01 30A 1500V Diode/Fuse Type Connector
PV-BY-F01 30A 1500V Diode/Fuse Type Connector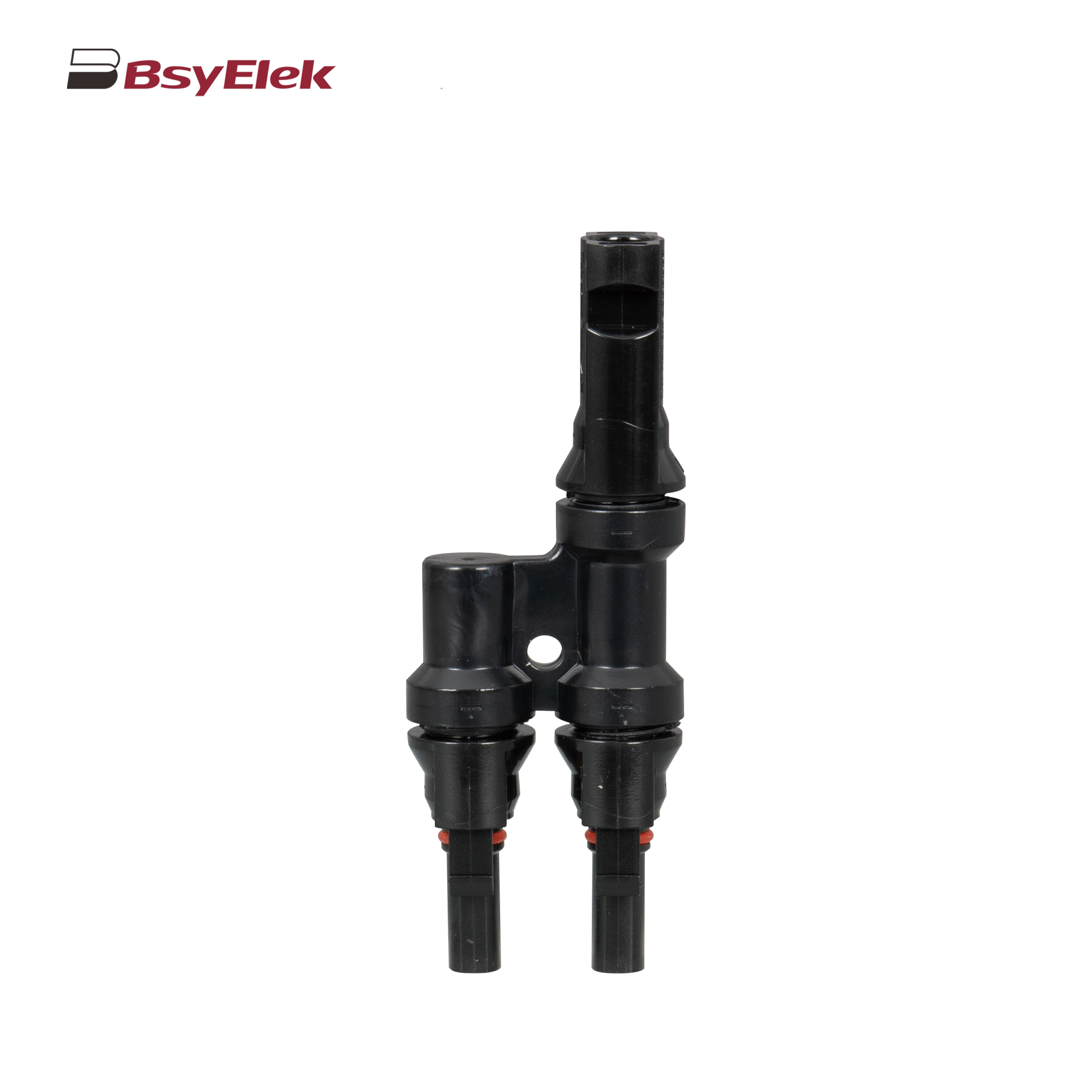 PV-BY-T 50A 1500V T Type Branch Connector
PV-BY-T 50A 1500V T Type Branch Connector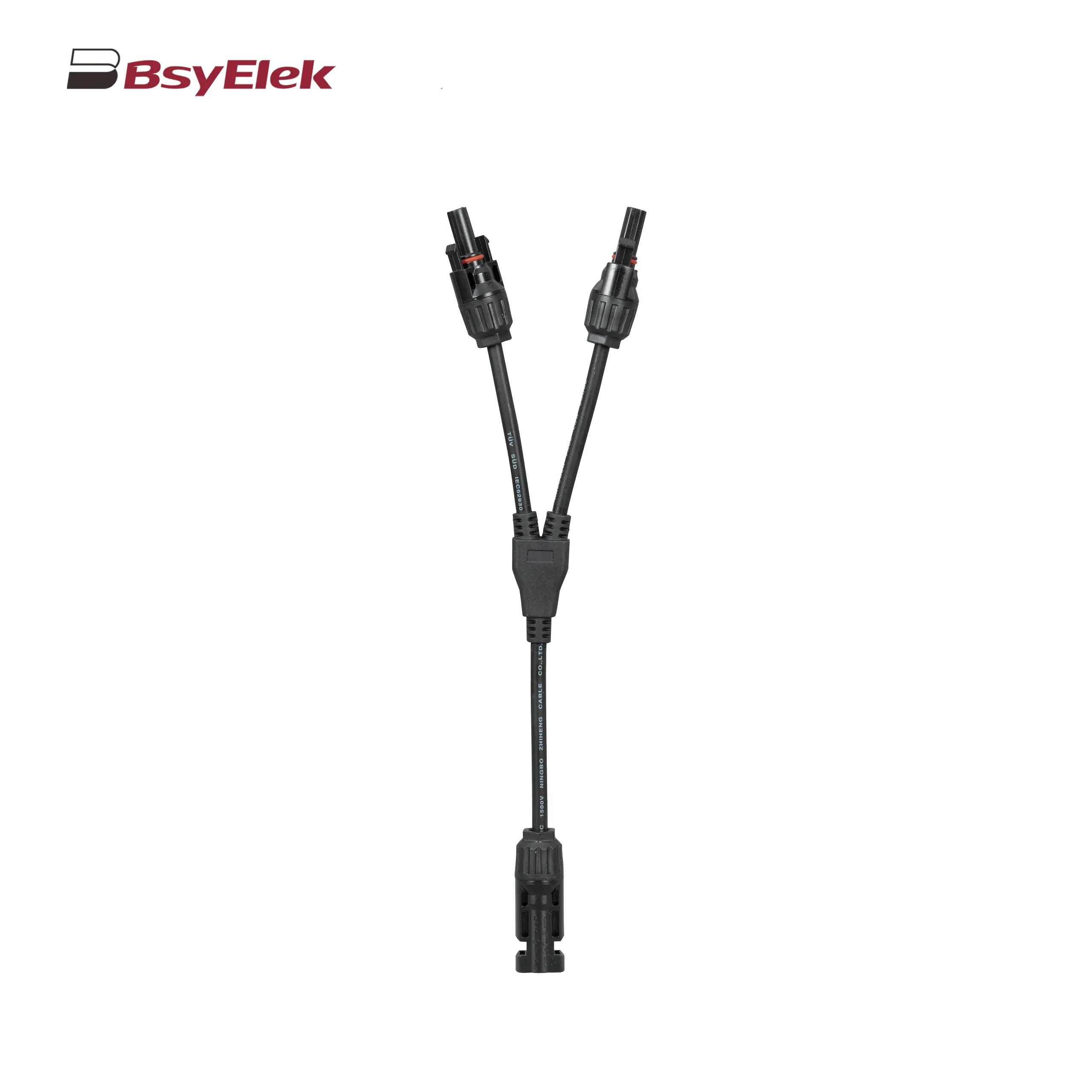 PV-BY-Y 30A 1500V Y Type Branch Connector
PV-BY-Y 30A 1500V Y Type Branch Connector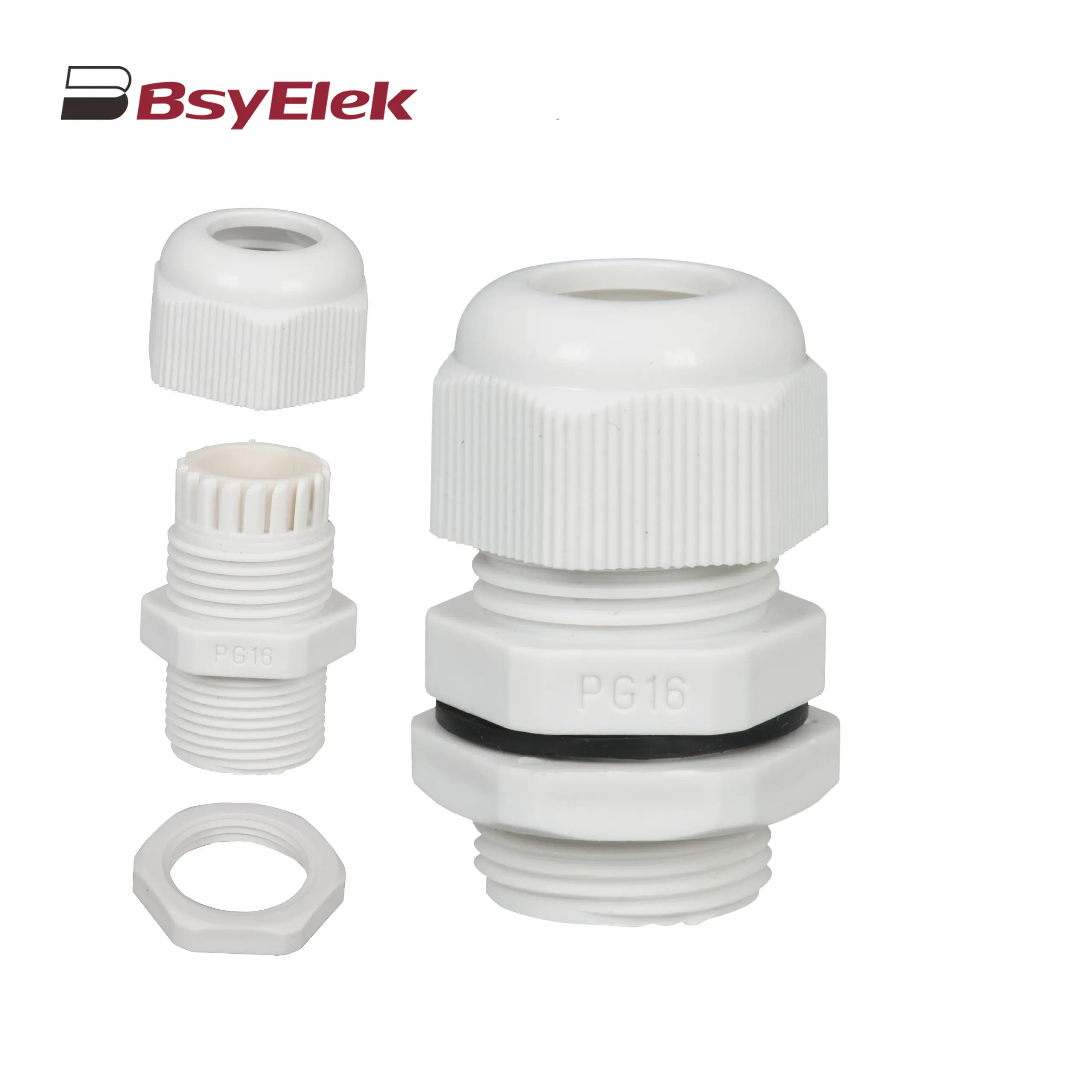 PG Waterproof Cable Gland with Washer
PG Waterproof Cable Gland with Washer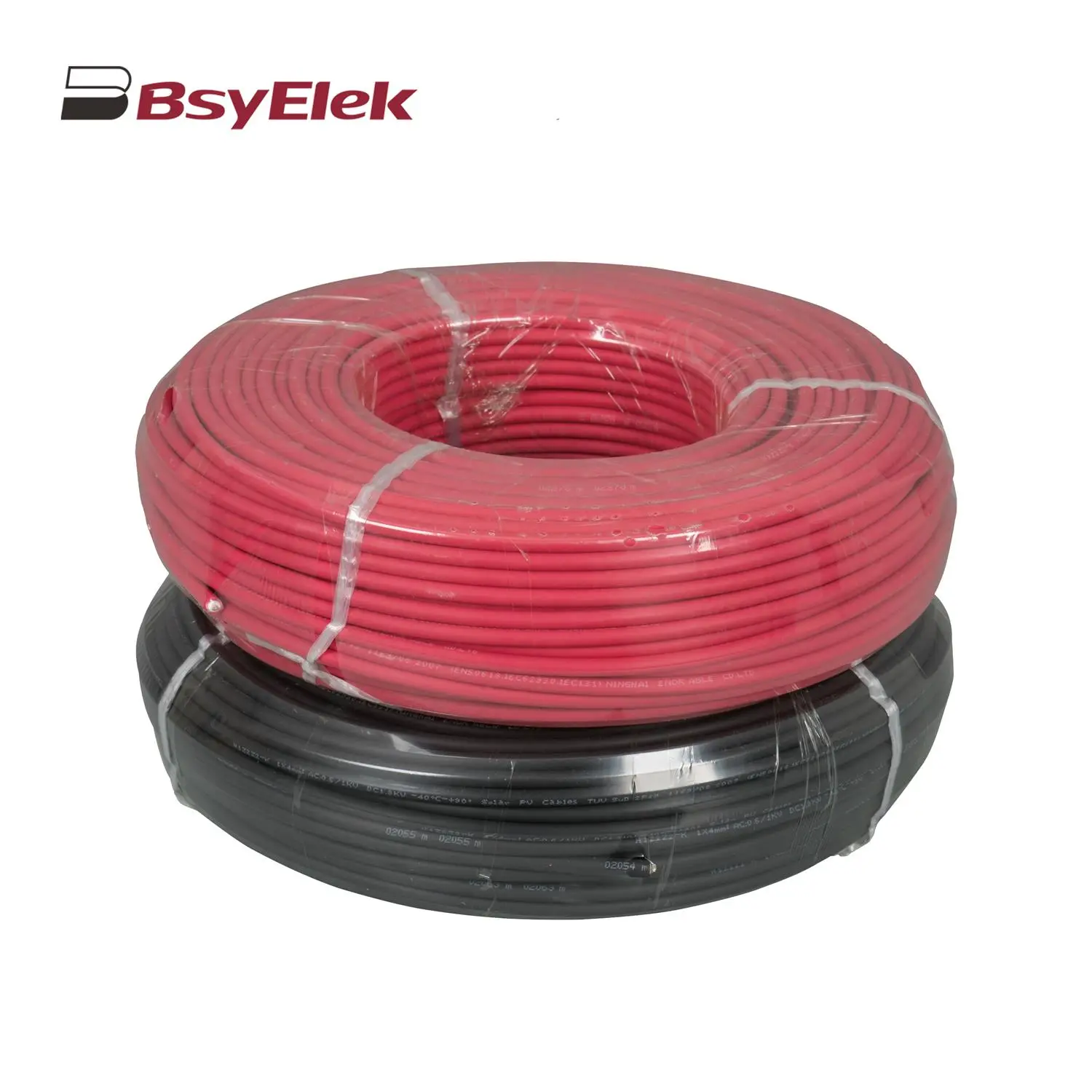 Photovoltaic Cable
Photovoltaic Cable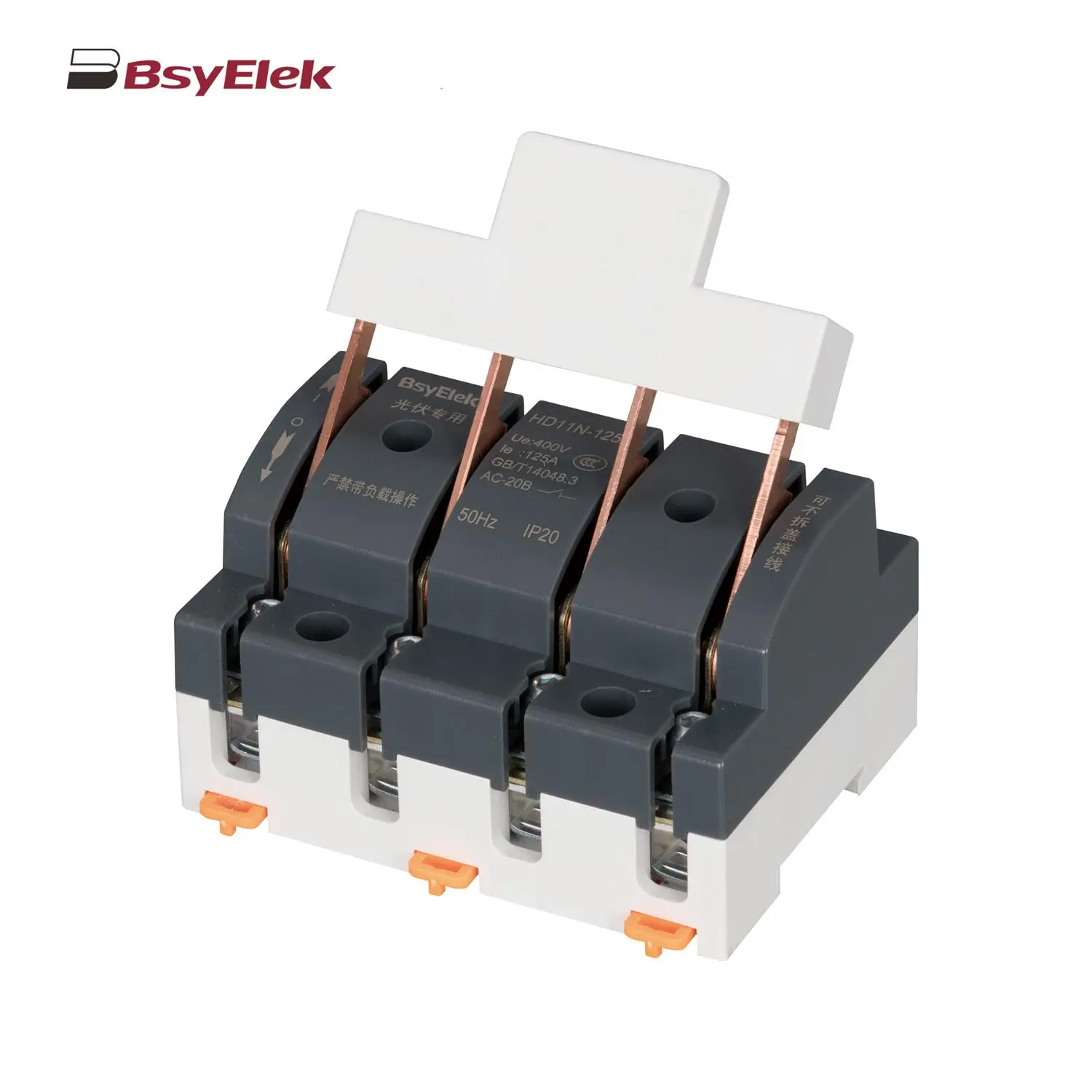 HD11N Photovoltaic Knife Switch
HD11N Photovoltaic Knife Switch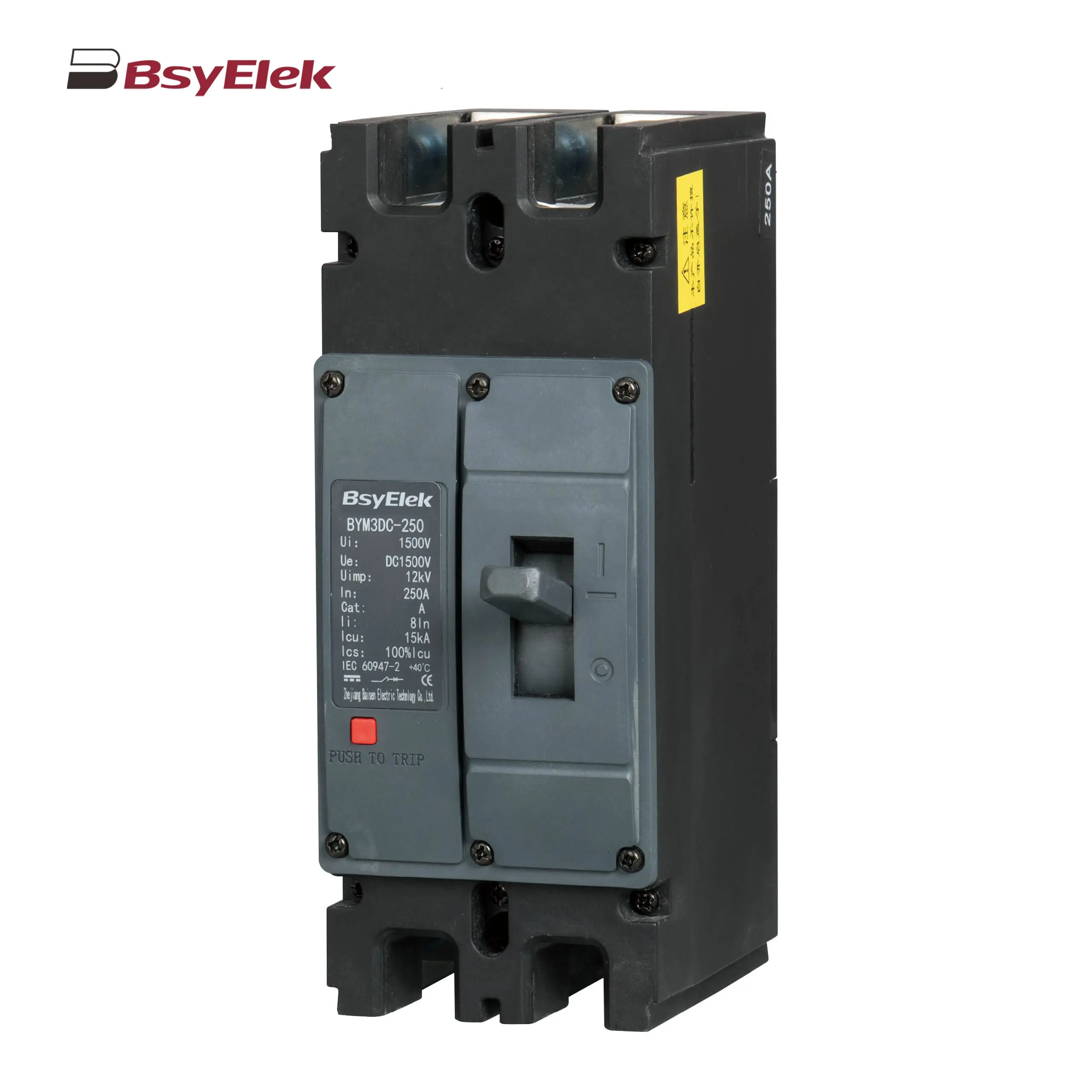 BYM3DC MCCB Photovoltaic DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM3DC MCCB Photovoltaic DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker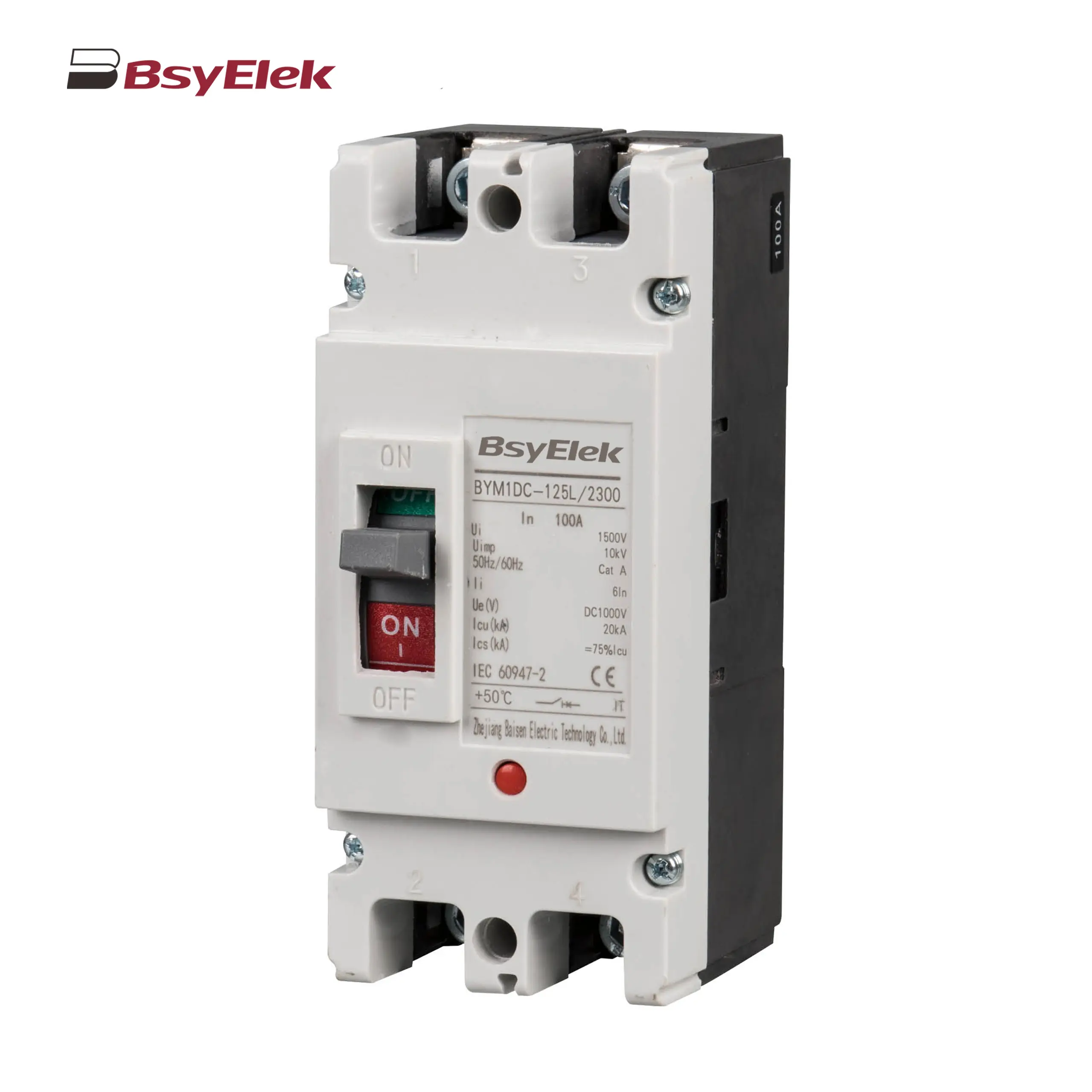 BYM1DC MCCB 1000VDC Thermal Magnetic Type DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1DC MCCB 1000VDC Thermal Magnetic Type DC Molded Case Circuit Breaker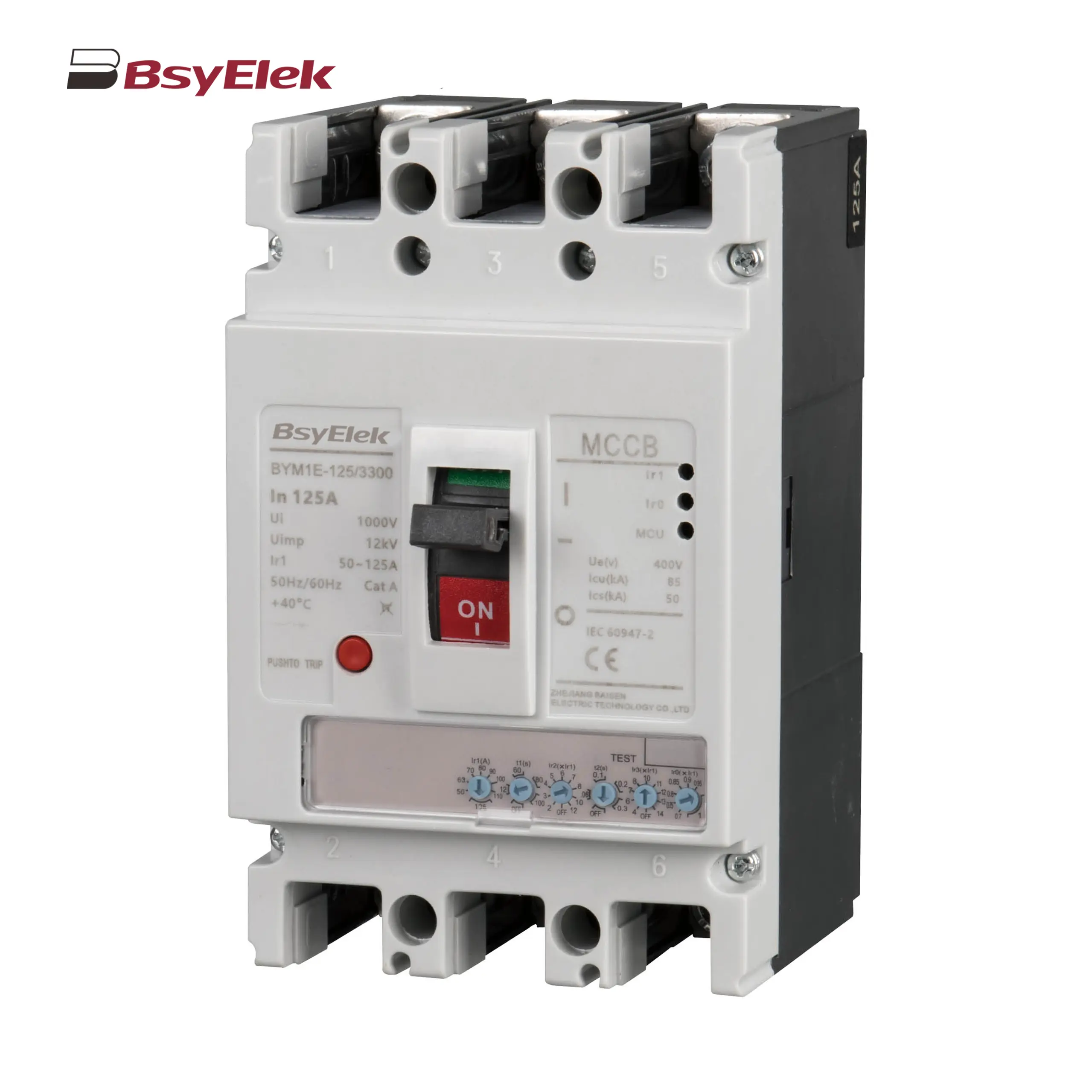 BYM1E MCCB Electronic Type Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1E MCCB Electronic Type Molded Case Circuit Breaker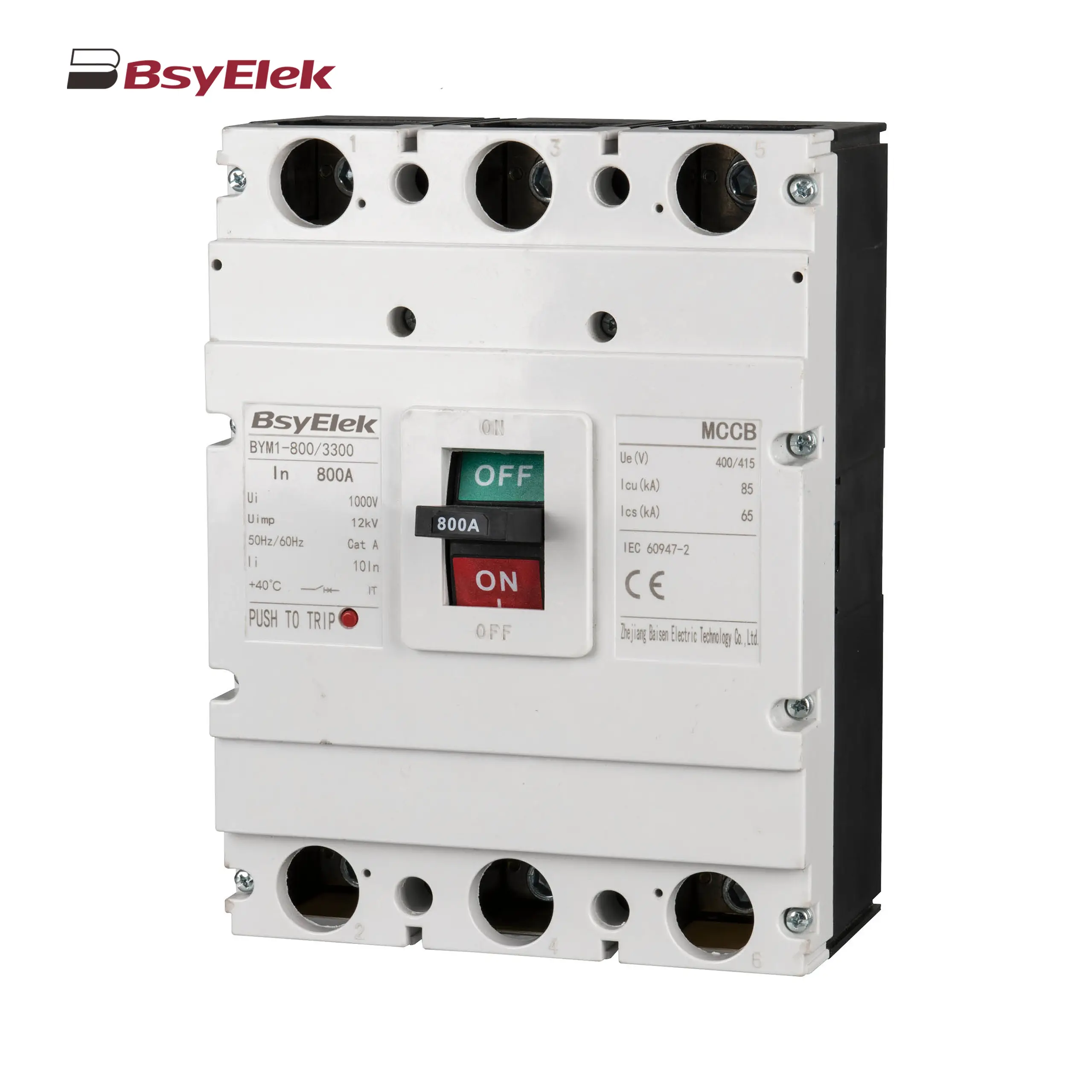 BYM1 MCCB Thermal Magnetic AC Molded Case Circuit Breaker
BYM1 MCCB Thermal Magnetic AC Molded Case Circuit Breaker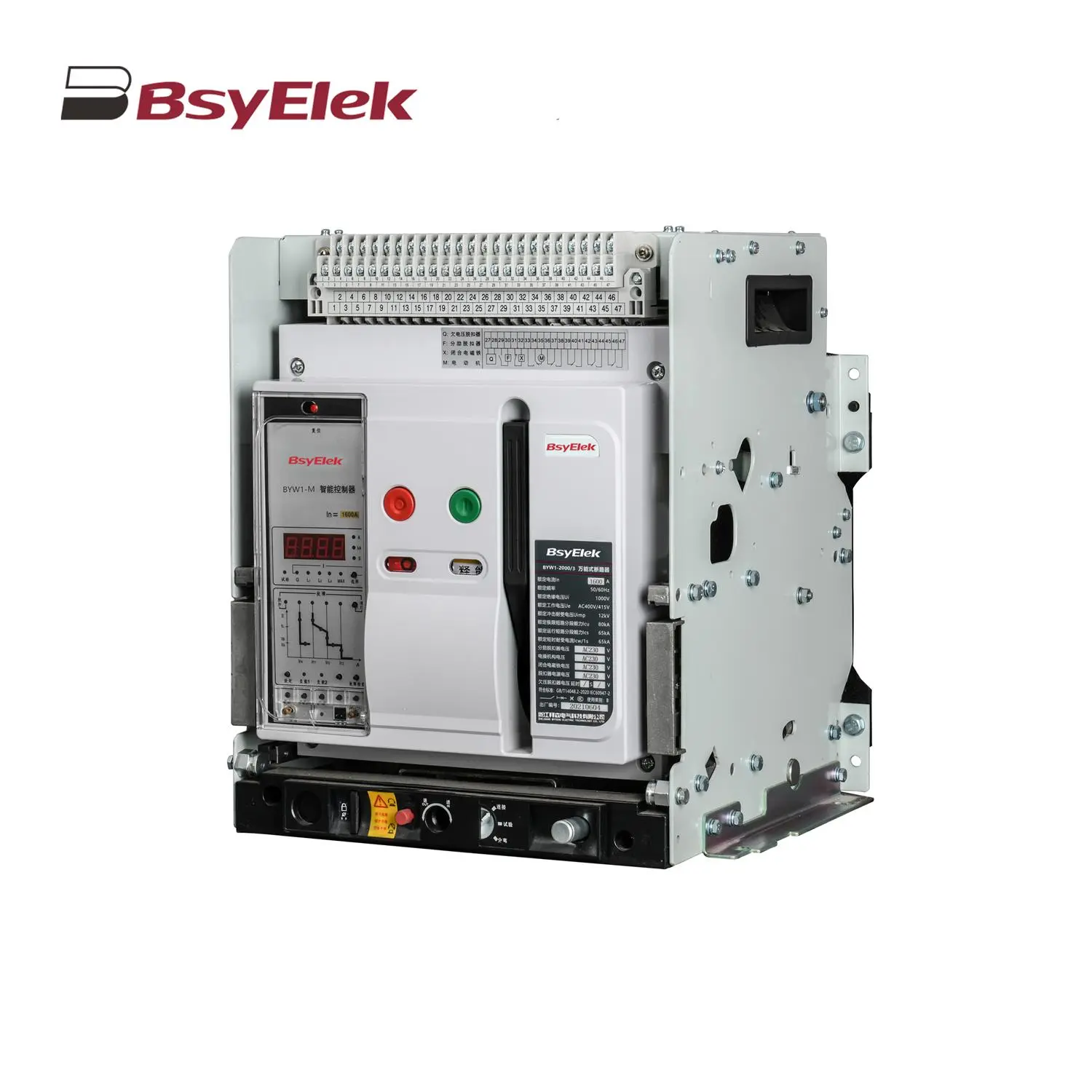 BYW1 ACB Intelligent Universal Air Circuit Breaker
BYW1 ACB Intelligent Universal Air Circuit Breaker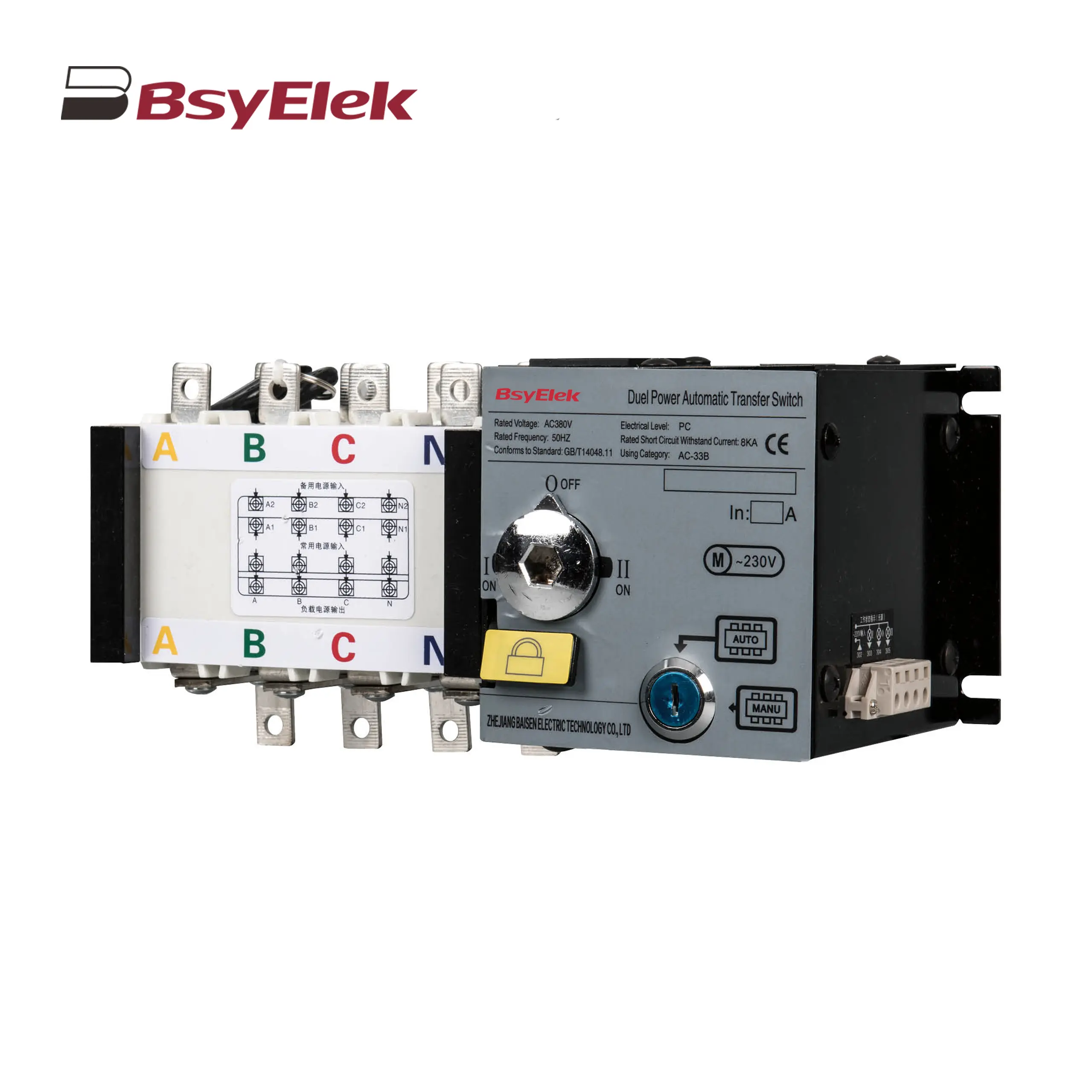 BYQ1 ATS Isolated Type PC Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Isolated Type PC Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch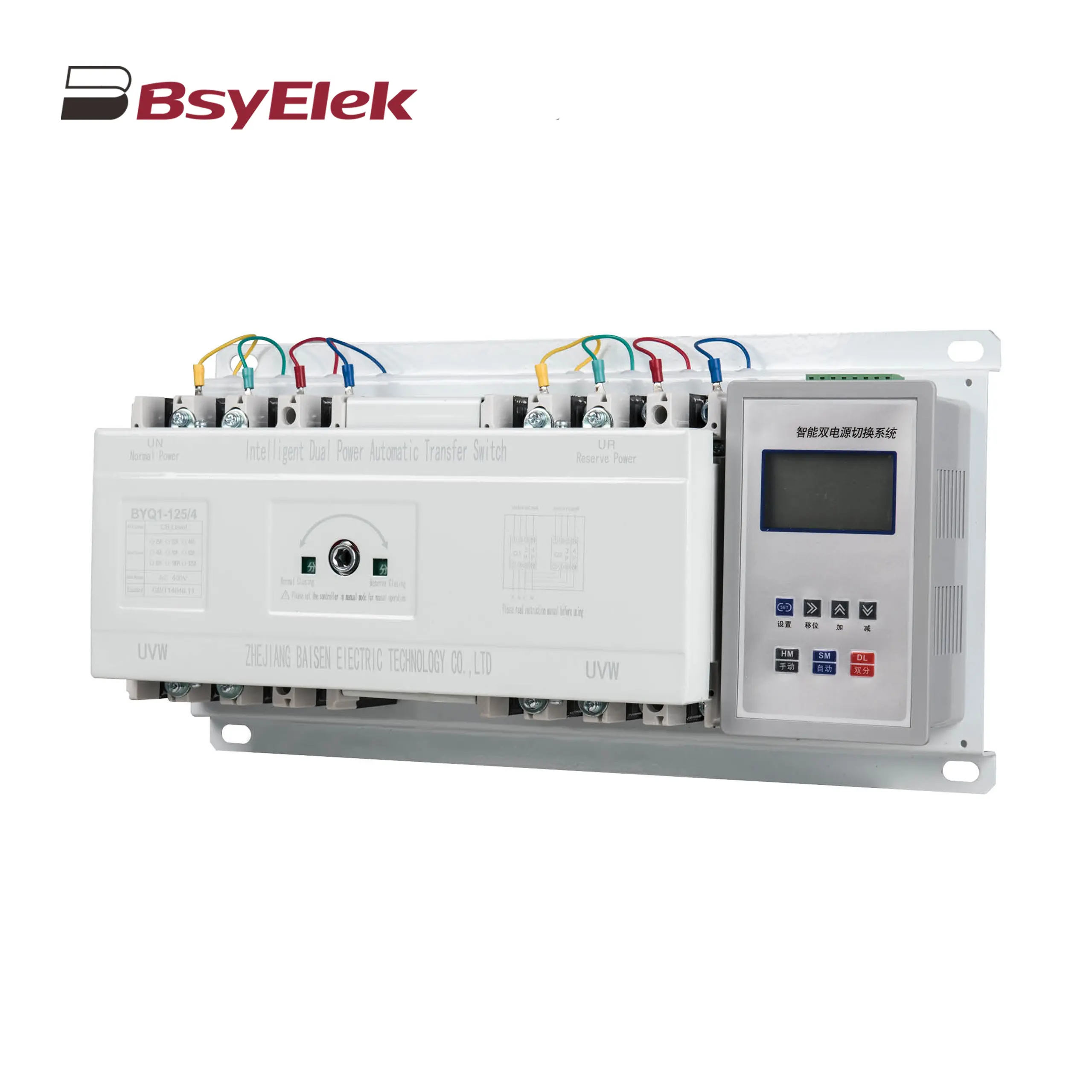 BYQ1 ATS Intelligent Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Intelligent Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch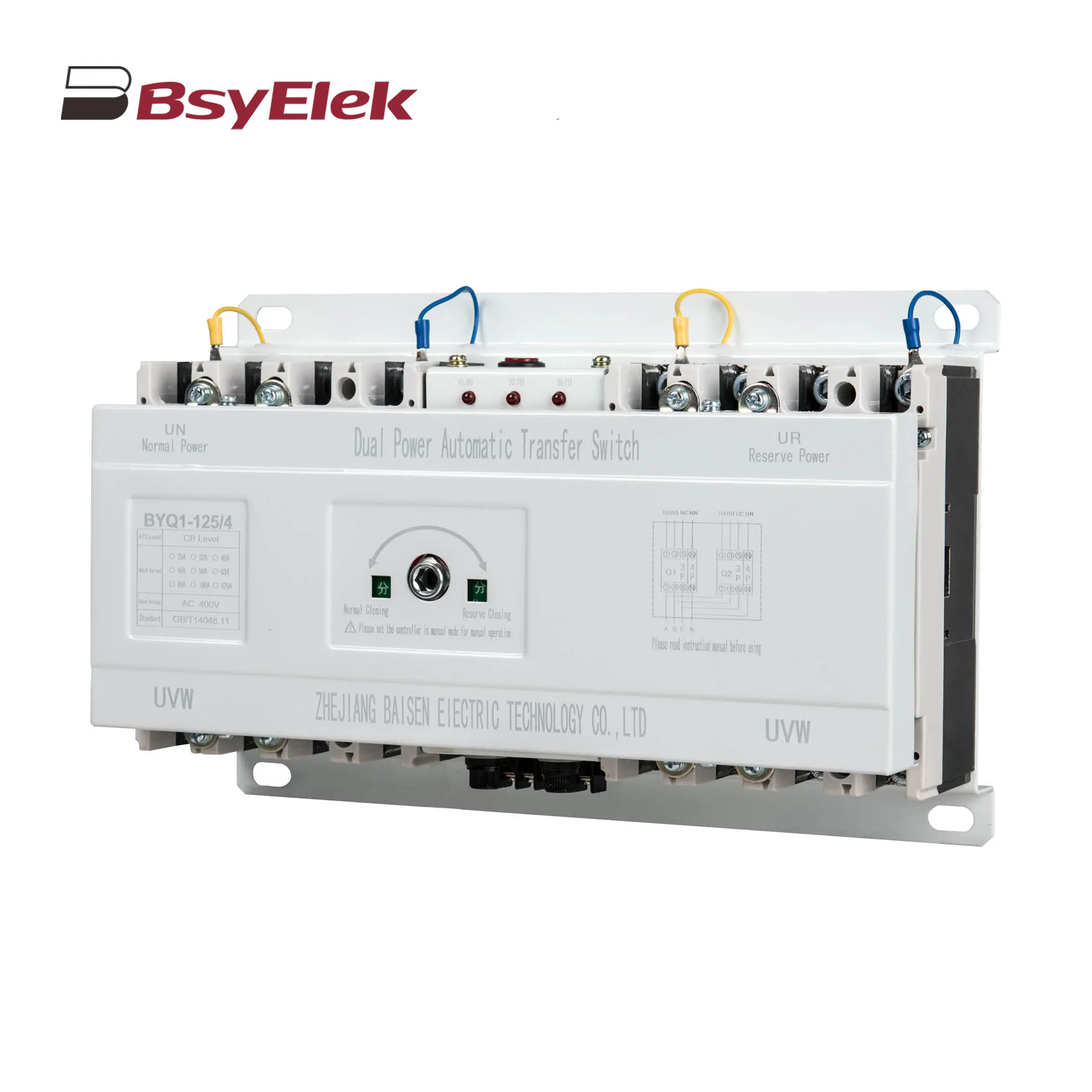 BYQ1 ATS End Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS End Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch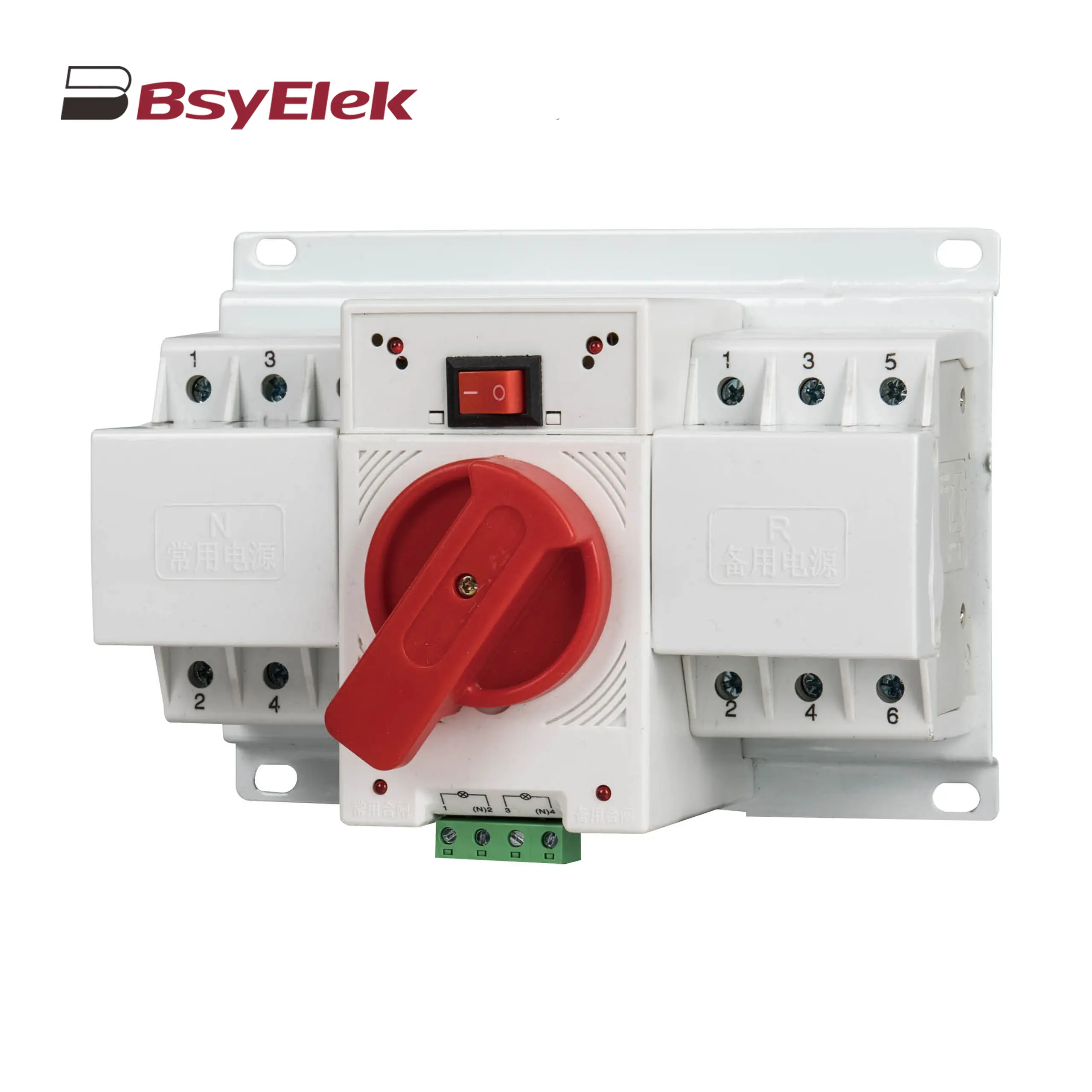 BYQ1 ATS Mini Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch
BYQ1 ATS Mini Type CB Level Dual Power Automatic Transfer Switch Stainless Steel Hinge Type Electrical Box
Stainless Steel Hinge Type Electrical Box HA Waterproof Distribution Box
HA Waterproof Distribution Box HT Waterproof Distribution Box
HT Waterproof Distribution Box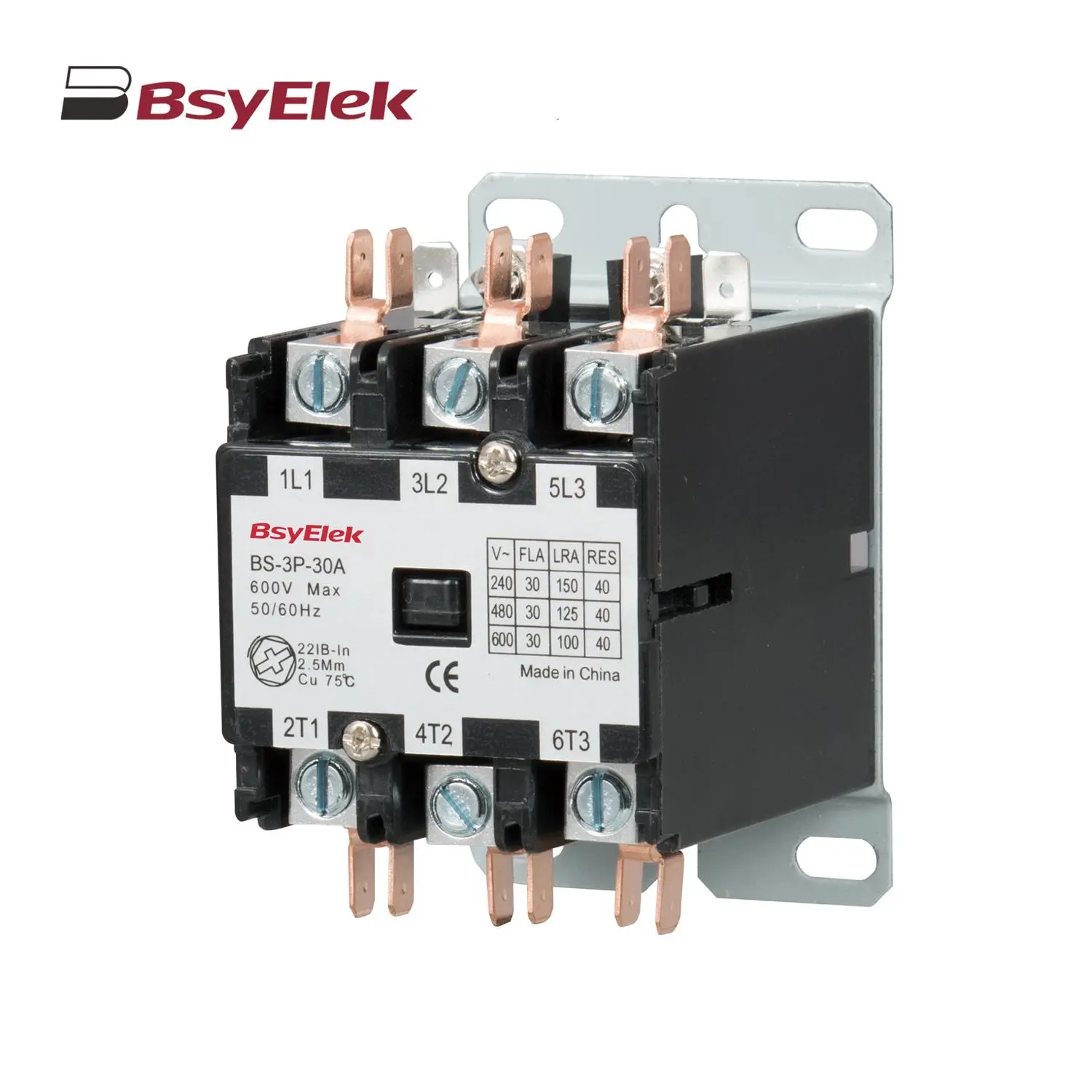 BS Definite Purpose Magnetic AC Contactor
BS Definite Purpose Magnetic AC Contactor